In the realm of modern manufacturing, efficiency, precision, and speed are paramount. As industries evolve and competition intensifies, companies continually seek innovative solutions to optimize their production processes. One such solution that has revolutionized manufacturing operations is the integration of robotic bending machines.
These advanced systems utilize robotics and automation to perform bending tasks with unparalleled accuracy and efficiency. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of robotic bending machines, exploring their benefits, applications, and the transformative impact they have on manufacturing operations worldwide.
Understanding Robotic Bending Machines
Robotic bending machines are sophisticated pieces of equipment designed to bend various materials, such as metal sheets, tubes, and profiles, with precision and consistency.
Unlike traditional manual or hydraulic bending methods, robotic bending machines leverage advanced robotics, computer numerical control (CNC) technology, and sophisticated software algorithms to execute bending tasks with remarkable speed and accuracy.
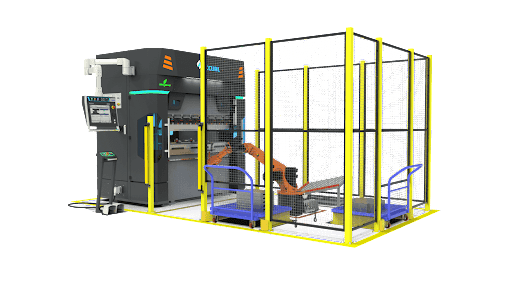
Components of Robotic Bending Machines
Robotic bending machines consist of several key components, each playing a crucial role in the bending process:
- Robotic Arm: The robotic arm serves as the primary mechanism for bending the workpiece. It is equipped with specialized grippers or tooling attachments that securely hold the material during the bending operation.
- Bending Tooling: Bending tooling refers to the components attached to the robotic arm that apply force to the workpiece to achieve the desired bend angle. These tooling components can vary depending on the material being bent and the complexity of the bend required.
- CNC Control System: The CNC control system acts as the brain of the robotic bending machine, interpreting design specifications and translating them into precise movements and commands for the robotic arm and bending tooling.
- Sensors and Vision Systems: Many robotic bending machines are equipped with sensors and vision systems that provide real-time feedback on the bending process. These systems ensure accuracy and detect any deviations from the intended bend parameters.
Benefits of Robotic Bending Machines
The adoption of robotic bending machines offers a wide range of benefits for manufacturers across various industries. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
1. Increased Efficiency
Robotic bending machines excel in high-volume production environments where speed and efficiency are essential.
By automating the bending process, these machines can significantly reduce cycle times and increase throughput compared to manual bending methods. This efficiency gain translates into higher productivity and lower production costs for manufacturers.
2. Enhanced Precision and Accuracy
One of the most significant advantages of robotic bending machines is their ability to achieve precise and consistent bend angles with minimal deviation.
The CNC control system ensures that each bend conforms precisely to the design specifications, resulting in high-quality finished parts. This level of accuracy is particularly crucial in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics, where tight tolerances are critical.
3. Flexibility and Versatility
Robotic bending machines are highly versatile and can accommodate a wide range of materials, geometries, and bending requirements.
Whether bending simple flat sheets or complex three-dimensional components, these machines can adapt to diverse production needs with ease. Additionally, quick tooling changeovers and programmable setups allow manufacturers to transition between different bending tasks efficiently, maximizing operational flexibility.
4. Improved Worker Safety
Automating repetitive and physically demanding tasks with robotic bending machines reduces the risk of work-related injuries and ergonomic strain on workers.
By eliminating manual bending processes that require heavy lifting and prolonged physical exertion, manufacturers can create safer and healthier work environments for their employees.
This not only enhances worker morale but also reduces the likelihood of costly workplace accidents and liabilities.
5. Cost Savings
While the initial investment in robotic bending machines may be substantial, the long-term cost savings associated with automation are significant.
By streamlining production processes, reducing scrap rates, and minimizing downtime, manufacturers can achieve a rapid return on investment (ROI) with robotic bending technology.
Moreover, the scalability of robotic systems allows manufacturers to ramp up production as demand grows without proportionally increasing labor costs.
Applications of Robotic Bending Machines
Robotic bending machines find applications across a wide range of industries and manufacturing sectors. Some common applications include:
1. Sheet Metal Fabrication
In the sheet metal fabrication industry, robotic bending machines are used to bend flat sheets of metal into various shapes and configurations.
From simple brackets and enclosures to complex structural components, these machines enable manufacturers to produce precise and intricate sheet metal parts with efficiency and consistency.
2. Automotive Manufacturing
In the automotive industry, robotic bending machines play a crucial role in the production of vehicle components such as chassis frames, body panels, and exhaust systems.
The ability to bend tubes and profiles with precision allows automotive manufacturers to achieve lightweight designs, optimize structural integrity, and enhance vehicle performance while meeting stringent quality standards.
3. Aerospace Engineering
In aerospace engineering and aircraft manufacturing, precision is paramount. Robotic bending machines are utilized to fabricate intricate components such as aircraft wings, fuselage sections, and engine parts.
The ability to bend aluminum, titanium, and other aerospace-grade materials with precision ensures the structural integrity and aerodynamic performance of aircraft components.
4. Consumer Electronics
In the consumer electronics industry, where product miniaturization and aesthetic appeal are critical, robotic bending machines are used to manufacture components such as smartphone frames, tablet enclosures, and computer chassis.
The ability to bend thin-gauge materials with tight tolerances enables manufacturers to produce sleek and durable electronic devices that meet consumer expectations for quality and performance.
Future Trends and Innovations
As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of robotic bending machines are expected to evolve further, driving innovation in manufacturing processes. Some emerging trends and developments in the field of robotic bending technology include:
1. Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms into robotic bending machines enables predictive maintenance, adaptive process control, and optimization of bending parameters based on real-time data analysis.
AI-powered systems can identify patterns, detect anomalies, and make adjustments to improve bend quality and efficiency continuously.
2. Collaborative Robotics (Cobots)
Collaborative robotics, or cobots, are designed to work alongside human operators in shared workspaces.
In the context of robotic bending machines, cobots can assist with material handling, part positioning, and quality inspection, enhancing workflow efficiency and productivity while ensuring safe interaction between humans and machines.
3. Additive Manufacturing Integration
The integration of robotic bending machines with additive manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing, opens up new possibilities for hybrid manufacturing processes.
By combining subtractive and additive techniques, manufacturers can create complex geometric shapes and optimize material usage, leading to more sustainable and cost-effective production methods.
4. Enhanced Material Compatibility
Advancements in materials science and engineering are expanding the range of materials that can be processed using robotic bending machines.
From advanced composites and lightweight alloys to exotic metals and bio-based materials, manufacturers are exploring new materials with unique properties and applications, driving demand for flexible bending solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, robotic bending machines represent a transformative technology that is reshaping the landscape of modern manufacturing. With their ability to streamline production processes, enhance precision, and improve operational efficiency, these advanced systems are indispensable assets for manufacturers seeking a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced market.
As technology continues to evolve and new innovations emerge, robotic bending machines will play an increasingly vital role in driving productivity, innovation, and growth across diverse industries worldwide.