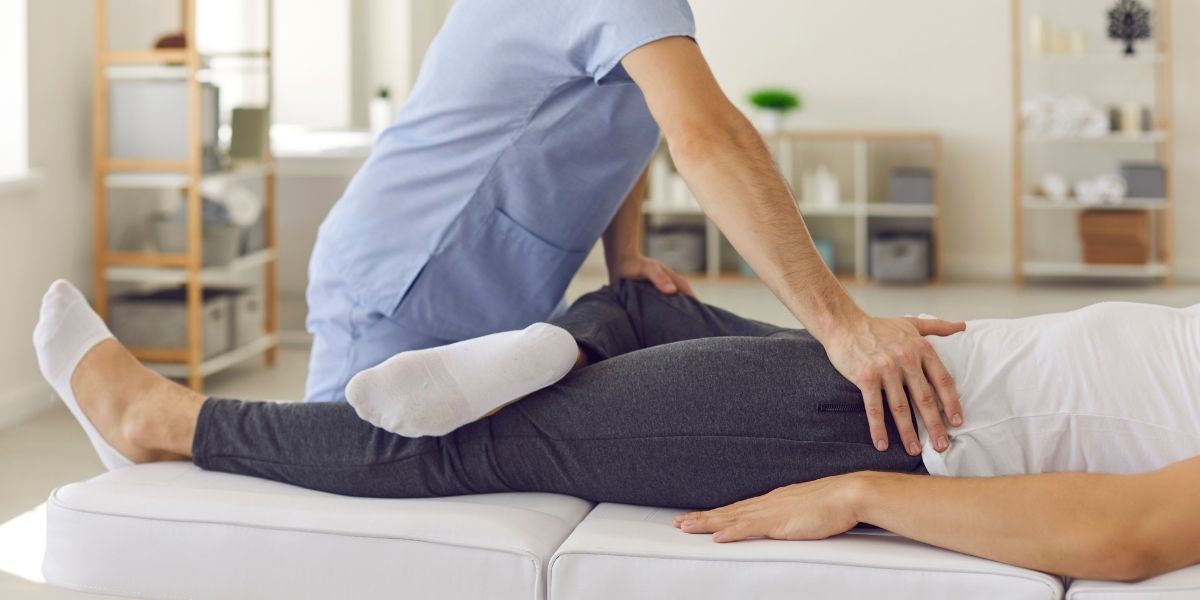
Physical therapy plays a critical role in the management and relief of pelvic pain, a complex symptom that affects many people due to various underlying health conditions. Pelvic pain can stem from issues related to musculoskeletal problems, pelvic floor dysfunction, post-surgical recovery, and conditions like endometriosis or interstitial cystitis. By addressing the root causes of pelvic pain through targeted exercises, manual therapy, and patient education, physical therapists help to alleviate pain and improve quality of life.
Understanding Pelvic Pain
Pelvic pain can manifest as acute, sudden pain or chronic, lingering discomfort. It may be associated with other symptoms such as urinary and bowel dysfunctions, sexual dysfunction, and lower back pain. The pain may be localized to the pelvic region or radiate to the abdominal area and thighs.
Role of Physical Therapy in Pelvic Pain Management
Physical therapy for pelvic pain is aimed at reducing symptoms, improving function, and educating patients on self-management techniques. Here are key aspects of how physical therapy helps in relieving pelvic pain:
1. Initial Assessment
A physical therapist begins with a comprehensive assessment that includes a detailed medical history, physical examination, and, when necessary, collaboration with other healthcare providers. This evaluation helps to identify the specific causes of pelvic pain and tailor a personalized treatment plan.
2. Pelvic Floor Muscle Training
One of the primary strategies is training and conditioning the pelvic floor muscles. Pelvic pain is often linked to either hypertonic (overly tight) or hypotonic (weak) pelvic floor muscles. Physical therapists teach exercises such as Kegels to strengthen the muscles or relaxation techniques to release tension from them.
3. Manual Therapy
Manual therapy techniques include massage, stretching, and mobilization of the pelvic region. These methods are used to alleviate muscle spasms, improve blood circulation, and enhance mobility. For patients with tight pelvic muscles, trigger point release can be particularly effective in reducing pain. Some people find a set of dilators helpful to relax pelvic muscles.
4. Biofeedback
Biofeedback is a technique that helps patients gain awareness and control of their pelvic floor muscles. Using sensors that monitor the muscle activity, patients learn how to modulate their muscle tension, which is vital for those who struggle with relaxing overly tight muscles.
5. Education and Lifestyle Modifications
Physical therapists also provide valuable education on lifestyle changes that can help to manage pelvic pain. This includes guidance on diet, posture, stress management, and proper ergonomics to avoid aggravating symptoms.
6. Exercise Programs
Beyond direct pelvic floor interventions, physical therapists develop comprehensive exercise programs that improve overall strength, flexibility, and endurance. These programs are designed to support the health of the pelvic region and prevent future issues.
7. Pain Management Techniques
Physical therapy incorporates various pain management techniques such as heat or cold therapy, electrical stimulation, and ultrasound therapy. These modalities help reduce inflammation, promote healing, and mitigate pain.
Conclusion
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of managing pelvic pain, offering a non-invasive, effective approach to treatment. By addressing both the symptoms and causes of pelvic pain, physical therapists enable patients to engage more fully in their daily activities and significantly improve their quality of life. For many suffering from pelvic pain, physical therapy provides a viable alternative or complement to medication and surgical options, emphasizing a holistic approach to health and recovery.