Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a powerful diagnostic tool that has revolutionised the field of medical imaging. If you are looking for an MRI scan in Birmingham, it’s essential to understand how this technology works and its benefits. This guide will explore the basics of MRI technology, its applications, and what you can expect during an MRI scan.
The Basics of MRI Technology
MRI technology uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the organs and tissues within the body. Unlike X-rays and CT scans, MRI does not use ionising radiation, making it a safer alternative for many patients. The core component of an MRI machine is a powerful magnet that generates a magnetic field around the body. This magnetic field aligns the hydrogen atoms in the body, which are then disturbed by a pulse of radio waves. When the radio waves are turned off, the hydrogen atoms return to their original positions, emitting signals that are used to create images.
The strength of the magnetic field is measured in teslas (T), with most clinical MRI machines operating at 1.5T or 3T. Higher magnetic field strengths can produce clearer and more detailed images. The resulting images allow doctors to diagnose a variety of conditions, from torn ligaments to brain tumours, with exceptional accuracy.
Applications of MRI Technology
MRI is a versatile imaging technique used to diagnose and monitor a wide range of medical conditions. One of the primary uses of MRI is in neuroimaging, where it provides detailed images of the brain and spinal cord. This capability is crucial for detecting abnormalities such as tumours, multiple sclerosis, and stroke.
In addition to neuroimaging, MRI is extensively used in musculoskeletal imaging. It is particularly effective in identifying injuries to soft tissues, such as ligaments and tendons, which are not visible on X-rays. Orthopaedic surgeons often rely on MRI scans to plan surgeries and monitor post-operative recovery.
Another significant application of MRI is in cardiovascular imaging. MRI can provide detailed images of the heart and blood vessels, helping doctors assess heart function, detect heart disease, and plan appropriate treatments. This non-invasive technique is invaluable for patients who require regular monitoring of their cardiovascular health.
What to Expect During an MRI Scan
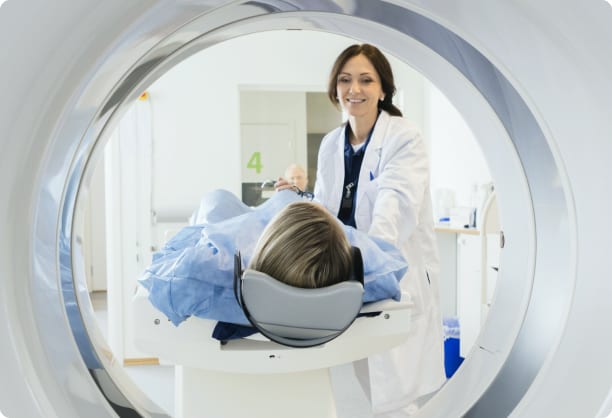
Understanding what to expect during an MRI scan can help alleviate any anxiety you might have about the procedure. Before the scan, you will be asked to remove any metal objects, such as jewellery or eyeglasses, as metal can interfere with the magnetic field. You will then lie down on a movable bed that slides into the MRI machine, which is a large, cylindrical tube.
During the scan, it is important to remain as still as possible to ensure clear images. The machine makes loud, repetitive knocking noises, which can be quite loud, but you will be provided with earplugs or headphones to minimise the noise. Some facilities even offer music to help you relax. The entire process can take anywhere from 15 minutes to over an hour, depending on the area being examined.
After the scan, a radiologist will analyse the images and send a report to your doctor. Your doctor will then discuss the results with you and explain any findings or necessary follow-up steps.
The Advantages of MRI Technology
One of the main advantages of MRI technology is its ability to produce highly detailed images of soft tissues, which are often difficult to see with other imaging methods. This level of detail makes MRI an invaluable tool for diagnosing a wide range of conditions, from sports injuries to neurological disorders.
Moreover, MRI is a non-invasive procedure that does not use ionising radiation, making it safer for repeated use, especially in patients who require ongoing monitoring. It is also particularly useful for imaging areas surrounded by bone, such as the brain and spinal cord, where other imaging techniques might not provide sufficient detail.
MRI technology continues to advance, with new techniques and applications being developed regularly. For example, functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow, providing insights into brain function and aiding in the study of neurological conditions.
MRI’s versatility and safety make it a cornerstone of modern medical diagnostics, offering patients and doctors a powerful tool for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning. Whether you’re undergoing an MRI scan in Birmingham or elsewhere, understanding this technology can help you feel more informed and at ease about the procedure.